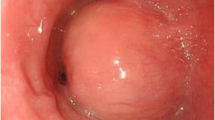
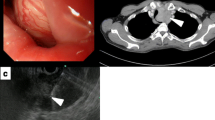
Abstract
Objective
Esophageal schwannoma (ES) are rare and mostly benign neurogenic tumors. The clinical misdiagnosis rate of it is high. In this study, the clinicopathologic features of ES in mainland China were studied to better understand the disease and improve the diagnosis and treatment rate.
Methods
A systematic review was conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. The keywords "esophageal schwannoma", "esophageal neurinoma" and "esophageal neurilemoma" were searched for databases such as Pubmed, EMbase, Wanfang Database and Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure. The search time frame for database was until July 2019. Combined with our patient, the clinicopathological data and the diagnosis and treatment of ES were summarized.
Results
ES occurs in the upper part of the mediastinum and in the thoracic esophagus in most patients in the neck, upper and middle segments. CT and PET/CT examinations can be used for diagnosis, but the differentiation value of both benign and malignant ES is similar. The histopathological findings of forceps biopsy specimens are often difficult to diagnose, and deep tissue biopsies may increase pathological accuracy. EUS-FNA is also recommended for ES diagnosis, but it may also be misdiagnosed. Pathological features include a fusiform arrangement in a palisade-like structure or a tumor cell arranged in a network to form a loose structure. ES characteristic immunohistochemistry results showed that S-100 protein has strong immunological activity.
Conclusion
The definitive diagnosis requires immunohistochemistry, especially immunological reaction with S-100 protein. The appropriate treatment plan should be selected according to the diameter of the lesion. The overall prognosis of ES is good, but attention should be paid to follow-up.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- ES:
-
Esophageal schwannoma
- EGD:
-
Esopghagogastroduodenoscopy
- EUS:
-
Endoscopic ultrasound
- MP:
-
Muscularis propria
- ESD:
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- PET/CT:
-
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- STER:
-
Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection
- SMT:
-
Submucosal tumors
- EUS-FNA:
-
Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration
References
Liu C, Yan L, Liu Q et al (2018) Lumbar intraspinal microcystic/reticular schwannoma: Case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore) 97:e12474
Wang S, Zheng J, Ruan Z et al (2011) Long-term survival in a rare case of malignant esophageal schwannoma cured by surgical excision. Ann Thorac Surg 92:357–358
Gu MJ, Choi JH (2014) Microcystic/reticular schwannoma of the esophagus: the first case report and a diagnostic pitfall. BMC Gastroenterol 14:193
Liegl B, Bennett MW, Fletcher CD (2008) Microcystic/reticular schwannoma: a distinct variant with predilection for visceral locations. Am J Surg Pathol 32:1080–1087
Souza L, Pinto T, Cavalcanti H et al (2019a) Esophageal schwannoma: Case report and epidemiological, clinical, surgical and immunopathological analysis. Int J Surg Case Rep 55:69–75
Jeon HW, Kim KS, Hyun KY et al (2014) Enucleation of giant esophageal schwannoma of the upper thoracic esophagus: reports of two cases. World J Surg Oncol 12:39
Chatelin CL, Fissore A (1969) Infiltrating form of cancer of the lower 3d part of the esophagus. Sem Hop 45:2510–2511
Yanagawa S, Kagemoto K, Tanji H et al (2020) A Rare Case of Gastric Schwannoma: A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Rep Oncol 13:330–335
Powley TL, Mittal RK, Baronowsky EA et al (2013) Architecture of vagal motor units controlling striated muscle of esophagus: peripheral elements patterning peristalsis? Auton Neurosci 179:90–98
Zhang XW, Yang J, Gu WQ et al (2018) Combined thoracic and laparoscopic treatment of giant Schwannoma of esophagus: report of one case. Chin J Min Inv Surg 18:572–573
Ahn D, Sohn JH, Kim H et al (2017) Large esophageal schwannoma mimicking thyroid tumor with egg-shell calcification on preoperative ultrasonography. Asian J Surg 40:236–239
