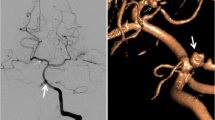
Abstract
Radiation therapy is a well-established, minimally invasive method of treating brain tumors. In recent years, the number of post-radiotherapy patients has increased, and delayed side effects are evident. De novo aneurysm formation after radiation often manifests as fatal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), resulting in severe clinical outcomes. Nevertheless, the prognosis and therapeutic efficacy of radiation-induced aneurysms (RIAs) remain unclear. Using the PubMed database from 1980 to 2021, we screened 45 articles (53 individual cases) on RIAs; approximately 70% of RIAs were diagnosed after rupture. Of 38 ruptured RIAs, 12 (31.6%) had modified Rankin scale (mRS) 5–6. On the other hand, all unruptured RIAs (15 cases) recovered without neurological deficits (p = 0.012). Ten of the 39 ruptured RIAs were treated surgically, and 22 were treated endovascularly. There was no significant difference in mRS between treatment modalities (p = 0.393), but conservative therapy was significantly related to unfavorable outcomes (p = 0.025). To improve clinical outcomes, RIAs need to be diagnosed before rupture. Surgeons should be aware of de novo aneurysm formation in patients long after radiation therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Aichholzer M, Gruber A, Haberler C, Bertalanffy A, Slavc I, Czech T (2001) Intracranial hemorrhage from an aneurysm encased in a pilocytic astrocytoma–case report and review of the literature. Childs Nervous Syst 17(3):173–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003810000364
Akamatsu Y, Sugawara T, Mikawa S, Saito A, Ono S, Takayama K, Jokura H, Seki H (2009) Ruptured pseudoaneurysm following Gamma knife surgery for a vestibular schwannoma. J Neurosurg 110:543–546. https://doi.org/10.3171/2008.8.JNS08177
Azzarelli B, Moore J, Gilmor R, Muller J, Edwards M, Mealey J (1984) Multiple fusiform intracranial aneurysms following curative radiation therapy for suprasellar germinoma. Case report. J Neurosurg 61(6):1141–1145. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1984.61.6.1141
Benson PJ, Sung JH (1989) Cerebral aneurysms following radiotherapy for medulloblastoma. J Neurosurg 70(4):545–550. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1989.70.4.0545
Chen HC, Lin CJ, Jen YM, Juan CJ, Hsueh CJ, Lee JC, Su WF (2004) Ruptured internal carotid pseudoaneurysm in a nasopharyngeal carcinoma patient with skull base osteoradionecrosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:388–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2003.08.010
Cheng KM, Chan CM, Cheung YL, Chiu HM, Tang KW, Law CK (2001) Endovascular treatment of radiation-induced petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm presenting with acute haemorrhage. A report of two cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 143(4):351–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010170089
Cheng KY, Lee KW, Chiang FY, Ho KY, Kuo WR (2008) Rupture of radiation-induced internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in a patient with nasopharyngeal carcinoma–spontaneous occlusion of carotid artery due to long-term embolizing performance. Head Neck 30(8):1132–1135. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.20753
Endo H, Fujimura M, Inoue T et al (2011) Simultaneous occurrence of subarachnoid hemorrhage and epistaxis due to ruptured petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm: association with transsphenoidal surgery and radiation therapy: case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51(3):226–229. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.51.226
Etminan N, Dreier R, Buchholz BA et al (2013) Exploring the age of intracranial aneurysms using carbon birth dating: preliminary results. Stroke 44(3):799–802. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.673806
Fujita K, Tamura M, Masuo O, Sasaki T, Yamoto T, Fukai J, Nakao N (2014) Ruptured internal carotid artery aneurysm presenting with catastrophic epistaxis after repeated stereotactic radiotherapies for anterior skull base tumor: case reports and review of the literature. J Neurol Surg Rep 75:e200–e205. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1383859
Ghoshhajra BB, McLean GK (2006) SIR Foundation. 2006 Annual Meeting Film Panel Case: radiation-induced cerebral aneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17(12):1891–1896. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.RVI.0000243615.07023.58
Gonzales-Portillo GA, Valdivia JM (2006) Uncommon presentation of pediatric ruptured intracranial aneurysm after radiotherapy for retinoblastoma. Case report. Surg Neurol 65(4):391–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2005.07.074
