Abstract
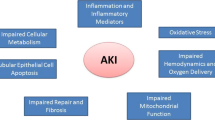
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by a rapid decrease in kidney function and increased serum creatinine. The term acute renal failure (ARF) has been applied to such clinical manifestations. Despite several advances in the treatment of ARF, such as pharmacologic treatment and renal replacement therapy (RRT), the mortality rate among patients with ARF has changed little over the past four decades. It is widely recognized that ARF is associated with significantly increased morbidity and mortality especially in critically ill patients with ARF requiring RRT. Therefore, in order to improve outcomes in ARF patients, a new concept of AKI has been proposed. Recently the paradigm shift from ARF to AKI has been received by the research and clinical communities. In this review we will discuss the therapeutic strategies for AKI and focus on its management with an emphasis on RRT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kellum JA, Levin N, Bouman C, Lameire N. Developing a consensus classification system for acute renal failure. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2002;8:509–14.
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P. The ADQI workgroup. Acute renal failure − definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: The Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care. 2004;8:R204–12.
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, et al. Acute kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2007;11:R31.
Coca SG, Peixoto AJ, Garg AX, Krumholz HM, Parikh CR, et al. The prognostic importance of a small acute decrement in kidney function in hospitalized patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;50:712–20.
Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3365–70.
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int 2012; Suppl 2:1–138.
Jo SK, Rosner MH, Okusa MD. Pharmacologic treatment of acute kidney injury: why drugs haven’t worked and what is on the horizon. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2:356–65.
Star RA. Treatment of acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1998;54:1817–31.
Coca SG, Yalavarthy R, Concato J, Parikh CR. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute kidney injury: a systemic review. Kidney Int. 2008;73:1008–16.
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes M, Ma Q, Kelly C, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet. 2005;365:1231–8.
Denton MD, Chertow GM, Brady HR. “Renal-dose” dopamine for the treatment of acute renal failure: scientific rationale experimental studies and clinical trials. Kidney Int. 1996;50:4–14.
Carcoana OV, Hines RL. Is renal dose dopamine protective or therapeutic? Yes. Crit Care Clin. 1998;12:677–85.
Friedrich JO, Adhikari N, Herridge MS, Beyene J. Meta-analysis: low-dose dopamine increases urine output but does not prevent renal dysfunction or death. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142:510–24.
Klahr S, Miller SB. Acute oliguria. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:671–5.
Wilson WC, Aronson S. Oliguria: a sign of renal success or impending renal failure? Anesthesiol Clin North Am. 2001;19:841–83.
Ho KM, Sheridan DJ. Meta-analysis of frusemide to prevent or treatment acute renal failure. BMJ. 2006;333:1333–7.
Allgren RL, Marbury TC, Rahman SN, Weisberg LS, Fenves AZ, Lafayette RA, et al. Anaritide in acute tubular necrosis. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:828–34.
Lewis J, Salem MM, Chertow GM, Weisberg LS, McGrew F, Marbury TC, et al. Atrial natriuretic factor in oliguric acute renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;36:767–74.
Nigwekar SU, Navaneethan SD, Parikh CR, Hix JK. Atrial natriuretic peptide for management of acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4:261–72.
Morikawa S, Sone T, Tsuboi H, Mukawa H, Morishima I, Uesugi M, et al. Renal protective effects and the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy by atrial natriuretic peptide. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:1040–6.
Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–8.
Mehta RL, Mcdonald B, Gabbai FB, Pahl M, Pascual MT, Farkas A, et al. A randomized clinical trial of continuous versus intermittent dialysis for acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2001;60:1154–63.
Augustine JJ, Sandy D, Seifert TH, Paganini EP. A randomized, controlled trial comparing intermittent with continuous dialysis in patients with ARF. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44:1000–7.
Uehlinger DE, Jakob SM, Ferrari P, Eichelberger M, Huynh-Do U, Marti HP, et al. Comparison of continuous and intermittent renal replacement therapy for acute renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20:1630–7.
Vinsonneau C, Camus C, Combes A, Costa de Beauregard MA, Klouche K, Boulain T, et al. Continuous venovenous haemofiltration versus intermittent haemodialysis for acute renal failure in patients with multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome: a multicentre randomized trial. Lancet. 2006;368:379–85.