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535
Chen X, Li Y, Liu X et al (2016) A report of three cases of surgical removal of esophageal schwannomas. J Thorac Dis 8:E353–E357
Liu BR, Song JT, Kong LJ et al (2013) Tunneling endoscopic muscularis dissection for subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria of the esophagus and gastric cardia. Surg Endosc 27:4354–4359
Liu D, Yang Y, Qi YU et al (2015) Schwannoma of the esophagus: A case report. Oncol Lett 10:3161–3162
Liu T, Liu H, Yang C et al (2013) Benign esophageal schwannoma compressing the trachea requiring esophagectomy: a case report. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 61:505–506
Wang YL, Sun JG, Wang J et al (2015) Schwannoma of the cervical esophagus: Report of 2 cases and a review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J 94:E10–E13
Wu C, Zhang Q, Hu B (2017) A huge mass in the upper esophagus. Gastroenterology 153:e7–e9
Yang H, Zhao H, Garfield DH et al (2013) Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis of non-lymph node thoracic lesions. Ann Thorac Med 8:14–21
Zhang Y, Han Y, Xiang J et al (2018) Robot-assisted enucleation of large dumbbell-shaped esophageal schwannoma: a case report. BMC Surg 18:36
Zhu L, Li W, Zhu Z et al (2019) Benign esophageal schwannoma: A case report and review of literature. Niger J Clin Pract 22:731–733
Wu CX, Yu QQ, Shou WZ et al (2020) Benign esophageal schwannoma: A case report and brief overview. Medicine (Baltimore) 99:e21527
Choong CK, Meyers BF (2003) Benign esophageal tumors: introduction, incidence, classification, and clinical features. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 15:3–8
Postlethwait RW, Musser AW (1974) Changes in the esophagus in 1000 autopsy specimens. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 68:953–956
Kitada M, Matsuda Y, Hayashi S et al (2013a) Esophageal schwannoma: a case report. World J Surg Oncol 11:253
Onodera Y, Nakano T, Takeyama D et al (2017a) Combined thoracoscopic and endoscopic surgery for a large esophageal schwannoma. World J Gastroenterol 23:8256–8260
Sanchez-Garcia RE, Cortes R, de Leon AR et al (2019) Esophageal schwannomas: A rarity beneath benign esophageal tumors a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep 58:220–223
Chen CT, Peng PC, Tsai T et al (2020a) A novel treatment modality for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor using a dual-effect liposome to combine photodynamic therapy and chemotherapy. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040317
Evans DG (2009) Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2): a clinical and molecular review. Orphanet J Rare Dis 4:16
Guo J, Chaney KE, Choi K et al (2020a) Polo-like kinase 1 as a therapeutic target for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST) and schwannomas. AM J Cancer Res 10:856–869
Lasota J, Wasag B, Dansonka-Mieszkowska A et al (2003) Evaluation of NF2 and NF1 tumor suppressor genes in distinctive gastrointestinal nerve sheath tumors traditionally diagnosed as benign schwannomas: s study of 20 cases. Lab Invest 83:1361–1371
Helbing DL, Schulz A, Morrison H (2020) Pathomechanisms in schwannoma development and progression. Oncogene 39(32):5421–5429
Kersigo J, Gu L, Xu L et al (2020) Effects of Neurod1 Expression on Mouse and Human Schwannoma Cells. Laryngoscope. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.28671
Sass H, Hansen M, Borup R et al (2020) Tumor miRNA expression profile is related to vestibular schwannoma growth rate. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 162:1187–1195
Kassis ES, Bansal S, Perrino C et al (2012a) Giant asymptomatic primary esophageal schwannoma. Ann Thorac Surg 93:e81–e83
Dutta R, Kumar A, Jindal T et al (2009) Concurrent benign schwannoma of oesophagus and posterior mediastinum. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 9:1032–1034
Tomono A, Nakamura T, Otowa Y et al (2015a) A case of benign esophageal schwannoma causing life-threatening tracheal obstruction. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 21:289–292
