Abstract
Background
Palliative therapeutic strategies in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients with dysphagia remain controversial. Only few studies have assessed therapeutic effect factors related to improvement in dysphagia score and nutrition-support-free survival (NSFS).
Objective
The present study assessed the efficacy and therapeutic effect factors related to the use of palliative radiotherapy (RT) and chemoradiotherapy (CRT) in ESCC patients with dysphagia.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated 70 patients with stage IVA/B ESCC. Patients received RT of 30 Gy in 10 fractions or concurrent CRT using 5-fluorouracil plus cisplatin of 40 Gy in 20 fractions. The change in the dysphagia score from before to after treatment was assessed, and NSFS was evaluated.
Results
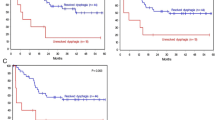
The median follow-up duration was 6 months (range 1–41 months). The overall rate of improvement in the dysphagia score was 60%. The median NSFS was 7.5 months. Craniocaudal tumor length < 6 cm, tumor circumference < 3/4, and CRT of 40 Gy in 20 fractions were associated with a significant improvement in the dysphagia score (p = 0.0036, p = 0.0069, and p = 0.03, respectively). NSFS was significantly longer with CRT than with RT (p = 0.048).
Conclusion
Palliative RT and CRT are effective treatment options for ESCC patients with dysphagia. Craniocaudal tumor length < 6 cm, tumor circumference < 3/4, and CRT of 40 Gy in 20 fractions may improve dysphagia. CRT of 40 Gy in 20 fractions may improve NSFS.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESCC:
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- RT:
-
Radiotherapy
- CRT:
-
Chemoradiotherapy
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- MST:
-
Median survival time
- FP:
-
5-fluorouracil and cisplatin
- NSFS:
-
Nutrition-support-free survival
- 5-FU:
-
5-fluorouracil
- CDDP:
-
Cisplatin
References
Iizuka T, Kakegawa T, Ide H et al (1992) Phase II evaluation of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a Japanese Esophageal Oncology Group Trial. Jpn J Clin Oncol 22(3):172–176
Bleiberg H, Conroy T, Paillot B et al (1997) Randomised phase II study of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) versus cisplatin alone in advanced squamous cell oesophageal cancer. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990) 33(8):1216–1220
Ohtsu A, Boku N, Muro K et al (1999) Definitive chemoradiotherapy for T4 and/or M1 lymph node squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J Clin Oncol 17(9):2915–2921. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.1999.17.9.2915
Hayashi K, Ando N, Watanabe H et al (2001) Phase II evaluation of protracted infusion of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a Japan Esophageal Oncology Group (JEOG) Trial (JCOG9407). Jpn J Clin Oncol 31(9):419–423
Ishida K, Ando N, Yamamoto S et al (2004) Phase II study of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil with concurrent radiotherapy in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a Japan Esophageal Oncology Group (JEOG)/Japan Clinical Oncology Group trial (JCOG9516). Jpn J Clin Oncol 34(10):615–619. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyh107
Lorenzen S, Schuster T, Porschen R et al (2009) Cetuximab plus cisplatin-5-fluorouracil versus cisplatin-5-fluorouracil alone in first-line metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a randomized phase II study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. Ann Oncol 20(10):1667–1673. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp069
Shinoda M, Ando N, Kato K et al (2015) Randomized study of low-dose versus standard-dose chemoradiotherapy for unresectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (JCOG0303). Cancer Sci 106(4):407–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12622
Watkinson AF, Ellul J, Entwisle K et al (1995) Esophageal carcinoma: initial results of palliative treatment with covered self-expanding endoprostheses. Radiology 195(3):821–827. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.195.3.7538682
Watt E, Whyte F (2003) The experience of dysphagia and its effect on the quality of life of patients with oesophageal cancer. Eur J Cancer care 12(2):183–193
Weigel TL, Frumiento C, Gaumintz E (2002) Endoluminal palliation for dysphagia secondary to esophageal carcinoma. Surg Clin N Am 82(4):747–761
Coia LR, Soffen EM, Schultheiss TE et al (1993) Swallowing function in patients with esophageal cancer treated with concurrent radiation and chemotherapy. Cancer 71(2):281–286
Urba SG, Turrisi AT 3rd (1995) Split-course accelerated radiation therapy combined with carboplatin and 5-fluorouracil for palliation of metastatic or unresectable carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer 75(2):435–439
Cwikiel M, Cwikiel W, Albertsson M (1996) Palliation of dysphagia in patients with malignant esophageal strictures. Comparison of results of radiotherapy, chemotherapy and esophageal stent treatment. Acta Oncol (Stockholm Sweden) 35(1):75–79
Hayter CR, Huff-Winters C, Paszat L et al (2000) A prospective trial of short-course radiotherapy plus chemotherapy for palliation of dysphagia from advanced esophageal cancer. Radiother Oncol 56(3):329–333
