Abstract
Background
The Ras-like nuclear protein (Ran) is involved in the regulation of nuclear transport, microtubule nucleation and dynamics, and spindle assembly. Its fundamental function is nucleocytoplasmic transport of RNA and proteins. The expression and potential role of Ran in colorectal cancer (CRC) remain unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between Ran expression and CRC characteristics. The potential role of Ran as a prognostic indicator was also evaluated.
Methods
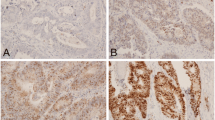
We used immunohistochemistry and western blotting to detect Ran expression in 287 CRC tissues. The relationships between Ran expression and clinicopathological characteristics and overall survival rate were statistically analyzed.
Results
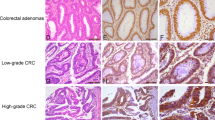
CRC tissues had significantly higher Ran expression than normal colorectal epithelial cells. Ran was positively correlated with depth of invasion, lymph node metastases, distant metastases, tumor differentiation, and tumor–node–metastasis stage. However, no correlation was found between Ran expression and patient age or sex. The overall survival rate was consistently and significantly lower in patients with Ran-positive tumors than in those with Ran-negative tumors.
Conclusion
Our findings emphasize the important role of Ran in differentiation, disease stage, and metastasis in human CRC. Ran may play an important role in the development of CRC and may serve as a novel prognostic indicator of CRC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2009) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62(1):10–29
Ross JS (2010) Biomarker update for breast, colorectal and non-small cell lung cancer. Drug News Perspect 23(1):82–88
Siena S, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di Nicolantonio F et al (2009) Biomarkers predicting clinical outcome of epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(19):1308–1324
Walther A, Johnstone E, Swanton C et al (2009) Genetic prognostic and predictive markers in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9(7):489–499
Hammarstrom S (1999) The carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family: structures, suggested functions and expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin Cancer Biol 9(2):67–81
Tanaka T, Tanaka M, Tanaka T et al (2010) Biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci 11(9):3209–3225
Lounsbury KM, Beddow AL, Macara IG (1994) A family of proteins that stabilize the Ran/TC4 GTPase in its GTP-bound conformation. J Biol Chem 269(15):11285–11290
Drivas GT, Shih A, Coutavas E et al (1990) Characterization of four novel ras-like genes expressed in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol 10(4):1793–1798
Bischoff FR, Ponstingl H (1991) Mitotic regulator protein RCC1 is complexed with a nuclear ras-related polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(23):10830–10834
Wennerberg K, Rossman KL, Der CJ (2005) The Ras superfamily at a glance. J Cell Sci 118:843–846
Frankel MB, Knoll LJ (2009) The ins and outs of nuclear trafficking: unusual aspects in apicomplexan parasites. DNA Cell Biol 28(6):277–284
Ren M, Drivas G, D’Eustachio P et al (1993) Ran/TC4: a small nuclear GTP-binding protein that regulates DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol 120(2):313–323
Fleig U, Salus SS, Karig I et al (2000) The fission yeast ran GTPase is required for microtubule integrity. J Cell Biol 151(5):1101–1111
Dasso M (2001) Running on Ran: nuclear transport and the mitotic spindle. Cell 104(3):321–324
Jallepalli PV, Lengauer C (2001) Chromosome segregation and cancer: cutting through the mystery. Nat Rev Cancer 1(2):109–117
Merkle T (2011) Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport of proteins and RNA in plants. Plant Cell Rep 30(2):153–176
Weis K (2003) Regulating access to the genome: nucleocytoplasmic transport throughout the cell cycle. Cell 112(4):441–451
Sanderson HS, Clarke PR (2006) Cell biology: ran, mitosis and the cancer connection. Curr Biol 16(12):R466–R468
Kahana JA, Cleveland DW (1999) Beyond nuclear transport. Ran-GTP as a determinant of spindle assembly. J Cell Biol 146(6):1205–1210
