Abstract
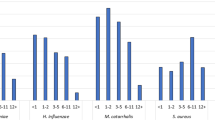
This report focuses on changes in the nasopharyngeal bacterial flora before and after administration of antimicrobial agents in 172 cases of acute upper respiratory infection in patients aged 6 years or younger. The antimicrobial agents administered were amoxicillin (AMPC) (34%), clavulanic acid/amoxicillin compound (11%), cefditren pivoxil (CDTR-PI) (43%), and others (12%). Changes in nasopharyngeal bacterial flora were investigated with reexaminations conducted after 2–5 days (day 2–5 subgroup), 6–10 days (day 6–10 subgroup), and 11 days and thereafter. There was a significant reduction in the Streptococcus pneumoniae detected in the group administered AMPC (AMPC group) in the day 2–5 subgroup and the day 6–10 subgroup. There was also a significant decrease in H. influenzae in the group administered CDTR-PI (CDTR-PI group) in the day 2–5 subgroup. From this it was inferred that for the most part significant changes in infectious nasopharyngeal bacteria occurred in the day 2–5 subgroups. However, a significant improvement in the degree of inflammation, as indicated by leukocyte infiltration images for the AMPC group, was observed in the day 2–5 subgroup, and for the CDTR-PI group in the day 6–10 subgroup. On the other hand, in both the antimicrobial agent groups, S. pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis were newly detected at reexamination. Furthermore, a difference in the incidence of these bacteria was observed between the 2 antimicrobial agent groups. It was suggested that such phenomena related to the survival of resistant strains or a recurrence otitis media.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SF Dowell SM Marcy WR Philips MA Gerber B Schwartz (1998) ArticleTitlePrinciple of judicious use of antimicrobial agents for pediatrics upper respiratory tract infections Pediatrics 101 IssueIDSuppl 163–5
SF Dowell SM Marcy WR Philips MA Gerber B Schwartz (1998) ArticleTitleOtitis media – Principles of judicious use of antimicrobial agents Pediatrics 101 IssueIDSuppl 165–71
B Schwartz SM Marcy WR Phillips MA Gerber SF Dowell (1998) ArticleTitlePharyngitis – Principles of judicious use of antimicrobial agents Pediatrics 101 IssueIDSuppl 171–4
KL O'Brien SF Dowell B Schwartz SM Marcy WR Phillips MA Gerber (1998) ArticleTitleAcute sinusitis – Principles of judicious use of antimicrobial agents Pediatrics 101 IssueIDSuppl 174–7
KL O'Brien SF Dowell B Schwartz SM Marcy WR Phillips MA Gerber (1998) ArticleTitleCough illness/bronchitis – Principles of judicious use of antimicrobial agents Pediatrics 101 IssueIDSuppl 178–81
N Rosenstein WR Philips MA Gerber SM Marcy B Schwartz SF Dowell (1998) ArticleTitleThe common cold – Principles of judicious use of antimicrobial agents Pediatrics 101 IssueIDSuppl 181–4
InstitutionalAuthorNameSubcommittee on Management of Sinusitis and Committee on Quality Improvement (2001) ArticleTitleClinical practice guidelines. Management of sinusitis Pediatrics 108 798–808 Occurrence Handle10.1542/peds.108.4.1033
InstitutionalAuthorNameSubcommittee on Management of Acute Otitis Media (2004) ArticleTitleDiagnosis and management of acute otitis media Pediatrics 113 1451–65 Occurrence Handle10.1542/peds.113.5.1451
M Konno K Ubukata (1999) Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae M Konno K Ubukata (Eds) Rev. ed. Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Kyowa Kikaku Tokyo 1–157
InstitutionalAuthorNameStudy Group for Community-Acquired Infection Caused InstitutionalAuthorNameby Streptococcus pneumoniae (1999) ArticleTitleCommunity-acquired infection for which reexamination is pressed. Let PRSP and BLNAR infection be subjects Jpn J Antibiotics 52 IssueIDSuppl B 2–120
InstitutionalAuthorNameStudy Group for Community-Acquired Infection caused InstitutionalAuthorNameby Streptococcus pneumoniae (2001) ArticleTitleCommunity-acquired infection for which reexamination is pressed. Let PRSP and BLNAR infection be subjects, 2nd report Jpn J Antibiotics 54 IssueIDSuppl B 4–111
InstitutionalAuthorNameStudy Group for Upper Respiratory Tract Bacterial Flora (2005) ArticleTitleBacterial dynamics of nasopharynx Jpn J Antibiotics 58 IssueIDSuppl A 2–130