Harvey JA, Bessell JR, Beller E et al (2004) Chemoradiation therapy is effective for the palliative treatment of malignant dysphagia. Dis Esophagus 17(3):260–265. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2050.2004.00420.x
Cho SH, Shim HJ, Lee SR et al (2008) Concurrent chemoradiotherapy with S-1 and cisplatin in advanced esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus 21(8):697–703. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2050.2008.00837.x
Kassam Z, Wong RK, Ringash J et al (2008) A phase I/II study to evaluate the toxicity and efficacy of accelerated fractionation radiotherapy for the palliation of dysphagia from carcinoma of the oesophagus. Clin Oncol (Royal College of Radiologists (Great Britain)) 20(1):53–60
Ikeda E, Kojima T, Kaneko K et al (2011) Efficacy of concurrent chemoradiotherapy as a palliative treatment in stage IVB esophageal cancer patients with dysphagia. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41(8):964–972. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyr088
Murray LJ, Din OS, Kumar VS et al (2012) Palliative radiotherapy in patients with esophageal carcinoma: a retrospective review. Pract Radiat Oncol 2(4):257–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2011.12.002
Akl FM, Elsayed-Abd-Alkhalek S, Salah T (2013) Palliative concurrent chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced and metastatic esophageal cancer patients with dysphagia. Ann Palliat Med 2(3):118–123. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2224-5820.2013.05.01
Suzuki G, Yamazaki H, Aibe N et al (2017) Palliative radiotherapy in the local management of stage IVB esophageal cancer: factors affecting swallowing and survival. Anticancer Res 37(6):3085–3092. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11664
Penniment MG, De Ieso PB, Harvey JA et al (2017) Palliative chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for dysphagia in advanced oesophageal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial (TROG 03.01). Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-1253(17)30363-1
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, McFadden ET, Carbone PP (1982) Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol 5 (6):649–655
Brierley J, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C (2017) TNM classification of malignant tumours. 8th edn. Wiley, Chichester
National Cancer Institute (U.S.) (2009) Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE). In: NIH publication. Rev. edn. U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, vol no 10–5410
Ogilvie AL, Dronfield MW, Ferguson R et al (1982) Palliative intubation of oesophagogastric neoplasms at fibreoptic endoscopy. Gut 23(12):1060–1067
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl 48(3):452–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.244
Royal College of Radiologists (2006) Board of the faculty of clinical oncology, the royal college of radiologists radiotherapy dose-fractionation. London
Feng JF, Huang Y, Zhao Q (2013) Tumor length in elderly patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: is it a prognostic factor? Upsala J Med Sci 118(3):145–152. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009734.2013.792887
Katada C, Muto M, Manabe T et al (2003) Esophageal stenosis after endoscopic mucosal resection of superficial esophageal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 57(2):165–169. https://doi.org/10.1067/mge.2003.73
Ono S, Fujishiro M, Niimi K et al (2009) Predictors of postoperative stricture after esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial squamous cell neoplasms. Endoscopy 41(8):661–665. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1214867
Shi Q, Ju H, Yao LQ et al (2014) Risk factors for postoperative stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal carcinoma. Endoscopy 46(8):640–644. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1365648
Burmeister BH, Smithers BM, Gebski V et al (2005) Surgery alone versus chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for resectable cancer of the oesophagus: a randomised controlled phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 6(9):659–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(05)70288-6
Hingorani M, Dixit S, Johnson M et al (2015) Palliative radiotherapy in the presence of well-controlled metastatic disease after initial chemotherapy may prolong survival in patients with metastatic esophageal and gastric cancer. Cancer Res Treat 47(4):706–717. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.174
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TK prepared the manuscript and the literature search; TK reviewed and edited the manuscript; and TK, KN, KS and KK reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
This study used no human or animal subjects.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
About this article
Cite this article
Kawamoto, T., Nihei, K., Sasai, K. et al. Palliative radiotherapy and chemoradiotherapy in stage IVA/B esophageal cancer patients with dysphagia. Int J Clin Oncol 23, 1076–1083 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-018-1324-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-018-1324-1