Abstract
Background
This study was conducted using irinotecan and cisplatin (IP) concurrently with thoracic radiation therapy to evaluate the response and toxicity of this protocol in the treatment of patients with limited-disease small cell lung cancer (LD-SCLC).
Methods
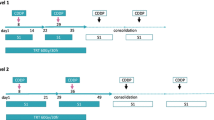
Twenty-seven chemotherapy-naive patients with LD-SCLC received two cycles of weekly irinotecan 60 mg/m2 and cisplatin 60 mg/m2 before the initiation of the thoracic radiation therapy.
Results
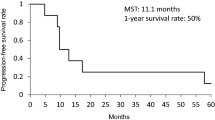
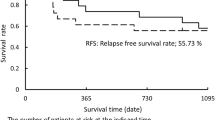
Of the 29 patients with LD-SCLC enrolled in the study, 27 were eligible for evaluation of response and toxicity. The median age was 62 years; 26 patients (90%) were men. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status was 0 in 5 patients (17%) and 1 in 18 patients (62%). Ten patients (37%) achieved a complete response (CR), 14 patients (52%) achieved a partial response (PR), while 3 patients (11%) had progressive disease (PD); one of the 3 nonresponders achieved a PR after commencing concurrent chemoradiotherapy; therefore, the overall response rate was 93%. The median survival time was 20.2 months and 1- and 2-year survival rates were 69% and 53.2%, respectively. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 11.8 months, and 1- and 2-year PFS times were 52% and 34.1%, respectively. Neutropenia was the most prevalent hematological toxicity and it was evident as grade 3 in 14 patients (52%). Asthenia was the most prevalent nonhematological toxicity, in 18 patients (67%); esophagitis occurred in 15 patients (56%). No treatment-related deaths (due to sepsis or bleeding) were reported in the study.
Conclusion
Irinotecan and cisplatin is considered to be an effective and safe chemotherapeutic regimen when used concurrently with thoracic radiation therapy for the treatment of patients with LD-SCLC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sekine I, Nishiwaki Y, Noda K, et al. (2003) Randomized phase II study of cisplatin, irinotecan and etoposide combinations administered weekly or every 4 weeks for extensive small-cell lung cancer (JCOG9902-DI). Ann Oncol 14:709–714
Murray N (1997) Treatment of small cell lung cancer: the state of the art. Lung Cancer 17:S75–S89
Mountain CF (1987) Staging of lung cancer: the new international system. Lung Cancer 3:4–11
Rosti G, Bevilacqua G, Bidoli P, et al. (2006) Small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 17(Suppl 2):ii5–ii10
Kurup A, Hanna NH (2004) Treatment of small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 52:117–126
Lassen U, Hansen HH (1999) Surgery in limited stage small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 25:67–72
Kubota K, Nishiwaki Y, Sugiura T, et al. (2005) Pilot study of concurrent etoposide and cisplatin plus accelerated hyperfractionated thoracic radiotherapy followed by irinotecan and cisplatin for limited-stage small cell lung cancer: Japan Clinical Oncology Group 9903. Clin Cancer Res 11:5534–5538
Han JY, Cho KH, Lee DH, et al. (2005) Phase II study of irinotecan plus cisplatin induction followed by concurrent twice-daily thoracic irradiation with etoposide plus cisplatin chemotherapy for limited-disease small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:3488–3494
Fried DB, Morris DE, Poole C (2004) Systematic review evaluating the timing of thoracic radiation therapy in combined modality therapy for limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:4837–4845
Ohe Y (2002) Treatment-related death from chemotherapy and thoracic radiotherapy for advanced cancer. Panminerva Med 44:205–212
Ettinger DS (2001) New drugs for chemotherapy-naive patients with extensive-disease small cell lung cancer. Semin Oncol 28: S27–S29
Kudoh S, Fujiwara Y, Takada Y, et al. (1998) Phase II study of irinotecan combined with cisplatin in patients with previously untreated small-cell lung cancer. West Japan Lung Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol 16:1068–1074
Noda K, Nishiwaki Y, Kawahara M, et al. (2002) Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 346:85–91
Fukuda M, Nishio K, Kanzawa F, et al. (1996) Synergism between cisplatin and topoisomerase I inhibitors, NB-506 and SN-38, in human small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 56:789–793