M Konno S Baba H Mikawa K Hara F Matsumoto K Kaga et al. (2006) ArticleTitleStudy of upper respiratory tract bacterial flora. First report. Variations in upper respiratory tract bacterial flora in patients with acute upper respiratory tract infection and healthy subjects, and variation by subject age J Infect Chemother 12 83–96 Occurrence Handle16648948 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10156-006-0433-3
M Konno K Ubukata N Chiba K Hasegawa Y Shibasaki K Sudoh et al. (2001) ArticleTitlePostmarketing special investigation and verification of precision for cefditoren pivoxil Jpn J Chemother 49 369–96
K Ubukata (1999) ArticleTitleCommunity-acquired infection for which reexamination is pressed. Problem institution for the bacteriological examination Jpn J Antibiotics 52 IssueIDSuppl B 4–13
K Ubukata (1999) ArticleTitleCommunity-acquired infection for which reexamination is pressed. Verification of the accuracy of bacteriological examination. Evaluation of the sample sent from each study group member Jpn J Antibiotics 52 IssueIDSuppl B 84–9
K Nagai Y Shibasaki K Hasegawa TA Davies MR Jacob K Ubukata et al. (2001) ArticleTitleEvaluation of PCR primers to screen for Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates and β-lactam resistance, and to detect common macrolide resistance determinants J Antimicrob Chemother 48 915–8 Occurrence Handle11733479 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xjt1ehsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/jac/48.6.915
K Ubukata Y Shibasaki K Yamamoto N Chiba K Hasegawa K Takeuchi et al. (2001) ArticleTitleAssociation of amino acid substitutions in penicillin-binding protein 3 with β-lactam resistance in β-lactamase-negative ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45 1693–9 Occurrence Handle11353613 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjslyqs7o%3D Occurrence Handle10.1128/AAC.45.6.1693-1699.2001
R Kobayashi M Konomi K Hasegawa M Morozumi K Sunakawa K Ubukata (2005) ArticleTitleIn vitro activity of tebipenem, a new oral carbapenem antibiotic, against penicillin-nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49 889–94 Occurrence Handle15728880 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXit12mt7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1128/AAC.49.3.889-894.2005
Hasegawa K, Chiba N, Kobayashi R, Murayama SY, Iwata S, Sunakawa K, et al. Rapidly increasing prevalence of β-lactamase-nonproducing, ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type b in patients with meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004;1509–14
M Elden E Leibovitz L Piglansky S Raiz J Press P Yagupsky et al. (2000) ArticleTitlePredictive value of pneumococcal nasopharyngeal cultures for the assessment of nonresponsive acute otitis media in children Pediatr Infect Dis J 19 298–303 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006454-200004000-00007
R Dagan E Leibovitz G Cheletz A Leiberman N Porat (2001) ArticleTitleAntibiotic treatment in acute otitis media promotes superinfection with resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae carried before initiation of treatment J Infect Dis 15 880–6 Occurrence Handle10.1086/319250
E Leibovitz D Greenberg L Piglansky S Raiz N Porat J Press et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRecurrent acute otitis media occurring within one month from completion of antibiotic therapy: relationship to original pathogen Pediatr Infect Dis J 22 209–16 Occurrence Handle12634580 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006454-200303000-00002
B Lund C Edlund B Rynnel-Dagoo Y Lundgren J Sterner GE Nord (2001) ArticleTitleEcological effects on the oro- and nasopharyngeal microflora in children after treatment of acute otitis media with cefuroxime axetil or amoxicillin-clavulanate as suspensions Clin Microbiol Infect 7 230–7 Occurrence Handle11422249 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXltFegtbc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-0691.2001.00242.x
