Abstract
Background
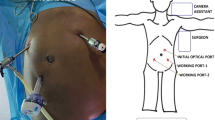
Ventral rectopexy to the promontory has become one of the most strongly advocated surgical treatments for patients with full-thickness rectal prolapse and deep enterocele. Despite its challenges, laparoscopic ventral rectopexy with or without robotic assistance for selected patients can be performed with relatively minimal patient trauma thus creating the potential for same-day discharge. The aim of this prospective case–controlled study was to assess the feasibility, safety, and cost of day case robotic ventral rectopexy compared with routine day case laparoscopic ventral rectopexy.
Methods
Between February 28, 2014 and March 3, 2015, 20 consecutive patients underwent day case laparoscopic ventral rectopexy for total rectal prolapse or deep enterocele at Michallon University Hospital, Grenoble. Patients were selected for day case surgery on the basis of motivation, favorable social circumstances, and general fitness. One out of every two patients underwent the robotic procedure (n = 10). Demographics, technical results, and costs were compared between both groups.
Results
Patients from both groups were comparable in terms of demographics and technical results. Patients operated on with the robot had significantly less pain (p = 0.045). Robotic rectopexy was associated with longer median operative time (94 vs 52.5 min, p < 0.001) and higher costs (9088 vs 3729 euros per procedure, p < 0.001) than laparoscopic rectopexy.
Conclusions
Day case robotic ventral rectopexy is feasible and safe, but results in longer operative time and higher costs than classical laparoscopic ventral rectopexy for full-thickness rectal prolapse and enterocele.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones OM, Cunningham C, Lindsey I (2011) The assessment and management of rectal prolapse, rectal intussusception, rectocoele, and enterocoele in adults. BMJ 342:325–329
Kariv Y, Delaney CP, Casillas S et al (2006) Long-term outcome after laparoscopic and open surgery for rectal prolapse: a case-control study. Surg Endosc 20:35–42
Sajid MS, Siddiqui MR, Baig MK (2010) Open versus laparoscopic repair of full-thickness rectal prolapse: a re-meta-analysis. Colorectal Dis 12:515–525
Faucheron JL, Voirin D, Riboud R, Waroquet PA, Noel J (2012) Laparoscopic anterior rectopexy to the promontory for full-thickness rectal prolapse in 175 consecutive patients: short- and long-term follow-up. Dis Colon Rectum 55:660–665
Jarry J, Moreau Gaudry A, Long JA, Chipon E, Cinquin P, Faucheron JL (2013) Miniaturized robotic laparoscope-holder for rectopexy: first results of a prospective study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 23:351–355
Faucheron JL, Barot S, Collomb D, Hohn N, Anglade D, Dubreuil A (2014) Dynamic cystocolpoproctography is superior to functional pelvic MRI in the diagnosis of posterior pelvic floor disorders: results of a prospective study. Colorectal Dis 16:240–247
D’Hoore A, Penninckx F (2006) Laparoscopic ventral rectocolpopexy for rectal prolapse: surgical technique and outcome for 109 patients. Surg Endosc 20:1919–1923
Boccasanta P, Rosati R, Venturi M et al (1998) Comparison of laparoscopic rectopexy with open technique in the treatment of complete rectal prolapse: clinical and functional results. Surg Laparosc Endosc 8:460–465
Solomon MJ, Young CJ, Eyers AA, Roberts RA (2002) Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic versus open abdominal rectopexy for rectal prolapse. Br J Surg 89:35–39
D’Hoore A, Cadoni R, Penninckx F (2004) Long-term outcome of laparoscopic ventral rectopexy for total rectal prolapse. Br J Surg 91:1500–1505
Purkayastha S, Tekkis P, Athanasiou T et al (2005) A comparison of open versus laparoscopic abdominal rectopexy for full-thickness rectal prolapse: a meta-analysis. Dis Colon Rectum 48:1930–1940
Slawik S, Soulsby R, Carter H, Payne H, Dixon AR (2008) Laparoscopic ventral rectopexy, posterior colporraphy and vaginal sacrocolpopexy for the treatment of recto-genital prolapse and mechanical outlet obstruction. Colorectal Dis 10:138–143
Buchs NC, Pugin F, Ris F, Volonte F, Morel P, Roche B (2013) Early experience with robotic rectopexy. Int J Med Robot 9:e61–e65
Mäkelä-Kaikkonen J, Rautio T, Klintrup K et al (2014) Robotic-assisted and laparoscopic ventral rectopexy in the treatment of rectal prolapse: a matched-pairs study of operative details and complications. Tech Coloproctol 18:151–155
De Hoog DENM, Heemskerk J, Nieman FHM, van Gemert WG, Baeten CGMI, Bouvy ND (2009) Recurrence and functional results after open versus conventional laparoscopic versus robot-assisted laparoscopic rectopexy for rectal prolapse: a case-control study. Int J Colorectal Dis 24:1201–1206
Wong MT, Meurette G, Rigaud J, Regenet N, Lehur PA (2011) Robotic versus laparoscopic rectopexy for complex rectocele: a prospective comparison of short-term outcomes. Dis Colon Rectum 54:342–346
Heemskerk J, de Hoog DENM, van Gemert WG, Baeten CGMI, Greve JWM, Bouvy ND (2007) Laparoscopic rectopexy for rectal prolapse: a comparative study on costs and time. Dis Colon Rectum 50:1825–1830
Mantoo S, Podevin J, Regenet N, Rigaud J, Lehur PA, Meurette G (2013) Is robotic-assisted ventral mesh rectopexy superior to laparoscopic ventral mesh rectopexy in the management of obstructed defaecation. Colorectal Dis 15:469–475
Perrenot C, Germain A, Scherrer ML, Ayav A, Brunaud L, Bresler L (2013) Long-term outcomes of robotic-assisted laparoscopic rectopexy for rectal prolapse. Dis Colon Rectum 56:909–1014
Germain A, Perrenot C, Scherrer ML et al (2014) Long-term outcome of robotic-assisted laparoscopic rectopexy for full-thickness rectal prolapse in elderly patients. Colorectal Dis 16:198–202
Faucheron JL, Trilling B, Girard E, Sage PY, Barbois S, Reche F (2015) Anterior rectopexy for full-thickness rectal prolapse: technical and functional results. World J Gastroenterol 21:5049–5055
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Genevieve Trilling for English proofreading, to Dr. Martine Richard, MD, and Mrs Sofia Kowalski who provided ambulatory data results, to Prof. Jean-Luc Bosson, MD, PhD, who provided methodology support and review, and to Mrs Kristina Skåre who provided statistical expertise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Prof. Jean-Luc Faucheron received honoraria for punctual interventions, punctual consultancies and had some reimbursed travels and prepaid subscriptions for meetings from AMI, Covidien, Medtronic, Ethicon, MSD, Legrand, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Fabian Reche has a commercial relationship with Endocontrol as a consultant and has been reimbursed for travel and meeting subscriptions by Covidien, Baxter, AMI, and Leo Pharma. Drs. Sandrine Barbois, Bertrand Trilling, Pierre-Yves Sage, and Pierre-Alexandre Waroquet have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
For this study, patients have signed an informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faucheron, JL., Trilling, B., Barbois, S. et al. Day case robotic ventral rectopexy compared with day case laparoscopic ventral rectopexy: a prospective study. Tech Coloproctol 20, 695–700 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-016-1518-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-016-1518-3