Tamura K, Takada M, Kawase I, et al. (1997) Enhancement of tumor radio-response by irinotecan in human lung tumor xenografts. Jpn J Cancer Res 88:218–223
Kudoh S, Nakamura S, Nakano T, et al. (2005) Irinotecan and etoposide for previously untreated extensive-disease small cell lung cancer: a phase II trial of West Japan Thoracic Oncology Group. Lung Cancer 49:263–269
Hanna N, Bunn PA Jr, Langer C, et al. (2006) Randomised phase III trial comparing irinotecan/cisplatin with etoposide/ cisplatin in patients with previously untreated extensive-stage disease small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:2038–2043
Schmittel A, von Weikersthal LF, Sebastian M, et al. (2006) A randomised phase II trial of irinotecan plus carboplatin versus etoposide plus carboplatin treatment in patients with extended disease small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 17:663–667
Auperin A, Arriagada R, Pignon JP, et al. (1999) Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission: Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Overview Collaborative Group. N Engl J Med 341:476–484
Gregor A, Drings P, Burghouts J, et al. (1997) Randomized trial of alternating versus sequential radiotherapy/chemotherapy in limited-disease patients with small-cell lung cancer: a European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Lung Cancer Cooperative Group Study. J Clin Oncol 15:2840–2849
WHO (1979) WHO Handbook for reporting results of cancer treatment. WHO, Geneva
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, et al. (1982) Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol 5:649–655
Byhardt RW, Martin L, Pajak TF (1993) The influence of field size and other treatment factors on pulmonary toxicity following hyperfractionated irradiation for inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) — analysis of a Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) protocol. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 27:537–544
Kaplan ES, Meier P (1958) Non-parametric estimation from incomplete observation. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Oka M, Fukuda M, Kuba M, et al. (2002) Phase I study of irinotecan and cisplatin with concurrent split-course radiotherapy in limited-disease small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer 38:1998–2004
Klautke G, Fähndrich S, Semrau S, et al. (2006) Simultaneous chemoradiotherapy with irinotecan and cisplatin in limited disease small cell lung cancer: a phase I study. Lung Cancer 53:183–188
Turrisi AT 3rd, Kim K, Blum R, et al. (1999) Twice-daily compared with once-daily thoracic radiotherapy in limited small-cell lung cancer treated concurrently with cisplatin and etoposide. N Engl J Med 340:265–271
Jeong HC, Lee SY, Lee SY, et al. (2006) Phase II study of irinotecan plus cisplatin with concurrent radiotherapy for the patients with limited-disease small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 53: 361–366
Sohn JH, Moon JW, Lee CG, et al. (2007) Phase II trial of irinotecan and cisplatin with early concurrent radiotherapy in limited-disease small-cell lung cancer. Cancer 109:1845–1850
Glisson B, Scott C, Komaki R, et al. (2000) Cisplatin, ifosfamide, oral etoposide, and concurrent accelerated hyperfractionated thoracic radiation for patients with limited small-cell lung carcinoma: results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Trial 93–12. J Clin Oncol 18:2990–2995
Takada M, Fukuoka M, Kawahara M, et al. (2002) Phase III study of concurrent versus sequential thoracic radiotherapy in combination with cisplatin and etoposide for limited-stage small cell lung cancer: results of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study 9104. J Clin Oncol 20:3054–3060
Schild SE, Bonner JA, Shanahan TG, et al. (2004) Long-term results of a phase III trial comparing once-daily radiotherapy with twice-daily radiotherapy in limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:943–951
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelwahab, S., Abdulla, H., Azmy, A. et al. Integration of irinotecan and cisplatin with early concurrent conventional radiotherapy for limited-disease SCLC (LD-SCLC). Int J Clin Oncol 14, 230–236 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-008-0842-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-008-0842-7