T Kilpi E Herva T Kaijalainen R Syrjanen AK Takala (2001) ArticleTitleBacteriology of acute otitis media in a cohort of Finnish children followed for the first two years of life Pediatr Infect Dis J 20 654–62 Occurrence Handle11465836 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FitlWitg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006454-200107000-00004
I Brook AE Gober (1998) ArticleTitleBacterial interference in the nasopharynx following antimicrobial therapy of acute otitis media J Antimicrob Chemother 41 489–92 Occurrence Handle9598781 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXisV2qu7g%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/jac/41.4.489
K Tano E Grahn-Hakansson SE Holm S Hellstrom (2000) ArticleTitleInhibition of OM pathogens by alpha-hemolytic streptococci from healthy children, children with SOM and children with rAOM Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 56 185–90 Occurrence Handle11137592 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7gvVGjtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0165-5876(00)00428-6
T Walls D Power J Tagg (2003) ArticleTitleBacteriocin-like inhibitory substance (BLIS) production by the normal flora of the nasopharynx: potential to protect against otitis media? J Med Microbiol 52 829–33 Occurrence Handle12909662 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXot1Ors74%3D Occurrence Handle10.1099/jmm.0.05259-0
I Brook AE Gober (2005) ArticleTitleLong-term effects on the nasopharyngeal flora of children following antimicrobial therapy of acute otitis media with cefdinir or amoxicillin-clavulante J Med Microbiol 54 552–6
H Faden J Stanievich L Brodsky J Bernstein PL Ogra (1990) ArticleTitleChanges in nasopharyngeal flora during otitis media of childhood Pediatr Infect Dis J 9 623–6 Occurrence Handle2122410 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M%2FksVKqtg%3D%3D
A Arrieta A Arguedas P Femandez SL Block P Emperanza SL Vargas et al. (2003) ArticleTitleHigh-dose azithromycin versus high-dose amoxicillin-clavulanate for treatment of children with recurrent or persistent acute otitis media Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47 3179–86 Occurrence Handle14506028 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnvVWmtr0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1128/AAC.47.10.3179-3186.2003
P Marchisio L Claut A Rognoni S Esposito D Passali L Bellussi et al. (2003) ArticleTitleDifferences in nasopharyngeal bacterial flora in children with nonsevere recurrent acute otitis media and chronic otitis media with effusion: implications for management Pediatr Infect Dis J 22 262–8 Occurrence Handle12634589 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006454-200303000-00012
I Brook AE Gober (2005) ArticleTitleAntimicrobial resistance in the nasopharyngeal flora of children with acute otitis media and otitis media recurring after amoxicillin therapy J Med Microbiol 54 83–5 Occurrence Handle15591260 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXktlertr8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1099/jmm.0.45819-0
T Haiman E Leibovitz L Piglansky J Press P Yagupsky A Leiberman et al. (2002) ArticleTitleDynamics of pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage in children with nonresponsive acute otitis media treated with two regimens of intramuscular ceftriaxone Pediatr Infect Dis J 21 642–7 Occurrence Handle12237596 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006454-200207000-00008
VM Howie JH Ploussard (1972) ArticleTitleEfficacy of fixed-combination antibiotics versus separate components in otitis media. Effectiveness of erythromycin estrolate, triple sulfonamide, ampicillin, erythromycin estrolate-triple sulfonamide, and placebo in 280 patients with acute otitis media under two and one-half years of age Clin Pediatr (Phila) 11 205–14 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE387otFarsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1177/000992287201100407
I Brook AE Gober (2000) ArticleTitleDynamics of nasopharyngitis in children Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 122 696–700 Occurrence Handle10793349 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3lsFCkuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0194-5998(00)70199-9
