Abstract
Background
We evaluated the efficacy and safety of superselective embolization with assistance of colonoscopy for acute colonic hemorrhage.
Methods
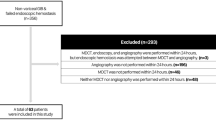
Of 92 cases of acute colonic hemorrhage requiring colonoscopic intervention, 11 (12 %) could not be successfully treated. Of these, 10 patients (9 men, mean age 65.5 years, range 39–75 years) underwent superselective embolization. Hemorrhage was caused by diverticular disease (n = 8), polypectomy (n = 1), and vascular malformation (n = 1). In all 10 cases, the radiopaque clips were placed at the bleeding point via colonoscopy. Microcatheters were used in all procedures, and embolization was performed at the level of the vasa recta leading to or near the clips with Gelfoam particles, microcoils, or both.
Results
Immediate hemostasis was achieved in all patients. In 6 of 10 patients (60 %), selective angiograms showed no active extravasation at the time of the procedure and the embolization was performed using clips as a landmark. In the remaining four patients, selective angiograms showed active extravasation from the vasa recta leading to the clips. The mean number of embolized vessels with no active extravasation and with active extravasation was 1.83 (range 1–3) and 1.25 (range 1–2), respectively. The mean duration of clinical follow-up was 11.6 months (range 1–29 months). One patient (10 %) bled from a different site than the treated site a month after embolization, but the bleeding ceased after endoscopic intervention. All the patients (100 %) were evaluated for objective evidence of ischemia by colonoscopy. Four of the 10 patients (40 %) were found endoscopically to have small areas of ischemia involving only the mucosa, but they remained asymptomatic. There was no bowel infarction or stricture.
Conclusions
Colonoscopy-assisted superselective embolization may be a safe and useful procedure for acute colonic hemorrhage without active extravasation on angiogram.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubo A, Kagaya T, Nakagawa H (1986) Studies on complications of diverticular disease of the colon. Japan J Med 24:39–43
Bokhari M, Vernava AM, Ure T, Longo WE (1996) Diverticular hemorrhage in the elderly—is it well tolerated? Dis Colon Rectum 39:191–195
Peck DJ, Mcloughlin RF, Hughson MN, Rankin RN (1998) Percutaneous embolotherapy of lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. J Vasc Interv Radiol 9:747–751
Ledermann HP, Schoch E, Jost R, Zollikofer CL (1999) Embolization of the vasa recta in acute lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage: a report of five cases. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 22:315–320
Guy GE, Shetty PC, Sharma RP, Burke MW, Burke TH (1992) Acute lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage: treatment by superselective embolization with polyvinyl alcohol particles. Am J Roentgenol 159:521–526
Gordon RL, Ahl KL, Kerlan RK et al (1997) Selective arterial embolization for the control of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Surg 174:24–28
Nicholson AA, Ettles DF, Hartley JE et al (1998) Transcatheter coil embolotherapy: a safe and effective option for major colonic hemorrhage. Gut 43:79–84
Luchtefeld MA, Senagore AJ, Szomstein M, Fedeson B, Erp JV, Rupp S (2000) Evaluation of transarterial embolization for lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Dis Colon Rectum 43:532–534
Funaki B, Kostelic JK, Lorenz J et al (2001) Superselective microcoil embolization of colonic hemorrhage. Am J Roentgenol 177:829–836
Funaki B (2004) Superselective embolization of lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage: a new paradigm. Abdom Imaging 29:434–438
Bandi R, Shetty PC, Sharma RP, Burke TH, Burke MW, Kastan D (2001) Superselective arterial embolization for the treatment of lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12:1399–1405
DeBarros J, Rosas L, Cohen J, Vignati P, Sardella W, Hallisey M (2002) The changing paradigm for the treatment of colonic hemorrhage. Dis Colon Rectum 45:802–808
Gady CJ, Reynolds CH, Blum A (2003) Selective arterial embolization for control of lower gastrointestinal bleeding: recommendations for a clinical management pathway. Curr Surg 60:344–347
Kuo WT, Lee DE, Saad WE, Patel N, Sahler LG, Waldman DL (2003) Superselective microcoil embolization for the treatment of lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:1503–1509
d’Othee BJ, Surapaneni P, Rabkin D, Nasser I, Clouse M (2006) Microcoil embolization for acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29:49–58
Ahmed TM, Cowley JB, Robinson G et al (2010) Long term follow-up of transcatheter coil embolotherapy for major colonic hemorrhage. Colorectal Dis 12:1013–1017
Mensel B, Kuhn JP, Kraft M et al (2012) Selective microcoil embolization of arterial gastrointestinal bleeding in the acute situation: outcome, complications, and factors affecting treatment success. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24:155–163
Teng HC, Liang HL, Lin YH et al (2013) The efficacy and long-term outcome of microcoil embolotherapy for acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Korean J Radiol 14:259–268
Adusumilli S, Gosselink MP, Ctercteko G et al (2013) The efficacy of selective arterial embolization in the management of colonic bleeding. Tech Coloproctol. doi:10.1007/s10151-013-1088-6
Billingham RP (1997) The conundrum of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Surg Clin North Am 77:241–252
Giacchino JL, Geis WP, Pickleman JR, Dando DV, Hadcock WE, Freeark RJ (1979) Changing perspective in massive lower intestinal hemorrhage. Surgery 86:368–376
Leitman IM, Paul AE, Shires GT (1989) Evaluation and management of massive lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Ann Sugr 209:175–180
Pennoyer WP, Vignati PV, Cohen JL (1996) Management of angiogram positive lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage: long term follow up of non operative treatments. Int J Colorectal Dis 11:279–282
Goldberger LE, Bookstein JJ (1977) Transcatheter embolization for treatment of diverticular haemorrhage. Radiology 122:613–617
Burgess AN, Evans PM (2004) Lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage and superselective angiographic embolization. ANZ J Surg 74:635–638
Duchat F, Soyer P, Boudiaf M et al (2010) Multi-detector row CT of patients with acute intestinal bleeding: a new perspective using multiplanar and MIP reformations from submillimeter isotropic voxels. Abdom Imaging 35:296–305
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heianna, J., Miyauchi, T., Yamano, H. et al. Management of angiogram-negative acute colonic hemorrhage: safety and efficacy of colonoscopy-guided superselective embolization. Tech Coloproctol 18, 647–652 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-013-1112-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-013-1112-x