Iwata Y, Tanaka C, Komori S et al (2018) Lobulated esophageal schwannoma resected with concurrent approach from the thorax and cervix. World J Surg Oncol 16:29
Jang KM, Lee KS, Lee SJ et al (2002) The spectrum of benign esophageal lesions: imaging findings. Korean J Radiol 3:199–210
Mishra B, Madhusudhan KS, Kilambi R et al (2016) Malignant schwannoma of the esophagus: A rare case report. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 49:63–66
Anil G, Tan TY (2010) Imaging characteristics of schwannoma of the cervical sympathetic chain: a review of 12 cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1408–1412
Watanabe T, Miyazaki T, Saito H et al (2016) Resection of an esophageal schwannoma with thoracoscopic surgery: a case report. Surg Case Rep 2:127
Kunigelis KE, Hosokawa P, Arnone G et al (2020) The predictive value of preoperative apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) for facial nerve outcomes after vestibular schwannoma resection: clinical study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 162:1995–2005
Bae H, Van Vrancken M, Kang TW et al (2018a) Peritumoral lymphoid cuff correlates well with lymph node enlargement in gastrointestinal schwannomas. Oncotarget 9:12591–12598
Ries M, Khreish F, Veith C et al (2019) Large Paraesophageal schwannoma with intense prostate-specific membrane antigen expression on 68Ga-PSMA-PET/CT mimicking lymph node metastasis in a patient with prostate cancer. Clin Nucl Med 44:153–154
Naus PJ, Tio FO, Gross GW (2001) Esophageal schwannoma: first report of successful management by endoscopic removal. Gastrointest Endosc 54:520–522
Pesenti C, Bories E, Caillol F et al (2019) Characterization of subepithelial lesions of the stomach and esophagus by contrast-enhanced EUS: A retrospective study. Endosc Ultrasound 8:43–49
Lee EJ, Kim TD, Oh HA et al (2005) Is the invasive approach for all the upper gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumors necessary? Korean J Gastroenterol 45:387–393
Vinhais SN, Cabrera RA, Nobre-Leitao C et al (2004) Schwannoma of the esophagus: computed tomography and endosonographic findings of a special type of schwannoma. Acta Radiol 45:718–720
Okai T, Minamoto T, Ohtsubo K et al (2003) Endosonographic evaluation of c-kit-positive gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Abdom Imaging 28:301–307
Jin JW, Xue ZX, Cai ZZ et al (2015) Three cases of esophageal neurilemmoma misdiagnosed as esophageal stromal tumors by endoscopic ultrasonography [J]. Chin J Dig Endosc 32:694–696
Cheng B, Zhong L, Ding F et al (2009) A comparative study of the diagnostic value of endoscopic ultrasonography with pathological features of upper gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumors. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 48:724–728
Moisini I, Amin K, Mallery S et al (2018) Efficacy of endoscopic-guided fine-needle aspiration in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal spindle cell tumors. Diagn Cytopathol 46:663–669
Ha C, Regan J, Cetindag IB et al (2015) Benign esophageal tumors. Surg Clin North Am 95:491–514
Yoon HY, Kim CB, Lee YH et al (2008) An obstructing large schwannoma in the esophagus. J Gastrointest Surg 12:761–763
Moro K, Nagahashi M, Hirashima K et al (2017a) Benign esophageal schwannoma: a brief overview and our experience with this rare tumor. Surg Case Rep 3:97
Tokunaga T, Takeda S, Sumimura J et al (2007) Esophageal schwannoma: report of a case. Surg Today 37:500–502
Lee SJ, Hwang CS, Kim A et al (2016a) Gastrointestinal tract spindle cell tumors with interstitial cells of Cajal: Prevalence excluding gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncol Lett 12:1287–1292
Kwon MS, Lee SS, Ahn GH (2002) Schwannomas of the gastrointestinal tract: clinicopathological features of 12 cases including a case of esophageal tumor compared with those of gastrointestinal stromal tumors and leiomyomas of the gastrointestinal tract. Pathol Res Pract 198:605–613
