Abstract
Background
Interleukin-18 (IL-18), a pro-inflammatory cytokine, is a predictor of cardiovascular and renal disease in diabetic patients. Postprandial hyperglycemia is one of the important factors contributing to an increase in the circulating pro-inflammatory cytokine levels. This study investigated the effect of miglitol, an α-glucosidase inhibitor, on postprandial hyperglycemia and IL-18 levels in diabetic patients with nephropathy.
Methods
Fifteen Japanese diabetic patients with persistent proteinuria and preserved renal function were recruited. The patients received 50 mg miglitol thrice daily after the baseline examinations and were followed up for 12 weeks. A meal tolerance test was performed on eight patients at baseline and week 12. The fasting miglitol concentration was measured in seven patients just before the meal tolerance test.
Results
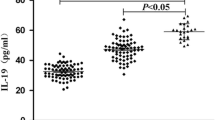
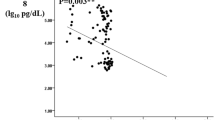
There were no changes in the body weight, blood pressure, liver and renal function, and proteinuria from baseline to week 12. However, the levels of glycated hemoglobin and interleukin 18 significantly decreased from baseline to week 12. During the meal tolerance test, plasma glucose was significantly decreased 60 min after treatment with miglitol, whereas the serum concentration of insulin was not changed. Fasting and postprandial levels of IL-18 were significantly decreased from baseline to week 12. Serum miglitol concentrations showed a significantly negative correlation with eGFR (r = −0.82, p = 0.02). However, the serum miglitol concentrations did not changed during the course of this study.
Conclusion
Miglitol improved postprandial hyperglycemia and reduced serum IL-18 levels in patients with stage 3 diabetic nephropathy. Miglitol may therefore prevent atherosclerotic diseases and diabetic micro-vascular complications through decreasing glucose swings and/or the circulating IL-18 level.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laakso M. Hyperglycemia and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 1999;48:937–42.
Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology and management. JAMA. 2002;2002:2570–81.
Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR. Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 64). Kidney Int. 2003;63:225–32.
Ross R. Atherosclerosis: an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:115–26.
Puren AJ, Fantuzzi G, Gu Y, Su MS, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-18 (IFNgamma-inducing factor) induces IL-8 and IL-1beta via TNFalpha production from non-CD14+ human blood mononuclear cells. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:711–21.
Zirlik A, Abdullah SM, Gerdes N, MacFarlane L, Schönbeck U, Khera A, et al. Interleukin-18, the metabolic syndrome, and subclinical atherosclerosis: results from the Dallas Heart Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:2043–9.
Everett BM, Bansal S, Rifai N, Buring JEPMR. Interleukin-18 and the risk of future cardiovascular disease among initially healthy women. Atherosclerosis. 2009;202:282–8.
Skopiński P, Rogala E, Duda-Król B, Lipińska A, Sommer E, Chorostowska-Wynimko J. Increased interleukin-18 content and angiogenic activity of sera from diabetic (Type 2) patients with background retinopathy. J Diabetes Complicat. 2005;19:335–8.
Nakamura A, Shikata K, Hiramatsu M, Nakatou T, Kitamura T, Wada J, et al. Serum interleukin-18 levels are associated with nephropathy and atherosclerosis in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2890–5.
Araki S, Haneda M, Koya D, Sugimoto T, Isshiki K, Chin-Kanasaki M, et al. Predictive impact of elevated serum level of IL-18 for early renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: an observational follow-up study. Diabetologia. 2007;50:867–73.
Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Heine RJ, Holman RR, Sherwin R, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in Type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy. A consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1963–72.
Ceriello A, Colagiuri S. International Diabetes Federation guideline for management of postmeal glucose: a review of recommendations. Diabet Med. 2008;25:1151–6.
Fischer CP, Perstrup LB, Berntsen A, Eskildsen P, Pedersen BK. Elevated plasma interleukin-18 is a marker of insulin-resistance in type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic humans. Clin Immunol. 2005;117:152–60.