L Piglansky E Leibovitz S Raiz D Greenberg J Press A Leiberman et al. (2003) ArticleTitleBacteriologic and clinical efficacy of high-dose amoxicillin for therapy of acute otitis media in children Pediatr Infect Dis J 22 405–13 Occurrence Handle12792379 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006454-200305000-00003
RM Donlan JW Costerton (2002) ArticleTitleSurvival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms Clin Microbiol Rev 15 167–93 Occurrence Handle11932229 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjslGrurg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1128/CMR.15.2.167-193.2002
MB Miller BL Bassler (2001) ArticleTitleQuorum sensing in bacteria Annu Rev Microbiol 55 165–99 Occurrence Handle11544353 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnslKjt70%3D Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.165
RK Budhani JK Struthers (1997) ArticleTitleThe use of Sorbarod biofilms to study the antimicrobial susceptibility of a strain of Streptococcus pneunoniae J Antimicrob Chemother 40 601–2 Occurrence Handle9372435 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXntl2gs70%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/jac/40.4.601
RK Budhani JK Struthers (1998) ArticleTitleInterraction of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Moraxella catrrhalis: investigation of the indirect pathogenic role of beta-lactamase-producing moraxella by use of a continuous-culture biofilm-system Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42 2521–6 Occurrence Handle9756750 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXms1CqurY%3D
CD Ehrlich R Veeh X Wang JW Costerton JD Hayes FZ Hu et al. (2002) ArticleTitleMucosal biofilm formation on middle-ear mucosa in the chinchilla model of otitis media JAMA 287 1710–5 Occurrence Handle11926896 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.287.13.1710
TF Murphy C Kirkham (2002) ArticleTitleBiofilm formation by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae: strain variability, outer membrane antigen expression and role of pili BMC Microbiol Apr 15 2–7
DR Cundell NP Gerard I Idanpaan-Heikkila EI Tuomanen (1995) ArticleTitle Streptococcus pneuminiae anchor to activate human cells by receptor for platelet-activating factor Nature 377 435–8 Occurrence Handle7566121 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXos1Slsrw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1038/377435a0
A Ring JN Weiser Tuomanen (1998) ArticleTitleMolecular analysis of a novel bi-directional pathway J Clin Invest 102 347–60 Occurrence Handle9664076 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXkslOkt7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.1172/JCI2406
JR Weber D Freyer C Alexader NW Schroder A Reiss C Kuster et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRecognition of pneumococcal peptideglycan: an expanded, pivotal role for LPS binding protein Immunity 19 155–6 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00205-X
MM Farley DS Stephan MH Mulks MD Cooper JV Bricker SS Mirra et al. (1986) ArticleTitlePathogenesis of IgA1 protease-producing and – nonproducing Haemophilus influenzae in human nasopharyngeal organ culture I Infect Dis 154 752–9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s%2FjsFSktA%3D%3D
JW St. Geme Suffix3rd S Falkow (1990) ArticleTitle Haemophilus influenzae adheres to and enters cultured human epithelial cells Infect Immun 58 4036–44 Occurrence Handle2254028 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXitFOgtA%3D%3D
J Foragren A Samuelson A Ahlin J Jonnasson B Rynnel-Dagoo A Lindberg (1994) ArticleTitle Haemophilus influenzae resides and multiplies intracellularly in human adenoid tissue as demonstrated by in situ hybridization and bacterial viability assay Infect Immun 62 673–9
MR Ketterer JQ Shao DB Hornick B Buscher VK Bandi MA Apicella (1999) ArticleTitleInfection of primary human bronchial epithelial cells by Haemophilus influenzae: macropinnocytosis as a mechanism of airway epithelial cell entry Infect Immun 67 4161–70 Occurrence Handle10417188 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXkvVKlt70%3D