Mustapar N, Zawawi M, Tuan SS (2020) The value of H3K27me3 immunohistochemistry in differentiating malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour with its histologic mimickers. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 21:699–705
Faulx AL, Kothari S, Acosta RD et al (2017) The role of endoscopy in subepithelial lesions of the GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc 85:1117–1132
Surgery Group, Digestive Endoscopy Society of Chinese Medical Association, Digestive Endoscopy Committee, Endoscopy Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Gastrointestinal Surgery Group and Surgery Society of Chinese Medical Association. Expert Consensus on Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment of Digestive Tract Submucosal Tumors in China (2018) Edition). Chinese J Diges 38:519–527 ((Chinese))
Goto O, Uraoka T, Horii J et al (2014) Expanding indications for ESD: submucosal disease (SMT/carcinoid tumors). Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 24:169–181
Park BJ, Carrasquillo J, Bains MS et al (2006) Giant benign esophageal schwannoma requiring esophagectomy. Ann Thorac Surg 82:340–342
Kent M, D’Amato T, Nordman C et al (2007) Minimally invasive resection of benign esophageal tumors. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 134:176–181
Murase K, Hino A, Ozeki Y et al (2001) Malignant schwannoma of the esophagus with lymph node metastasis: literature review of schwannoma of the esophagus. J Gastroenterol 36:772–777
Bae H, Van Vrancken M, Kang TW et al (2018b) Peritumoral lymphoid cuff correlates well with lymph node enlargement in gastrointestinal schwannomas. Oncotarget 9:12591–12598
Xu H, Li J, Sun Y et al (2014) Robotic versus laparoscopic right colectomy: a meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol 12:274
Mulchandani MH, Chattopadhyay D, Obafunwa JO et al (2005) Gastrointestinal autonomic nerve tumours–report of a case and review of literature. World J Surg Oncol 3:46
Leung K, Lam N, Chan E et al (2020) Primary recurrent orbital schwannoma treated with surgical excision and Mitomycin-C. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep 19:100784
Chen CT, Peng PC, Tsai T et al (2020b) A Novel treatment modality for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor using a dual-effect liposome to combine photodynamic therapy and chemotherapy. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040317
Guo J, Chaney KE, Choi K et al (2020b) Polo-like kinase 1 as a therapeutic target for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST) and schwannomas. AM J Cancer Res 10:856–869
Sagers JE, Beauchamp RL, Zhang Y et al (2020) Combination therapy with mTOR kinase inhibitor and dasatinib as a novel therapeutic strategy for vestibular schwannoma. Sci Rep 10:4211
An B, Abe T, Uemura N et al (2019) Simultaneous resections of left lung cancer and esophageal schwannoma using video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: A case report. Asian J Endosc Surg 12:348–353
von Rahden BH, Stein HJ, Feussner H et al (2004) Enucleation of submucosal tumors of the esophagus: minimally invasive versus open approach. Surg Endosc 18:924–930
Kang SK, Yun JS, Kim SH et al (2015) Retrospective analysis of thoracoscopic surgery for esophageal submucosal tumors. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 48:40–45
Chen T, Zhou PH, Chu Y et al (2017a) Long-term outcomes of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors. Ann Surg 265:363–369
Song X, Jiang JK, Meng XM et al (2015) Treatment of esophagus neurolemmoma by endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection: one case report. Chinese J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24(1318):1323 ((Chinese))
Liu X, Dou L, Liu Y et al (2017) Evaluation of a new closure technique of large defects after endoscopic full-thickness resection. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 20:775–781
Chen T, Zhou PH, Chu Y et al (2017b) Long-term outcomes of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors. Ann Surg 265:363–369
Kassis ES, Bansal S, Perrino C et al (2012b) Giant asymptomatic primary esophageal schwannoma. Ann Thorac Surg 93:e81–e83