O’Connell CB, Khodjakov AL (2007) Cooperative mechanisms of mitotic spindle formation. J Cell Sci 120:1717–1722
Li HY, Cao K, Zheng Y (2003) Ran in the spindle checkpoint: a new function for a versatile GTPase. Trends Cell Biol 13(11):553–557
Heald R, Weis K (2000) Spindles get the ran around. Trends Cell Biol 10(1):1–4
Carazo-Salas RE, Gruss OJ, Mattaj IW et al (2001) Ran-GTP coordinates regulation of microtubule nucleation and dynamics during mitotic-spindle assembly. Nat Cell Biol 3(3):228–234
Cao YK, Zhong ZS, Chen DY et al (2005) Cell cycle-dependent localization and possible roles of the small GTPase Ran in mouse oocyte maturation, fertilization and early cleavage. Reproduction 130(4):431–440
Abe H, Kamai T, Shirataki H et al (2008) High expression of Ran GTPase is associated with local invasion and metastasis of human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 122(10):2391–2397
Barres V, Ouellet V, Lafontaine J et al (2010) An essential role for Ran GTPase in epithelial ovarian cancer cell survival. Mol Cancer 9:272
Azuma K, Sasada T, Takedatsu H et al (2004) Ran, a small GTPase gene, encodes cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitopes capable of inducing HLA-A33-restricted and tumor-reactive CTLs in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 10(19):6695–6702
Frankel MB, Knoll LJ (2009) The ins and outs of nuclear trafficking: unusual aspects in apicomplexan parasites. DNA Cell Biol 28(6):277–284
Ren M, Drivas G, D’Eustachio P et al (1993) Ran/TC4: a small nuclear GTP-binding protein that regulates DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol 120(2):313–323
Zlobec I, Lugli A (2008) Prognostic and predictive factors in colorectal cancer. Postgrad Med J 84(994):403–411
Chu D, Li Y, Wang W et al (2010) High level of notch1 protein is associated with poor overall survival in colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 17(5):1337–1342
Zafirellis K, Agrogiannis G, Zachaki A et al (2008) Prognostic significance of VEGF expression evaluated by quantitative immunohistochemical analysis in colorectal cancer. J Surg Res 147(1):99–107
Redmond HP (2003) Systemic inflammatory response predicts survival following curative resection of colorectal cancer (Br J Surg 2003; 90: 215–219). Br J Surg 90(7):889
Crozier JE, McKee RF, McArdle CS et al (2006) The presence of a systemic inflammatory response predicts poorer survival in patients receiving adjuvant 5-FU chemotherapy following potentially curative resection for colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 94(12):1833–1836
Eberhard J, Gaber A, Wangefjord S et al (2012) A cohort study of the prognostic and treatment predictive value of SATB2 expression in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 106(5):931–938
Benevolo M, Mottolese M, Tremante E et al (2011) High expression of HLA-E in colorectal carcinoma is associated with a favorable prognosis. J Transl Med 9:184
Garcia-Aguilar J, Chen Z, Smith DD et al (2011) Identification of a biomarker profile associated with resistance to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in rectal cancer. Ann Surg 254(3):486–492
Chien CC, Tu TC, Huang CJ et al (2012) Lowly expressed ribosomal protein s19 in the feces of patients with colorectal cancer. ISRN Gastroenterol 2012:394545
Duesberg P, Rausch C, Rasnick D et al (1998) Genetic instability of cancer cells is proportional to their degree of aneuploidy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(23):13692–13697
Berg M, Soreide K (2011) Genetic and epigenetic traits as biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci 12(12):9426–9439
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30973410 and No. 30971337). We are grateful to Dr. Qingchuan Zhao and Dr. Qiong Wu for their advice on our studies.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Fan, Y. Lu and H. Qin contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, H., Lu, Y., Qin, H. et al. High Ran level is correlated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 18, 856–863 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-012-0465-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-012-0465-x