WE Swords BA Buscher K Ver Steeg Ii A Preston WA Nichols JN Weiser et al. (2000) ArticleTitleNon-typable Haemophilus influenzae adhere to and invade human bronchial epithelial cells via an interaction of lipooligosaccharide with the PAF receptor Mol Microbiol 37 13–37 Occurrence Handle10931302 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlsFOksb4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01952.x
C Rosenow P Ryan JN Weiser S Johnson P Fontan A Ortqvist et al. (1997) ArticleTitleContribution of novel choline-binding proteins to adherence, colonization and immmunogenicity of Streptococcus pneumoniae Mol Microbiol 25 819–29 Occurrence Handle9364908 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmsVKisb4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2958.1997.mmi494.x
JR Zhang KE Moctov ME Lamm M Nanno S Shimida M Ohwaki et al. (2000) ArticleTitleThe polymeric immunogloblin receptor translocates pneumococci across human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells Cell 102 827–37 Occurrence Handle11030626 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmvFSht74%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00071-4
KK Gosink ER Mann C Guglielmo EI Tuomanen HR Masure (2000) ArticleTitleRole of novel choline binding proteins in virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae Infect Immun 68 5690–5 Occurrence Handle10992472 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmvVGnsL4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1128/IAI.68.10.5690-5695.2000
C Fernandez-Tornero R Lopez E Garcia G Gimenz-Gallego A Romero (2001) ArticleTitleA novel solenoid fold in the cell wall anchoring domain of the pneumococcal virulence factor LytA Nat Struct Biol 8 1020–4 Occurrence Handle11694890 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXovVCqtLw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1038/nsb724
JW St. Geme Suffix3rd ML de la Morena S Falkow (1994) ArticleTitleA Haemophilus influenzae IgA protease-like protein promotes intimate interaction with human epithelial cells Mol Microbiol 14 217–33 Occurrence Handle7830568 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXhslehtr4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01283.x
SJ Barenkamp JW St. Geme Suffix3rd (1994) ArticleTitleGenes encoding high-molecular-weight adhesion proteins of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae are part of gene clusters Infect Immun 62 3320–8 Occurrence Handle8039903 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjslegsA%3D%3D
SJ Barenkamp JW St. Geme Suffix3rd (1996) ArticleTitleIdentification of a second family of high-molecular-weight adhesion proteins expressed by non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae Mol Microbiol 19 1215–23 Occurrence Handle8730864 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XitFenuro%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02467.x
JW St. Geme Suffix3rd D Cutter SJ Barenkamp (1996) ArticleTitleCharacterization of the genetic locus encoding Haemophilus influenzae type b surface fibrils J Bacteriol 178 6281–7 Occurrence Handle8892830 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xms1WiurY%3D
WE Sword ML Moore L Godzicki G Bukofzer MJ Mitten J VonCannon (2004) ArticleTitleSialylation of lipooligosaccharides promotes biofilm formation by nontypeable Heamophilus influenzae Infect Immun 72 106–13 Occurrence Handle10.1128/IAI.72.1.106-113.2004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXpvFah
RM Donlan JA Piede CD Heyes L Sanili R Murga P Edomonds et al. (2004) ArticleTitleModel system for growing and quantifying Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilm in situ and real time Appl Environ Microbiol 70 4980–8 Occurrence Handle15294838 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXms1eks7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.70.8.4980-4988.2004
TF DeMaria RB Prior BR Briggs DJ Lim HG Birck (1984) ArticleTitleEndotoxin in middle-ear effusion from patients with chronic otitis media with effusion J Clin Microbiol 20 15–7 Occurrence Handle6611350 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2c3msFWntA%3D%3D