Herder C, Schneitler S, Rathmann W, Haastert B, Schneitler H, Winkler H, et al. Low-grade inflammation, obesity, and insulin resistance in adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4569–74.
Altinova AE, Yetkin I, Akbay E, Bukan N, Arslan M. Serum IL-18 levels in patients with type 1 diabetes: relations to metabolic control and microvascular complications. Cytokine. 2008;42:217–21.
Ahr HJ, Boberg M, Brendel E, Krause HP, Steinke W. Pharmacokinetics of miglitol Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion following administration to rats, dogs, and man. Arzneimittelforschung. 1997;47:734–45.
Guerrant GO, Moss CW. Determination of monosaccharides as aldononitrile, o-methyloxime, alditol, and cyclitol acetate derivatives by gas chromatography. Anal Chem. 1984;56:633–8.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:982–92.
Sowers JR, Epstein M, Frohlich ED. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: an update. Hypertension. 2001;37:1053–9.
Solomon CG. Reducing cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:457–9.
Mallat Z, Corbaz A, Scoazec A, Besnard S, Lesèche G, Chvatchko Y, et al. Expression of interleukin-18 in human atherosclerotic plaques and relation to plaque instability. Circulation. 2001;104:1598–603.
Welsh P, Woodward M, Rumley A, Lowe G. Associations of circulating TNFalpha and IL-18 with myocardial infarction and cardiovascular risk markers: the Glasgow Myocardial Infarction Study. Cytokine. 2009;47:143–7.
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1111–9.
Dickhout JG, Krepinsky JC. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and renal disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11:2341–52.
Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001;414:813–20.
Vidal-Vanaclocha F, Fantuzzi G, Mendoza L, Fuentes AM, Anasagasti MJ, Martín J, et al. L-18 regulates IL-1β-dependent hepatic melanoma metastasis via vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. PNAS. 2000;97:734–9.
Berneis K, Rizzo M, Evans J, Rini GB, Spinas GA, Goedecke JH. Interleukin-18 levels are associated with low-density lipoproteins size. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010;40:54–5.
Porazko T, Kúzniar J, Kusztal M, Kúzniar TJ, Weyde W, Kuriata-Kordek M, et al. IL-18 is involved in vascular injury in end-stage renal disease patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:589–96.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ. 1999;12:703–13.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes––2009. Diabetes Care. 2009;2009(Suppl 1):S13–61.
Charpentier G, Riveline JP, Varroud-Vial M. Management of drugs affecting blood glucose in diabetic patients with renal failure. Diabetes Metab. 2000;26(Suppl4):73–85.
Baer DJ, Judd JT, Clevidence BA, Tracy RP. Dietary fatty acids affect plasma markers of inflammation in healthy men fed controlled diets: a randomized crossover study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:969–73.
Ghanim H, Abuaysheh S, Sia CL, Korzeniewski K, Chaudhuri A, Fernandez-Real JM. Increase in plasma endotoxin concentrations and the expression of Toll-like receptors and suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 in mononuclear cells after a high-fat, high-carbohydrate meal: implications for insulin resistance. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:2281–7.
Arakawa M, Ebato C, Mita T, Fujitani Y, Shimizu T, Watada H, et al. Miglitol suppresses the postprandial increase in interleukin 6 and enhances active glucagon-like peptide 1 secretion in viscerally obese subjects. Metabolism. 2008;57:1299–306.
Assaloni R, Da Ros R, Quagliaro L, Piconi L, Maier A, Zuodar G, et al. Effects of S21403 (mitiglinide) on postprandial generation of oxidative stress and inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2005;48:1919–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Uzu, T., Yokoyama, H., Itoh, H. et al. Elevated serum levels of interleukin-18 in patients with overt diabetic nephropathy: effects of miglitol. Clin Exp Nephrol 15, 58–63 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-010-0343-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-010-0343-7