Abstract
Background
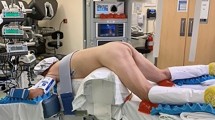
The EndoLuminal Surgical System (ELS) is an emerging non-linear robotic system specifically designed for transanal surgery that allows for excision of colorectal neoplasia and luminal defect closure.
Methods
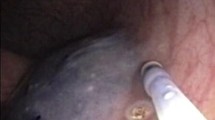
An evaluation of ELS was conducted by a single surgeon in a preclinical setting at the EndoSurgical Center of Florida in Orlando, between October 1st, 2020 and December 31st, 2020, using porcine colon as a model. Mock lesions measured 2.5 to 3.5 cm were excised partial-thickness. Specimen quality and excision time was assessed and evaluated.
Results
Twenty consecutive robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery (TAMIS) operations utilizing the ELS system were successfully performed without fragmentation. The mean and standard deviation procedure time for all 20 cases was 18.41 ± 14.15 min. The latter 10 cases were completed in substantially less time, suggesting that ELS requires at least 10 preclinical cases for a surgeon to become familiar with the technology. A second task, namely suture closure of the partial-thickness defect, was performed in 9 of the 20 cases. Mean time and standard deviation for this task measured 27.89 ± 10.07 min. There were no adverse events.
Conclusions
ELS was successful in performing the tasks of partial-thickness disc excision and closure in a preclinical evaluation. Further study is necessary to determine its clinical applicability.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atallah S, Albert M, Larach S (2010) Transanal minimally invasive surgery: a giant leap forward. Surg Endosc 24(9):2200–2205
deBeche-Adams T, Nassif G (2015) Transanal minimally invasive surgery. Clin Colon Rec Surg 28(3):176
Keller DS, Haas EM (2016) Transanal minimally invasive surgery: state of the art. J Gastrointest Surg 20(2):463–469
Atallah S, Larach S (2020) Transanal minimally invasive surgery. JAMA Surg. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2020.4994 (Published online November 18, 2020)
Atallah S, Albert MR, deBeche-Adams TH, Larach SW (2011) Robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery in a cadaveric model. Tech Coloproct 15(4):461–464
Atallah S, Parra-Davila E, DeBeche-Adams T, Albert M, Larach S (2012) Excision of a rectal neoplasm using robotic transanal surgery (RTS): a description of the technique. Tech Coloproct 16(5):389–392
Atallah S, Martin-Perez B, Parra-Davila E, deBeche-Adams T, Nassif G, Albert M, Larach S (2015) Robotic transanal surgery for local excision of rectal neoplasia, transanal total mesorectal excision, and repair of complex fistulae: clinical experience with the first 18 cases at a single institution. Tech Coloproct 19(7):401–410
Yao HL, Ngu JC, Lin YK, Chen CC, Chang SW, Kuo LJ (2020) Robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery for rectal lesions. Surg Innov 27(2):181–186. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350619892490 (Epub 2020 Jan 10. PMID: 31920153)
Baker EJ, Waters PS, Peacock O, Narasimhan V, Larach T, McCormick J, Heriot AG, Warrier S, Lynch C (2020) Robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery - technical, oncological and patient outcomes from a single institution. Colorectal Dis 22(10):1422–1428. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.15045 (Epub 2020 May 19. PMID: 32198787)
Liu S, Suzuki T, Murray BW, Parry L, Johnson CS, Horgan S, Ramamoorthy S, Eisenstein S (2019) Robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery (TAMIS) with the newest robotic surgical platform: a multi-institutional North American experience. Surg Endosc 33(2):543–548
Tomassi MJ, Taller J, Yuhan R, Ruan JH, Klaristenfeld DD (2019) Robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery for the excision of rectal neoplasia: clinical experience with 58 consecutive patients. Dis Colon Rectum 62(3):279–285. https://doi.org/10.1097/DCR.0000000000001223
Hompes R, Rauh SM, Ris F, Tuynman JB, Mortensen NJ (2014) Robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery for local excision of rectal neoplasms. Br J Surg 101(5):578–581. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.9454 (PMID: 24633833)
Keller D, Atallah S, Seela R, Seeliger B, Parra-Davila E (2020) Nonlinear robotics in surgery. In: Atallah S (ed) Digital surgery. Springer, Cham, pp 285–310
Stipa F, Tierno SM, Russo G, Burza A (2021) Transanal minimally invasive surgery (TAMIS) versus trans-anal endoscopic microsurgery (TEM): a comparative case–control matched-pairs analysis. Surg Endosc 12:1–6
Lee L, Edwards K, Hunter IA, Hartley JE, Atallah SB, Albert MR, Hill J, Monson JR (2017) Quality of local excision for rectal neoplasms using transanal endoscopic microsurgery versus transanal minimally invasive surgery: a multi-institutional matched analysis. Dis Colon Rectum 60(9):928–935
Lee L, Burke JP, deBeche-Adams T, Nassif G, Martin-Perez B, Monson JR, Albert MR, Atallah SB (2018) Transanal minimally invasive surgery for local excision of benign and malignant rectal neoplasia: outcomes from 200 consecutive cases with midterm follow up. Ann Surg 267(5):910–916
