Abstract
Background
We carried out robot-assisted lateral pelvic lymph node dissection (LPLND) for rectal cancer with a stereotactic navigation system. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy and feasibility of the system.
Methods
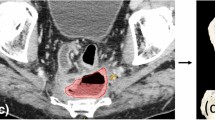
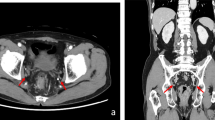
We constructed a navigation system based on the Polaris Spectra optical tracking device (Northern Digital Inc., Canada) and the open-source software 3D Slicer (version 3.8.1; http://www.slicer.org). We used the landmark-based registration method for patient-to-image registration. Body surface landmarks and intra-abdominal landmarks were used. We evaluated the time required for registration and target registration error (TRE; the distance between corresponding points after registration) for the root of the superior gluteal artery the root of the obturator or superior vesical artery, and the obturator foramen during minimally invasive LPLND for rectal cancer. Five patients who had LPLND for rectal cancer at the University of Tokyo Hospital between September 2020 and May 2021 were enrolled.
Results
The mean time required for registration was 49 s with the body surface landmarks and 88 s with the intra-abdominal landmarks. The mean TRE improved markedly when the registration was performed using intra-abdominal landmarks. The mean TRE of the root of the superior gluteal artery, the root of the obturator or superior vesical artery, and the obturator foramen were 55.8 mm, 53.4 mm, and 55.2 mm with the body surface landmarks and 11.8 mm, 10.0 mm, and 12.6 mm with the intra-abdominal landmarks, respectively. There were no adverse events related to the registration process.
Conclusions
When stereotactic navigation systems are used for minimally invasive LPLND, the use of intra-abdominal landmarks for registration is feasible and may allow simpler and more accurate navigation than the use of body surface landmarks.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakanishi R, Yamaguchi T, Akiyoshi T, Nagasaki T, Nagayama S, Mukai T, Ueno M, Fukunaga Y, Konishi T (2020) Laparoscopic and robotic lateral lymph node dissection for rectal cancer. Surg Today 50(3):209–216
Kiyomatsu T, Ishihara S, Murono K, Otani K, Yasuda K, Nishikawa T, Tanaka T, Hata K, Kawai K, Nozawa H, Yamaguchi H, Watanabe T (2016) Anatomy of the middle rectal artery: a review of the historical literature. Surg Today 47:14–19
Toda S, Kuroyanagi H, Matoba S, Hiramatsu K, Okazaki N, Tate T, Tomizawa K, Hanaoka Y, Moriyama J (2018) Laparoscopic treatment of rectal cancer and lateral pelvic lymph node dissection: are they obsolete? Minerva Chir 73(6):558–573
Zelhart M, Kaiser AM (2018) Robotic versus laparoscopic versus open colorectal surgery: towards defining criteria to the right choice. Surg Endosc 32(1):24–38
Ogura A, Akiyoshi T, Nagasaki T, Konishi T, Fujimoto Y, Nagayama S, Fukunaga Y, Ueno M, Kuroyanagi H (2017) Feasibility of laparoscopic total mesorectal excision with extended lateral pelvic lymph node dissection for advanced lower rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiotherapy. World J Surg 41(3):868–875
Kawahara H, Watanabe K, Enomoto H, Tomoda M, Akiba T, Yanaga K (2015) Sentinel node navigation surgery for lower rectal cancer. Anticancer Res 35(6):3489–3493
Horie H, Koinuma K, Ito H, Sadatomo A, Naoi D, Kono Y, Inoue Y, Morimoto M, Tahara M, Lefor AK, Sata N, Sasaki T, Sugimoto H (2018) Utility of preoperative 3-D simulation of laparoscopic lateral pelvic lymph node dissection for advanced rectal cancer: surgical outcomes of 10 initial cases. Asian J Endosc Surg 11(4):355–361
Hojo D, Murono K, Nozawa H, Kawai K, Hata K, Tanaka T, Ishihara S (2020) Utility of a three-dimensional printed pelvic model for lateral pelvic lymph node dissection. Int J Colorectal Dis 35(5):905–910
Saito Y, Sugimoto M, Imura S, Morine Y, Ikemoto T, Iwahashi S, Yamada S, Shimada M (2019) Intraoperative 3D hologram support with mixed reality techniques in liver surgery. Ann Surg 271:e4–e7
Kiyomatsu H, Ma L, Wang J, Kiyomatsu T, Tsukihara H, Kobayashi E, Sakuma I, Ishihara S (2021) Deformation of the pelvic arteries caused by pneumoperitoneum and postural changes in an animal model. In Vivo 35(1):275–281
