Abstract
Background
The transcriptional regulator in embryonic development, KAP1, has been proved could promote cell proliferation and metastatic progression in a variety of human cancers. However, the role of KAP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship of KAP1 expression with the progression and prognosis of HCC.
Methods
We measured the expression level of KAP1 in both human hepatoma cell lines and HCC tissues obtained from HCC patients by real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blot. Furthermore, the effect of KAP1 expression on hepatoma cell proliferation was investigated through KAP1 knock-down strategy. Besides that, the correlation between KAP1 expression and HCC progression was analyzed.
Results
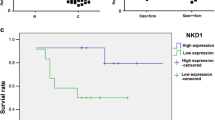
KAP1 overexpression was proved broadly existed in the human hepatoma cell lines. Furthermore, down-regulate the expression of KAP1 by specific siRNA could inhibit cell proliferation which was partly originated from the activation of p53 mediated signal pathway. Moreover, comparisons between the cancer tissues and noncancerous tissues proved the expression level of KAP1 was significant higher in tumor tissues obtained from HCC patients. In addition, KAP1 overexpression was significantly correlated with tumor size and tumor stage and also a predictor for poor prognosis of HCC patients.
Conclusion
Our results presented here demonstrate that KAP1 plays an important role in HCC and could be regarded as a valuable biomarker for tumor diagnosis and prognosis prediction, as well as a potential target for the treatment of HCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang JD, Roberts LR (2010) Hepatocellular carcinoma: a global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:448–458
Lafaro KJ, Demirjian AN, Pawlik TM (2015) Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 24:1–17
Kew MC (2010) Epidemiology of chronic hepatitis B virus infection, hepatocellular carcinoma, and hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Biol 58:273–277
Chaiteerakij R, Addissie BD, Roberts LR (2015) Update on biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:237–245
Friedman JR, Fredericks WJ, Jensen DE et al (1996) KAP-1, a novel corepressor for the highly conserved KRAB repression domain. Gene Dev 10:2067–2078
Li X, Lee Y-K, Jeng J-C et al (2007) Role for KAP1 serine 824 phosphorylation and sumoylation/desumoylation switch in regulating KAP1-mediated transcriptional repression. J Biol Chem 282:36177–36189
Sripathy SP, Stevens J, Schultz DC (2006) The KAP1 corepressor functions to coordinate the assembly of de novo HP1-demarcated microenvironments of heterochromatin required for KRAB zinc finger protein-mediated transcriptional repression. Mol Cell Biol 26:8623–8638
Allouch A, Di Primio C, Alpi E et al (2011) The TRIM family protein KAP1 inhibits HIV-1 integration. Cell Host Microbe 9:484–495
Rambaud J, Desroches J, Balsalobre A et al (2009) TIF1β/KAP-1 is a coactivator of the orphan nuclear receptor NGFI-B/Nur77. J Biol Chem 284:14147–14156
Venkov CD, Link AJ, Jennings JL et al (2007) A proximal activator of transcription in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest 117:482–491
Yokoe T, Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y et al (2010) KAP1 is associated with peritoneal carcinomatosis in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 17:821–828
Cui Y, Yang S, Fu X et al (2015) High levels of KAP1 expression are associated with aggressive clinical features in ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci 16:363–377
Liu L, Zhao E, Li C et al (2013) TRIM28, a new molecular marker predicting metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol 37:71–78
Addison JB, Koontz C, Fugett JH et al (2015) KAP1 promotes proliferation and metastatic progression of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 75:344–355
Wang Y-Y, Jiang J-X, Ma H et al (2014) Role of ZIC1 methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical significance. Tumor Biol 35:7429–7433
Zhang K, Jiang L, He R et al (2014) Prognostic value of CYP2W1 expression in patients with human hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol 35:7669–7673
Lee Y-K, Thomas SN, Yang AJ et al (2007) Doxorubicin down-regulates Krüppel-associated box domain-associated protein 1 sumoylation that relieves its transcription repression on p21WAF1/CIP1 in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J Biol Chem 282:1595–1606
Acknowledgments
This project is funded by Key Disciplines Group Construction Project of Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai (PWZxq2014-04); Shanghai medical key specialty (ZK2012A26); Outstanding Leaders Training Program of Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai (Grant No. PWRl2013-02) and Outstanding Leaders Training Program of Pudong Health and Family Planning Commission of Shanghai (Grant No. PWRL2014-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Yanying Wang, Jianxin Jiang and Qun Li contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Jiang, J., Li, Q. et al. KAP1 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical significance. Int J Clin Oncol 21, 927–933 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-016-0979-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-016-0979-8