Abstract
Background
The intrarenal renin−angiotensinogen system (RAS) plays a major role in the progression of chronic kidney disease. Urinary angiotensinogen (UAGT) provides a specific index of the intrarenal RAS status. This study was conducted to find the role of UAGT as a predictive marker in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN).
Methods
Thirty-six patients with IgAN, 14 non-IgAN and 15 healthy controls were included. The UAGT concentration was measured using human ELISA kits and adjusted by urinary creatinine.
Results
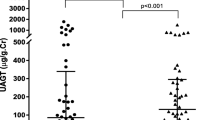
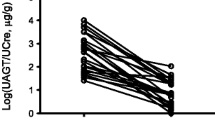
UAGT levels were significantly higher in patients with IgAN and non-IgAN than in healthy subjects (104.96 vs. 6.71 ng/mgCr, p < 0.01). Using univariate regression analysis, UAGT was found to correlate with the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR), serum creatinine, and systolic and diastolic blood pressure in patients with IgAN. Multivariate regression analysis revealed that UAGT correlated positively with UPCR. Patients with levels of UAGT >100 ng/mgCr showed higher serum creatinine after treatment than patients with UAGT levels <100 ng/mgCr.
Conclusion
This study showed that UAGT levels are increased and correlate positively with the UPCR in IgAN. Patients with high levels of UAGT may have poor renal function following treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J. Angiotensin II modulates cell growth-related events and synthesis of matrix proteins in renal interstitial fibroblasts. Kidney Int. 1997;52:1497–510.
Navar LG, Harrison-Bernard LM, Nishiyama A, Kobori H. Regulation of intrarenal angiotensin II in hypertension. Hypertension. 2002;39:316–22.
Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG, Nishiyama A. The intrarenal renin–angiotensin system: from physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2007;59:251–87.
Kobori H, Ozawa Y, Satou R, Katsurada A, Miyata K, Ohashi N, et al. Kidney-specific enhancement of ANG II stimulates endogenous intrarenal angiotensinogen in gene-targeted mice. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2007;293:F938–45.
Kobori H, Nishiyama A, Harrison-Bernard LM, Navar LG. Urinary angiotensinogen as an indicator of intrarenal angiotensin status in hypertension. Hypertension. 2003;41:42–9.
Kobori H, Harrison-Bernard LM, Navar LG. Expression of angiotensinogen mRNA and protein in angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:431–9.
Kobori H, Prieto-Carrasquero MC, Ozawa Y, Navar LG. AT1 receptor mediated augmentation of intrarenal angiotensinogen in angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Hypertension. 2004;43:1126–32.
Yamamoto T, Nakagawa T, Suzuki H, Ohashi N, Fukasawa H, Fujigaki Y, et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a marker of intrarenal angiotensin II activity associated with deterioration of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:1558–65.
Kobori A, Alper AB Jr, Shenava R, Katsurada A, Satio T, Ohashi N, et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a novel biomarker of the intrarenal renin–angiotensin system status in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 2009;53:344–50.
Kobori H, Ozawa Y, Suzaki Y, Prieto-Carrasquero MC, Nishiyama A, Shoji T, et al. Young Scholars Award Lecture: Intratubular angiotensinogen in hypertension and kidney diseases. Am J Hypertens. 2006;19:541–50.
Urushihara M, Kondo S, Kagami S, Kobori H. Urinary angiotensinogen accurately reflects intrarenal renin–angiotensin system activity. Am J Nephrol. 2010;31:318–25.
Kobori H, Katsurada A, Ozawa Y, Satou R, Miyata K, Hase N, et al. Enhanced intrarenal oxidative stress and angiotensinogen in IgA nephropathy patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;358:156–63.
Ohashi N, Katsurada A, Miyata K, Satou R, Satio T, Urushihara M, et al. Activation of reactive oxygen species and the renin–angiotensin system in IgA nephropathy model mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009;36(5–6):509–15.
Nishiyama A, Konishi Y, Ohashi N, Morikawa T, Urshihara M, Maeda I, et al. Urinary angiotensinogen reflects the activity of intrarenal renin–angiotensin system in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;26(1):170–7.
Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T, Stevens LA, Zhang YL, Hendriksen S, et al. Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145:247–54.
Lee HS, Lee MS, Lee SM, Lee SY, Lee ES, Lee EY, et al. Histological grading of IgA nephropathy predicting renal outcome: revisiting H. S. Lee’s glomerular grading system. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20:342–8.
Rohrwasser A, Morgan T, Dillon HF, Zhao L, Callaway CW, Hillas E, et al. Elements of a paracrine tubular renin–angiotensin system along the entire nephron. Hypertension. 1999;34:1265–74.
Kobori H, Ohashi N, Katsurada A, Miyata K, Satou R, Satio T, et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a potential biomarker of severity of chronic kidney diseases. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2008;2:349–54.
Ogawa S, Mori T, Nako K, Kato T, Takeuchi K, Ito S. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers reduce urinary oxidative stress markers in hypertensive diabetic nephropathy. Hypertension. 2006;47:699–705.
Mezzano SA, Aros CA, Droguett A, Burgos ME, Ardiles LG, Flores CA, et al. Renal angiotensin II up-regulation and myofibroblast activation in human membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl. 2003;86:S39–45.
Saito T, Urushihara M, Kotani Y, Kagami S, Kobori H. Increased urinary angiotensinogen is precedent to increased urinary albumin in patients with type 1 diabetes. Am J Med Sci. 2009;338:478–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YG., Song, SB., Lee, SH. et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a predictive marker in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol 15, 720–726 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0475-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0475-4