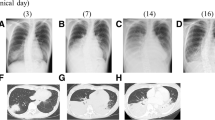
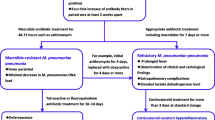
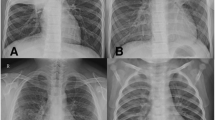
Abstract
A macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae strain was isolated from two patients with community-acquired pneumonia. The pneumonia severity score of both patients was mild, and rapid clinical improvement was seen after administration of fluoroquinolone. Clinical features of macrolide-resistant M. pneumoniae pneumonia were identical to those of macrolide-sensitive M. pneumoniae pneumonia. An A-to-G transition at position 2063 and 2064, respectively, in domain V of the 23S rRNA gene was identified. The minimum inhibitory concentration of erythromycin of these isolates was greatly elevated. In Japan, macrolide-resistant M. pneumoniae infections are common in pediatric patients but not in adults. However, physicians should pay attention to macrolide-resistant M. pneumoniae not only in children but also in adults.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson TP, Balish MF, Waites KB. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, pathogenesis, and laboratory detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008;32:956–73.
Arnold FW, Summersgill JT, Lajoie AS, Peyrani P, Marrie TJ, Rossi P, et al. A worldwide perspective of atypical pathogens in community-acquired pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:1086–93.
Miyashita N, Fukano H, Mouri K, Fukuda M, Yoshida K, Kobashi Y, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia in Japan: a prospective ambulatory and hospitalized patient study. J Med Microbiol. 2005;54:395–400.
Okazaki N, Narita M, Yamada S, Izumikawa K, Umetsu M, Kenri T, et al. Characteristics of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains isolated from patients and induced with erythromycin in vitro. Microbiol Immunol. 2001;45:617–20.
Matsuoka M, Narita M, Okazaki N, Ohya H, Yamazaki T, Ouchi K, et al. Characterization and molecular analysis of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae clinical isolates obtained in Japan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:4624–30.
Morozumi M, Iwata S, Hasegawa K, Chiba N, Takayanagi R, Matsubara K, et al. Increased macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in pediatric patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:348–50.
Isozumi R, Yoshimine H, Morozumi M, Ubukata K, Ariyoshi K. Adult community-acquired pneumonia caused by macrolide resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Respirology. 2009;14:1206–8.
The committee for the JRS guidelines in management of respiratory infections. In: Matsushima T, Kohno S, Saito A, Nakata K, Yamaguchi K, Watanabe A, editors. The JRS guidelines for the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults (in Japanese). Tokyo: The Japanese Respiratory Society; 2005.
Miyashita N, Obase Y, Ouchi K, Kawasaki K, Kawai Y, Kobashi Y, et al. Clinical features of severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae in adults admitted to an intensive care unit. J Med Microbiol. 2007;56:1625–9.
Kawai Y, Yamaguchi T, Oda K, Miyashita N, Tabuchi M, Kishi F, et al. High prevalence of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Japan. In: Abstracts of the Forty-eighth Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Washington, DC, 2008. Abstract C2-1975. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Pereyre S, Charron A, Renaudin H, Bebear C, Bebear CM. First report of macrolide-resistant strains and description of a novel nucleotide sequence variation in the P1 adhesin gene in Mycoplasma pneumoniae clinical strains isolated in France over 12 years. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:3534–9.
Peuchant O, Menard A, Renaudin H, Morozumi M, Ubukata K, Bebear CM, et al. Increased macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in France directly detected in clinical specimens by real-time PCR and melting curve analysis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;64:52–8.
Wolff BJ, Thacker WL, Schwartz SB, Winchell JM. Detection of macrolide resistance in Mycoplasma pneumoniae by real-time PCR and high-resolution melt analysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:3542–9.
Li X, Atkinson TP, Hagood J, Makris C, Duffy LB, Waites KB. Emerging macrolide resistance in Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children: detection and characterization of resistant isolates. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009;28:693–6.
Liu Y, Ye X, Zhang H, Xu X, Li W, Zhu D, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates and molecular analysis of macrolide-resistant strains from Shanghai, China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:2160–2.
Xin D, Mi Z, Han X, Qin L, Li J, Wei T, et al. Molecular mechanisms of macrolide resistance in clinical isolates of Mycoplasma pneumoniae from China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:2158–9.
Morozumi M, Takahashi T, Ubukata K. Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: characteristics of isolates and clinical aspects of community-acquired pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 2010;16:78–86.
Suzuki S, Yamazaki T, Narita M, Okazaki N, Suzuki I, Andoh T, et al. Clinical evaluation of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:709–12.
Matsubara K, Morozumi M, Okada T, Matsushima T, Komitama O, Shoji M, et al. A comparative clinical study of macrolide-sensitive and macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in pediatric patients. J Infect Chemother. 2009;15:380–3.
Miyashita N, Ouchi K, Kawasaki K, Oda K, Kawai Y, Shimizu H, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in the elderly. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14:CR387–91.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by MEXT KAKENHI (19591190 and 21591304) and Project Research Grants from Kawasaki Medical School (13-401, 14-402, 15-405A, 16-405M, 17-402M, 18-401, 19-402M, 20-4030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Miyashita, N., Maruyama, T., Kobayashi, T. et al. Community-acquired macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in patients more than 18 years of age. J Infect Chemother 17, 114–118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-010-0093-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-010-0093-1