Souza L, Pinto T, Cavalcanti H et al (2019b) Esophageal schwannoma: Case report and epidemiological, clinical, surgical and immunopathological analysis. Int J Surg Case Rep 55:69–75
Degheili JA, Sfeir P, Khalifeh I et al (2019) Large esophageal schwannoma: En-bloc resection with primary closure by esophagoplasty. Int J Surg Case Rep 61:77–81
George M, Augustine AM, Mathew J et al (2009) Ancient schwannoma of the oesophagus presenting with stridor: case report. J Laryngol Otol 123:1384–1386
Mizuguchi S, Inoue K, Imagawa A et al (2008) Benign esophageal schwannoma compressing the trachea in pregnancy. Ann Thorac Surg 85:660–662
Tomono A, Nakamura T, Otowa Y et al (2015b) A case of benign esophageal schwannoma causing life-threatening tracheal obstruction. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 21:289–292
Morales-Maza J, Pastor-Sifuentes FU, Sanchez-Morales GE et al (2019) Clinical characteristics and surgical treatment of schwannomas of the esophagus and stomach: A case series and systematic review. World J Gastrointest Oncol 11:750–760
Kitada M, Matsuda Y, Hayashi S et al (2013b) Esophageal schwannoma: a case report. World J Surg Oncol 11:253
Moro K, Nagahashi M, Hirashima K et al (2017b) Benign esophageal schwannoma: a brief overview and our experience with this rare tumor. Surg Case Rep 3:97
Lee SJ, Hwang CS, Kim A et al (2016b) Gastrointestinal tract spindle cell tumors with interstitial cells of Cajal: Prevalence excluding gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncol Lett 12:1287–1292
Sanchez A, Mariangel P, Carrasco C et al (2004) Malignant nerve sheath tumor of the esophagus (malignant esophageal schwannoma). Gastroenterol Hepatol 27:467–469
Aoki T, Nakamura T, Oshikiri T et al (2018) Strategy for esophageal non-epithelial tumors based on a retrospective analysis of a single facility. Esophagus 15:286–293
Onodera Y, Nakano T, Takeyama D et al (2017b) Combined thoracoscopic and endoscopic surgery for a large esophageal schwannoma. World J Gastroenterol 23:8256–8260
Azoulay A, Cros J, Vullierme MP et al (2020) Morphological imaging and CT histogram analysis to differentiate pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor grade 3 from neuroendocrine carcinoma. Diagn Interv Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2020.06.006
Su XJ, Zhang ZY, Jiang XL et al (2012) A case of esophageal malignant schwannoma. Chinese J Clin Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg 19:461
Manger T, Pross M, Haeckel C et al (2000) Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor of the esophagus. Dig Surg 17:627–631
Mavroeidis VK, Kandilaris K, Matthioudakis DI et al (2017) Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour of the oesophagus Review of the literature and report of a case with lymph node and distant metastases. Ann Ital Chir 88:26–38
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank all the authors and study participants for their support in this study.
Funding
This study was funded by Scientific research project of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (Q20102112), Shiyan City Science and Technology Bureau Guiding Research Project (19Y44) and the Foundation of Taihe Hospital (2019JJXM032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z-YG, X-BL, and S-BL conceived and designed this study. Z-YG and X-BL searched and collected the data. X-BL, SP, and Q-HZ contributed to data extraction and data analysis. X-BL and BG wrote the manuscript. SP, PL, and S-BL reviewed and revised the paper. X-BL, Y-JG, and S-BL approved and submitted the final manuscript. All authors read, and approved the final manuscript and its submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this work have nothing to disclose and the authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Zy., Liu, XB., Pandey, S. et al. Clinicopathological features of esophageal schwannomas in mainland China: systematic review of the literature. Int J Clin Oncol 26, 284–295 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-020-01809-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-020-01809-4