Lins RL, Elseviers MM, Van der Niepen P, Hoste E, Malbrain ML, Damas P, et al. Intermittent versus continuous renal replacement therapy for acute kidney injury patients admitted to the intensive care unit: results of a randomized clinical trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:512–8.
Tonelli M, Manns B, Feller-Kopman D. Acute renal failure in the intensive care unit: a systematic review of the impact of dialytic modality on mortality and renal recovery. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;40:875–85.
Kellum J, Angus DC, Johnson JP, Leblanc M, Griffin M, Ramarkrishnan N, et al. Continuous versus intermittent renal replacement therapy: a meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2002;28:29–37.
Pannu N, Klarenbach S, Wiebe N, Manns B, Tonelli M. For the Alberta Kidney Disease Network. Renal replacement therapy in patients with acute renal failure. JAMA. 2008;299:793–805.
Kumar VA, Craig M, Depner TA, Yeun JY. Extended daily dialysis: a new approach to renal replacement for acute renal failure in the intensive care unit. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;36:294–300.
Marshall MR, Golper TA, Shaver MJ, Alam MG, Chatoth DK. Sustained low-efficiency dialysis for critically ill patients requiring renal replacement therapy. Kidney Int. 2001;60:777–85.
Naka T, Baldwin I, Bellomo R, Fealy N, Wan L. Prolonged daily intermittent renal replacement therapy in ICU patients by ICU nurses and ICU physicians. Crit Care Med. 2004;27:380–7.
Ronco C, Bellomo R, Homel P, Brendolan A, Dan M, Piccinni P, La Greca G. Effects of different doses in continuous veno-venous haemofiltration on outcomes of acute renal failure: a prospective randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;356:26–30.
Saudan P, Niederberger M, De Seigneux S, Romand J, Pugin J, Perneger T, et al. Adding a dialysis dose to continuous hemofiltration increases survival in patients with acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2006;70:1312–7.
Schiffl H, Lang SM, Fischer R. Daily hemodialysis and the outcome of acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:305–10.
Tolwani AJ, Campbell RC, Stofan BS, Lai KR, Oster RA, Wille KM. Standard versus high-dose CVVHDF for ICU-relate acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19:1233–8.
The VA/NIH Acute Renal Failure Trial Network. Intensity of renal support in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:7–20.
The RENAL Replacement Therapy Study Investigators, Bellomo R, Cass A, Cole L, Finfer S, Gallagher M, Lo S, et al. Intensity of continuous renal-replacement therapy in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1627–38.
Prowle JR, Schneider A, Bellomo R. Clinical review: optimal dose of continuous renal replacement therapy in acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2011;15:207–14.
Seabra VF, Balk EM, Liangos O, Sosa MA, Cendoroglo M, Jaber BL. Timing of renal replacement therapy initiation in acute renal failure: a meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;52:272–84.
Bagshaw SM, Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, et al. Timing of renal replacement therapy and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients with severe acute kidney injury. J Crit Care. 2009;24:129–40.
Ricci Z, Ronco C, D’Amico G, De Felice R, Rossi S, Bolgan I, et al. Practice patterns in the management of acute renal failure in the critically ill patients: an international survey. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:690–6.
Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, et al. Discontinuation of continuous renal replacement therapy: a post hoc analysis of a prospective multicenter observational study. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:2576–82.
Chertow GM, Christiansen CL, Cleary PD, Munro C, Lazarus JM. Prognostic stratification in critically ill patients with acute renal failure requiring dialysis. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155:1505–11.
Mehta RL, Pascual MT, Gruta CG, Zhuang S, Chertow GM. Refining predictive models in critically ill patients with acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:1350–7.
Kramer AA, Postler G, Salhab KF, Mendez C, Carey LC, Rabb H. Renal ischemia/reperfusion leads to macrophage-mediated increase in pulmonary vascular permeability. Kidney Int. 1999;55:2362–7.
Li X, Hassoun HT, Santora R, Rabb H. Organ crosstalk: the role of the kidney. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2009;15:481–7.
Scheel PJ, Liu M, Rabb H. Uremic lung: new insights into a forgotten condition. Kidney Int. 2008;74:849–51.
Conflict of interest
All the authors have declared no competing interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Negi, S., Shigematsu, T. Current therapeutic strategies for acute kidney injury. Clin Exp Nephrol 16, 672–678 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-012-0685-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-012-0685-4