Abstract
Background
Obesity and decreased kidney function have been shown to be prevalent in Western patients with heart failure; however, whether this phenomenon exists in Chinese patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) is not known.
Methods and results
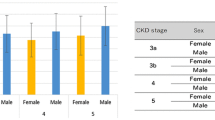
One thousand and nine patients with CHF from the China Heart Survey were assessed. The prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) was 34.2%, and there was a stepwise increase in the prevalence of CKD with New York Heart Association (NYHA) classes (P < 0.001). Moreover, patients with CKD had a significantly elevated risk for developing severe extent of CHF (OR = 1.69, 95% CI: 1.27–2.24, P < 0.001). The prevalence of obesity and central obesity was 35.7% and 62.5%, respectively. Notably, there was a downward trend in the prevalence of obesity with advanced NYHA classes (trend test, P = 0.003). Multivariate analysis further supported the finding that obesity, but not central obesity, was inversely associated with the extent of CHF (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.55–0.94, P = 0.017).
Conclusions
Renal dysfunction is common in Chinese patients with CHF and is independently associated with advanced NYHA classes. Obesity was inversely associated with the extent of CHF, which further supports the notion that obesity confers improved prognosis in patients with heart failure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang H, Ge J. Epidemiology and clinical management of cardiomyopathies and heart failure in China. Heart. 2009;95(21):1727–31.
Ahmed A, Rich MW, Sanders PW, Perry GJ, Bakris GL, Zile MR, Love TE, Aban IB, Shlipak MG. Chronic kidney disease associated mortality in diastolic versus systolic heart failure: a propensity matched study. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(3):393–8.
Anand IS, Bishu K, Rector TS, Ishani A, Kuskowski MA, Cohn JN. Proteinuria, chronic kidney disease, and the effect of an angiotensin receptor blocker in addition to an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in patients with moderate to severe heart failure. Circulation. 2009;120(16):1577–84.
Go AS, Yang J, Ackerson LM, Lepper K, Robbins S, Massie BM, Shlipak MG. Hemoglobin level, chronic kidney disease, and the risks of death and hospitalization in adults with chronic heart failure: the Anemia in Chronic Heart Failure: Outcomes and Resource Utilization (ANCHOR) Study. Circulation. 2006;113(23):2713–23.
Hamaguchi S, Tsuchihashi-Makaya M, Kinugawa S, Yokota T, Ide T, Takeshita A, Tsutsui H. Chronic kidney disease as an independent risk for long-term adverse outcomes in patients hospitalized with heart failure in Japan. Report from the Japanese Cardiac Registry of Heart Failure in Cardiology (JCARE-CARD). Circ J. 2009;73(8):1442–7.
Heywood JT, Fonarow GC, Costanzo MR, Mathur VS, Wigneswaran JR, Wynne J. High prevalence of renal dysfunction and its impact on outcome in 118, 465 patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: a report from the ADHERE database. J Card Fail. 2007;13(6):422–30.
Horwich TB, Fonarow GC, Hamilton MA, MacLellan WR, Woo MA, Tillisch JH. The relationship between obesity and mortality in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;38(3):789–95.
Khan NA, Ma I, Thompson CR, Humphries K, Salem DN, Sarnak MJ, Levin A. Kidney function and mortality among patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(1):244–53.
McAlister FA, Ezekowitz J, Tonelli M, Armstrong PW. Renal insufficiency and heart failure: prognostic and therapeutic implications from a prospective cohort study. Circulation. 2004;109(8):1004–9.
Smith GL, Lichtman JH, Bracken MB, Shlipak MG, Phillips CO, DiCapua P, Krumholz HM. Renal impairment and outcomes in heart failure: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(10):1987–96.
Arena R, Myers J, Abella J, Pinkstaff S, Brubaker P, Moore B, Kitzman D, Peberdy MA, Bensimhon D, Chase P, et al. Influence of etiology of heart failure on the obesity paradox. Am J Cardiol. 2009;104(8):1116–21.
