Abstract
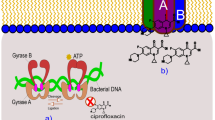
We determined the minimum inhibitory concentrations of six types of antimicrobial agents for 523 strains of Campylobacter jejuni that were isolated from diarrheal patients in a general hospital in Tokyo during the period between 2003 and 2005. It was revealed that 20.2%, 22.9%, 6.7%, and 0.6% of all the C. jejuni strains tested were resistant to ciprofloxacin (CPFX), nalidixic acid, ampicillin, and fosfomycin, respectively. All the strains were susceptible to clarithromycin and erythromycin. To elucidate the mechanism of quinolone resistance, in a total of 55 strains selected randomly, we carried out sequence determination and analysis of the quinolone-resistance determining regions (QRDRs) of their gyrA and gyrB genes. Amino-acid substitution at codon 86 (Thr → IIe) of GyrA was found in all the 37 CPFX-resistant strains. There was no amino-acid substitution in the QRDR of the gyrB gene. All of the genomic DNAs of these 55 strains showed distinct pulsed-field gel electrophoresis patterns. Taken together, these results suggested that the quinolone resistance of C. jejuni was attributable mainly to the mutation at codon 86 (Thr → IIe) in the QRDR of GyrA, and that this particular mutation and other silent mutations could be found not only in a certain clone of C. jejuni but also universally in a wide variety of strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osano O, Arimi SM. Retail poultry and beef as sources of Campylobacter jejuni. East Afr Med J 1999;76:141–143.
Nachamkin I. Campylobacter and Arcobacter. In: Murray PR, Barron EJ, Pfaller MA, Tenover FC, Yolken RH, editors. Manual of clinical microbiology. 6th ed. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology; 1995. p. 483–491.
Taylor DN, Blaser MJ. Campylobacter infections. In: Evans AS, Brachmann PS, editors. Bacterial infections in humans. New York, NY: Plenum; 1991. p. 151–172.
Sagara H, Mochizuki A, Okamura N, Nakaya R. Antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli with special resistance to plasmid profiles of Japanese clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1987;31:713–719.
Kakimoto S, Fukuyama M, Furuhata K, Onaka K, Yoshinami M, Tanikawa T, et al. Drug sensitivity test of Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from human diarrheal stools, chicken meat, and chicken feces, and gene mutation of quinolone-resistant strain (in Japanese). Kansenshogaku Zasshi 2007;81:363–369.
Smith K, Besser JM, Hedberg CW, Leano FT, Bender JB, Wicklund JH, et al. Quinolone-resistant Campylobacter jejuni infections in Minnesota, 1992–1998. N Engl J Med 1999;340:1525–1532.
Gibreel A, Sjogren E, Kaijser B, Wretlind B, Skold O. Rapid emergence of high-level resistance to quinolones in Campylobacter jejuni associated with mutational changes in gyrA and parC. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1998;42:3276–3278.
Drlica K, X Zhao. DNA gyrase topoisomerase IV, and the 4-quinolones. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 1997;61:377–392.
Maxwell A. The molecular basis of quinolone action. J Antimicrob Chemother 1992;30:409–414.
Lou N, Sahin O, Lin J, Michel LO, Zhang Q. In vivo selection of Campylobacter isolates with high levels of fluoroquinolone resistance associated with gyrA mutations and the function of the CmeABC efflux pump. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2003;47:390–394.
Ge B, McDermott PF, White DG, Meng J. Role of efflux pumps and topoisomerase mutation in fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005;49:3347–3354.
Bachual R, Ouabdesselam S, Mory F, Lascols C, Soussy CJ, Tankovic J. Single or double mutational alterations of gyrA associated with fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Microb Drug Resist 2001;7:257–261.
Ruiz J, Goni P, Marco F, Gallardo F, Mirelis B, De Anta TJ, Vila J. Increased resistance to quinolone in Campylobacter jejuni: a genetic analysis of gyrA gene mutations in quinolone-resistant clinical isolates. Microbiol Immunol 1998;42:223–226.
Kinana AD, Cardinale E, Bahsoun I, Tall F, Sire JM, Garin B, et al. Analysis of topoisomerase mutation in fluoroquinolone-resistant and-susceptible Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated in Senegal. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2007;29:397–401.
Wang Y, Huang WM, Taylor DE. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Campylobacter jejuni gyrA gene and characterization of quinolone resistance mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1993;37:457–463.
Zirnstein G, Li Y, Swaminathan B, Angulo F. Ciprofloxacin resistance in Campylobacter jejuni isolates: detection of gyrA resistance mutations by mismatch amplification mutation assay PCR and DNA sequence analysis. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37:3276–3280.
Fukushima M, Kakinuma K, Kawaguchi R. Phylogenetic analysis of Salmonella, Shigella, and Escherichia coli strains on the basis of the gyrB gene sequence. J Clin Microbiol 2002;40:2779–2785.
Boonmar S, Morita Y, Fujita M, Sangsuk L, Suthivarakom K, Padungtod P, et al. Serotypes, antimicrobial susceptibility, and gyrA gene mutation of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from humans and chickens in Thailand. Microbiol Immunol 2007;51:531–537.
Gaudreau CH, Gilbert H. Antimicrobial resistance of clinical strains of Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni isolated from 1985 to 1997 in Quebec, Canada. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1998;42:2106–2108.
Sáenz Y, Zarazaga M, Lantero M, Gastañares MJ, Baquero F, Torres C. Antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter strains isolated from animals, foods, and humans in Spain in 1997–1998. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2000;44:267–271.
Ishihara K, Yamamoto T, Satake S, Takayama S, Kubota S, Negishi H, et al. Comparison of Campylobacter isolated from humans and food-producing animals in Japan. J Appl Microbiol 2006;100:153–160.
Obana M, Matsuoka Y, Irimajiri S, Tonooka H. Clinical studies on the treatment of Campylobacter enteritis-emergence of quinoloneresistant Campylobacter jejuni after treatment with new quinolones (in Japanese). Kansenshogaku Zasshi 1992;66:923–929.
Ge B, White DG, McDermott PF, Girard W, Zhao S, Hubert S, et al. Antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter species from retail raw meats. Appl Environ Microbiol 2003;69:3005–3007.
Jesse TW, Englen MD, Pittenger-Alley LG, Fedorka-Cray PJ. Two distinct mutations in gyrA lead to ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid resistance in Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni isolated from chickens and beef cattle. J Appl Microbiol 2006;100:682–688.
Payot S, Cloeckaert A, Chaslus-Dancla E. Selection and characterization of fluoroquinolone-resistant mutants of Campylobacter jejuni using enrofloxacin. Microb Drug Resist 2002;8:335–343.
Piddock LJ, Ricci VL, Pumbwe L, Everett MJ, Griggs DJ. Fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter species from man and animals: detection of mutations in topoisomerase genes. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003;51:19–26.
Cooper R, Segal H, Lastovica AJ, Elisha BG. Genetic basis of quinolone resistance and epidemiology of resistant and susceptible isolates of porcine Campylobacter coli strains. J Appl Microbiol 2002;93:241–249.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Bakeli, G., Sato, K., Kumita, W. et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility and mechanism of quinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from diarrheal patients in a hospital in Tokyo. J Infect Chemother 14, 342–348 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-008-0631-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-008-0631-2