JR Dingman MG Rayner S Mishra Y Zhang MD Ehrlich JC Post et al. (1998) ArticleTitleCorrelation between presence of viable bacteria and presence of endotoxin in middle-ear effusions J Clin Microbiol 36 3417–9 Occurrence Handle9774611 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvkvFyrtg%3D%3D
MW Dunne T Latiolais B Lewis B Pistorius G Bottenfield WH Moore et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRandomized double-blind study of the clinical efficacy of 3 days of aziyhromycin compared with co-amoxiclav for the treatment of acute otitis media J Antimicrob Chemother 52 469–72 Occurrence Handle12888586 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnt1KjtLs%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/jac/dkg358
SL Block TA Busman MM Paris S Bukofzer (2004) ArticleTitleComparison of five-day cefdinir treatment with ten-day low-dose amoxicillin/clavulanate treatment for acute otitis media Pediatr Infect Dis J 23 834–8 Occurrence Handle15361722
JA Hedrick LD Sher RH Schwartz P Pierce (2001) ArticleTitleCefprozil versus high-dose amoxicillin/clavulanate in children with acute otitis media Clin Ther 23 193–204 Occurrence Handle11293553 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXivVOgsbw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0149-2918(01)80002-3
SL Block JM McCarty JA Hedrick MA Nemeth CH Keyserling KJ Tack et al. (2000) ArticleTitleComparative safety and efficacy of cefdinir vs amoxicillin/clavulanate for treatment of suppurative acute otitis media in children Pediatr Infect Dis J 19 IssueIDSuppl S159–165 Occurrence Handle11144398 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3it12ntQ%3D%3D
SL Block J Kratzer MA Nemeth KJ Tack (2000) ArticleTitleFive-day cefdinir course vs ten-day cefprozil course for treatment of acute otitis media Pediatr Infect Dis J 19 IssueIDSuppl S147–152 Occurrence Handle11144396 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3it12ntw%3D%3D
Dagan R, Johnson CE, McLinn N, Feris J, Leivovitz E, Burch DJ, Bacteriologic and clinical efficacy of amoxicillin/clavulanate vs. azithromycin in acute otitis media. 200;19:95–104
ME Pichichero SM Marsocci ML Murphy W Hoeger AB Francis JL Green (2001) ArticleTitleA prospective observational study of 5-, 7-, and 10-day antibiotic treatment for acute otitis media Otolaryngol Head Surg 124 381–7 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzjvF2ktA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1067/mhn.2001.114311
CR Manarey BD Westerberg SA Marion (2002) ArticleTitleClinical decision analysis in the treatment of acute otitis media in a child over 2 years of age J Otolaryngol 31 23–30 Occurrence Handle11883437
SL Block JA Hedrick RD Tyler RA Smith GJ Harrison (2001) ArticleTitleMicrobiology of acute otitis recently treated with aminopenicillins Pediatr Infect Dis J 20 1017–21 Occurrence Handle11734704 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MnoslKltQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006454-200111000-00003
R Cohen E Bingen E Varon F de La Rocque N Brahimi C Levy et al. (1997) ArticleTitleChange in nasopharyngeal carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae resulting from antibiotic therapy for acute otitis media in children Pediatr Infect Dis J 16 555–60 Occurrence Handle9194104 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2szjsleltg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006454-199706000-00004
M Hotomi N Yamanaka J Shimada Y Ikeda H Faden (2004) ArticleTitleFactors associated with clinical outcomes in acute otitis media Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 113 845–52
M Hotomi N Yamanaka T Samukawa M Suzumot A Sasaki J Shimada et al. (2005) ArticleTitleTreatment and outcome of severe and non-severe acute otitis media Eur J Pediatr 164 3–8 Occurrence Handle15549378 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00431-004-1564-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Konno, M., Baba, S., Mikawa, H. et al. Study of nasopharyngeal bacterial flora. Second report. Variations in nasopharyngeal bacterial flora in children aged 6 years or younger when administered antimicrobial agents. Part 2. J Infect Chemother 12, 305–330 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-006-0469-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-006-0469-4