Curtis JP, Selter JG, Wang Y, Rathore SS, Jovin IS, Jadbabaie F, Kosiborod M, Portnay EL, Sokol SI, Bader F, et al. The obesity paradox: body mass index and outcomes in patients with heart failure. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(1):55–61.
Hall JA, French TK, Rasmusson KD, Vesty JC, Roberts CA, Rimmasch HL, Kfoury AG, DG Renlund. The paradox of obesity in patients with heart failure. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2005;17(12):542–6.
Lavie CJ, Osman AF, Milani RV, Mehra MR. Body composition and prognosis in chronic systolic heart failure: the obesity paradox. Am J Cardiol. 2003;91(7):891–4.
Uretsky S, Messerli FH, Bangalore S, Champion A, Cooper-Dehoff RM, Zhou Q, Pepine CJ. Obesity paradox in patients with hypertension and coronary artery disease. Am J Med. 2007;120(10):863–70.
Hu DY, Pan CY, Yu JM. The relationship between coronary artery disease and abnormal glucose regulation in China: the China Heart Survey. Eur Heart J. 2006;27(21):2573–9.
Liu H, Yu J, Chen F, Li J, Hu D. Inpatients with coronary heart disease have a high prevalence of chronic kidney disease based on estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in China. Heart Vessels. 2007;22(4):223–8.
Liu H, Yu J, Chen F, Wang J, Chen S, Wang F, Hu D. Does obesity attenuate the effect of metabolic syndrome on chronic kidney disease in patients with coronary artery disease? Report from China Heart Survey. Circ J. 2010;74(3):462–7.
Ma YC, Zuo L, Chen JH, Luo Q, Yu XQ, Li Y, Xu JS, Huang SM, Wang LN, Huang W, et al. Modified glomerular filtration rate estimating equation for Chinese patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(10):2937–44.
National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(2 Suppl 1):S1–266.
The Criteria Committee of the New York Heart Association. In: Nomenclature and criteria for diagnosis of diseases of the heart and great vessels. Boston: Little, Brown & Co;1994. p. 253–6.
Bei-Fan Z. Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain related diseases in Chinese adults: study on optimal cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese adults. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2002, 11 Suppl 8:S685–93.
Tan CE, Ma S, Wai D, Chew SK, Tai ES. Can we apply the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel definition of the metabolic syndrome to Asians? Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1182–6.
Wildman RP, Gu D, Reynolds K, Duan X, He J. Appropriate body mass index and waist circumference cutoffs for categorization of overweight and central adiposity among Chinese adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80(5):1129–36.
Hillege HL, Nitsch D, Pfeffer MA, Swedberg K, McMurray JJ, Yusuf S, Granger CB, Michelson EL, Ostergren J, Cornel JH, et al. Renal function as a predictor of outcome in a broad spectrum of patients with heart failure. Circulation. 2006;113(5):671–8.
Oreopoulos A, Padwal R, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Fonarow GC, Norris CM, McAlister FA. Body mass index and mortality in heart failure: a meta-analysis. Am Heart J. 2008;156(1):13–22.
Wang Y, Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Hu FB. Comparison of abdominal adiposity and overall obesity in predicting risk of type 2 diabetes among men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;81(3):555–63.
Feldman AM, Combes A, Wagner D, Kadakomi T, Kubota T, Li YY, McTiernan C. The role of tumor necrosis factor in the pathophysiology of heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35(3):537–44.
Romero-Corral A, Somers VK, Sierra-Johnson J, Jensen MD, Thomas RJ, Squires RW, Allison TG, Korinek J, Lopez-Jimenez F. Diagnostic performance of body mass index to detect obesity in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(17):2087–93.
Acknowledgments
The involvement of the study coordinators and their hospitals are acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Liu and H. Shi contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Shi, H., Yu, J. et al. Obesity and chronic kidney disease in patients with chronic heart failure: an insight from the China Heart Survey. Clin Exp Nephrol 15, 522–528 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0443-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0443-z