Arezzo A, Passera R, Marchese N, Galloro G, Manta R, Cirocchi R (2016) Systematic review and meta-analysis of endoscopic submucosal dissection vs endoscopic mucosal resection for colorectal lesions. UEG J 4(1):18–29
Toyonaga T, Man-i M, Chinzei R, Takada N, Iwata Y, Morita Y, Sanuki T, Yoshida M, Fujita T, Kutsumi H, Hayakumo T (2010) Endoscopic treatment for early stage colorectal tumors: the comparison between EMR with small incision, simplified ESD, and ESD using the standard flush knife and the ball tipped flush knife. Acta Chir Iugosl 57(3):41–46
Lee E, Lee JB, Lee SH et al (2013) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors–1000 colorectal ESD cases: one specialized institute’s experiences. Surg Endosc 27:31–39
Draganov PV, Aihara H, Karasik MS, Ngamruengphong S, Aadam AA, Othman MO, Sharma N, Grimm IS, Rostom A, Elmunzer BJ, Jawaid SA, Westerveld D, Perbtani YB, Hoffman BJ, Schlachterman A, Siegel A, Coman RM, Wang AY, Yang D (2021) Endoscopic submucosal dissection in north America: a large prospective multicenter study. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.036
Shigita K, Oka S, Tanaka S, Sumimoto K, Hirano D, Tamaru Y, Ninomiya Y, Asayama N, Hayashi N, Shimamoto F, Arihiro K (2017) Long-term outcomes after endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial colorectal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc 85(3):546–553
Wexner SD (2020) Robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery. Colorectal Dis 22(10):1217–1218. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.15172
Hompes R (2015) Robotics and transanal minimal invasive surgery (TAMIS): The “sweet spot” for robotics in colorectal surgery? Tech Coloproctol 19(7):377–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-015-1326-1
Hussain T, Lang S, Haßkamp P, Holtmann L, Höing B, Mattheis S (2020) The Flex robotic system compared to transoral laser microsurgery for the resection of supraglottic carcinomas: first results and preliminary oncologic outcomes. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277(3):917–924. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05767-0
Sethi N, Gouzos M, Padhye V, Ooi EH, Foreman A, Krishnan S, Hodge JC (2020) Transoral robotic surgery using the Medrobotic Flex® system: the Adelaide experience. J Robot Surg 14(1):109–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-019-00941-2
Carmichael H, D’Andrea AP, Skancke M, Obias V, Sylla P (2019) Feasibility of transanal total mesorectal excision (taTME) using the Medrobotics Flex® system. Surg Endosc 34(1):485–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-07019-y
Paull JO, Graham A, Parascandola SA, Hota S, Pudalov N, Arnott S, Skancke M, Obias V (2020) The outcomes of two robotic platforms performing transanal minimally invasive surgery for rectal neoplasia: a case series of 21 patients. J Robot Surg 14(4):573–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-019-01021-1
Atallah S (2017) Assessment of a flexible robotic system for endoluminal applications and transanal total mesorectal excision (taTME): could this be the solution we have been searching for? Tech Coloproct 21(10):809–814
Marks JH, Kunkel E, Salem JF, Martin C, Anderson B, Agarwal S (2020) First clinical experience with single-port robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery (SP rTAMIS) for benign rectal neoplasms. Tech Coloproctol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-020-02358-8
Liu S, Kelley SR, Behm KT (2020) Single-port robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery (SPR-TAMIS) approach to local excision of rectal tumors. Tech Coloproctol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-020-02286-7
Rex DK, Hassan CC, Dewitt JM (2017) Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection in the United States: why do we hear so much about it and do so little of it? Gastrointest Endosc 85(3):554–558
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Sam Atallah is a constultant and clinical trial principle investigator for ColubrisMX. Dr. Alexis Sanchez is a research coordinator who received fees for activity related to ColubrisMX ELS investigational research. Dr. Sergio Larach and Dr. Elisa Bianchi have no financial relationships to disclose. The research conducted represents the authors’ own work.
Ethical Approval
This research was performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not applicable as the work represented herein did not involve human subjects. Cadaveric research was conducted in accordance with the standards set forth by ethics and scientific laboratory regulations.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atallah, S., Sanchez, A., Bianchi, E. et al. Envisioning the future of colorectal surgery: preclinical assessment and detailed description of an endoluminal robotic system (ColubrisMX ELS). Tech Coloproctol 25, 1199–1207 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-021-02481-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-021-02481-0