Ochiai K, Kobayashi E, Tsukihara H, Nozawa H, Kawai K, Sasaki K, Murono K, Ishihara S, Sakuma I (2021) Stereotactic navigation system for laparoscopic lateral pelvic lymph node dissection. Dis Colon Rectum 64(6):e372–e377
Watanabe T, Muro K, Ajioka Y, Hashiguchi Y, Ito Y, Saito Y, Hamaguchi T, Ishida H, Ishiguro M, Ishihara S, Kanemitsu Y, Kawano H, Kinugasa Y, Kokudo N, Murofushi K, Nakajima T, Oka S, Sakai Y, Tsuji A, Uehara K, Ueno H, Yamazaki K, Yoshida M, Yoshino T, Boku N, Fujimori T, Itabashi M, Koinuma N, Morita T, Nishimura G, Sakata Y, Shimada Y, Takahashi K, Tanaka S, Tsuruta O, Yamaguchi T, Yamaguchi N, Tanaka T, Kotake K, Sugihara KC (2018) Japanese Society for Cancer of the, and Rectum, Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (JSCCR) guidelines 2016 for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 23(1):1–34
Watanabe T, Hata K (2016) Robotic surgery for rectal cancer with lateral lymph node dissection. Br J Surg 103(13):1755–1757
Kikinis R, Pieper SD, Vosburgh KG (2014) 3D slicer: a platform for subject-specific image analysis, visualization, and clinical support. In: Jolesz FA (ed) Intraoperative imaging and image-guided therapy. Springer, New York, pp 277–289
Murono K, Kawai K, Kazama S, Ishihara S, Yamaguchi H, Sunami E, Kitayama J, Watanabe T (2015) Anatomy of the inferior mesenteric artery evaluated using 3-dimensional CT angiography. Dis Colon Rectum 58(2):214–219
Moghari MH, Abolmaesumi P (2009) Distribution of fiducial registration error in rigid-body point-based registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(11):1791–1801
Kok END, van Veen R, Groen HC, Heerink WJ, Hoetjes NJ, van Werkhoven E, Beets GL, Aalbers AGJ, Kuhlmann KFD, Nijkamp J, Ruers TJM (2020) Association of image-guided navigation with complete resection rate in patients with locally advanced primary and recurrent rectal cancer: a nonrandomized controlled trial. JAMA Netw Open 3(7):e208522
Elhusseini M, Aly EH (2020) Lateral pelvic lymph node dissection in the management of locally advanced low rectal cancer: summary of the current evidence. Surg Oncol 35:418–425
Zhou SC, Tian YT, Wang XW, Zhao CD, Ma S, Jiang J, Li EN, Zhou HT, Liu Q, Liang JW, Zhou ZX, Wang XS (2019) Application of indocyanine green-enhanced near-infrared fluorescence-guided imaging in laparoscopic lateral pelvic lymph node dissection for middle-low rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 25(31):4502–4511
Wijsmuller AR, Romagnolo LGC, Agnus V, Giraudeau C, Melani AGF, Dallemagne B, Marescaux J (2018) Advances in stereotactic navigation for pelvic surgery. Surg Endosc 32(6):2713–2720
Okada T, Kawada K, Sumii A, Itatani Y, Hida K, Hasegawa S, Sakai Y (2020) Stereotactic navigation for rectal surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 63(5):693–700
Nijkamp J, Kuhlmann KFD, Ivashchenko O, Pouw B, Hoetjes N, Lindenberg MA, Aalbers AGJ, Beets GL, Van Coevorden F, Kok N, Ruers TJM (2018) Prospective study on image-guided navigation surgery for pelvic malignancies. J Surg Oncol 119:510–517
Hayashi Y, Misawa K, Hawkes DJ, Mori K (2016) Progressive internal landmark registration for surgical navigation in laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(5):837–845
Kwak JM, Romagnolo L, Wijsmuller A, Gonzalez C, Agnus V, Lucchesi FR, Melani A, Marescaux J, Dallemagne B (2019) Stereotactic pelvic navigation with augmented reality for transanal total mesorectal excision. Dis Colon Rectum 62(1):123–129
Funding
This study was supported by Canon Medical Systems (no. 170300001258), the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science-National Natural Foundation of China joint research project (no. 120197410) and JST (Japan Science and technology Agency) COI Grant number JPMJCE1304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the University of Tokyo (No. 2019281NI).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 73285 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ochiai, K., Kobayashi, E., Sasaki, K. et al. Stereotactic navigation using registration based on intra-abdominal landmarks in robotic-assisted lateral pelvic lymph node dissection. Tech Coloproctol 26, 735–743 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-022-02643-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-022-02643-8