Hasegawa T, Kida Y, Kato T, Iizuka H, Kuramitsu S, Yamamoto T (2013) Long-term safety and efficacy of stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: evaluation of 440 patients more than 10 years after treatment with gamma Knife surgery. J Neurosurg 118:557–565. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.10.JNS12523
Hughes JD, Osetinsky LM, Jacob JT, Carlson ML, Lanzino G, Link MJ (2015) Incidentally discovered unruptured AICA aneurysm after radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma: a case report and review of the literature. Otol Neurotol 36(8):1428–1431. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000000807
Huh W, Bang JS, Oh CW, Kwon OK, Hwang G (2012) Intracranial aneurysm following cranial radiation therapy. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg 14:300–304. https://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2012.14.4.300
Inoue H, Kawano T, Ohmori Y, Amadatsu T, Yamamoto H, Nishi T, Mukasa A (2019) Internal carotid artery aneurysms diagnosed after stereotactic radiosurgery for a growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenoma: a case report and literature review. Acta Neurochir 161(6):1191–1195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-03840-5
Jensen FK, Wagner A (1997) Intracranial aneurysm following radiation therapy for medulloblastoma. A case report and review of the literature. Acta Radiol 38(1):37–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/02841859709171239
Kamide T, Mohri M, Misaki K, Uchiyama N, Nakada M (2016) Intracranial aneurysm formation after radiotherapy for medulloblastoma. Surg Neurol Int 7(Suppl 37):S880–S882. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.194501
Kellner CP, McDowell MM, Connolly ES Jr, Sisti MB, Lavine SD (2014) Late onset aneurysm development following radiosurgical obliteration of a cerebellopontine angle meningioma. J Neurointerv Surg 7(6):e21. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011206.rep
Lam HC, Abdullah VJ, Wormald PJ, Van Hasselt CA (2001) Internal carotid artery hemorrhage after irradiation and osteoradionecrosis of the skull base. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125(5):522–527. https://doi.org/10.1067/mhn.2001.118248
Lau WY, Chow CK (2005) Radiation-induced petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 114(12):939–940. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940511401208
Mak WK, Chow TL, Kwok SP (2000) Radionecrosis of internal carotid artery in nasopharyngeal carcinoma presenting as epistaxis. Aust N Z J Surg 70(3):237–238. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1622.2000.01795.x
Maruyama K, Mishima K, Saito N, Fujimaki T, Sasaki T, Kirino T (2000) Radiation-induced aneurysm and moyamoya vessels presenting with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142(2):139–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050016
Mascitelli JR, McNeill IT, Mocco J, Berenstein A, DeMattia J, Fifi JT (2015) Ruptured distal AICA pseudoaneurysm presenting years after vestibular schwannoma resection and radiation. BMJ Case Rep. 2015:bcr2015011736. Published 2015 May 6. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2015-011736
Matsumoto H, Minami H, Yamaura I, Yoshida Y (2014) Radiation-induced cerebral aneurysm treated with endovascular coil embolization. A case report. Interv Neuroradiol 20:448–453. https://doi.org/10.15274/INR-2014-10039
Murakami N, Tsukahara T, Toda H, Kawakami O, Hatano T (2002) Radiation-induced cerebral aneurysm successfully treated with endovascular coil embolization. Acta Neurochir Suppl 82:55–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6736-6_11
Nanney AD III, El Tecle NE, El Ahmadieh TY, Daou MR, Bit Ivan EN, Marymont MH, Batjer HH, Bendok BR (2014) Intracranial aneurysms in previously irradiated fields: literature review and case report. World Neurosurg 81:511–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2013.10.044
Paolucci A, Schisano L, Pluderi M, Grimoldi N, Caranci F, Angileri A, Arrichiello A, Costa A (2020) Giant intracranial aneurysm following radiation therapy: literature review with a novel case discussion. Acta Biomed 91:e2020005. https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v91i10-S.10281
Parag S, Arif Z, Chittoor R (2016) Radiotherapy-related intracranial aneurysms: a role for conservative management. Surg Neurol Int 7(Suppl 14):S387–S390. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.183496
Park KY, Ahn JY, Lee JW, Chang JH, Huh SK (2009) De novo intracranial aneurysm formation after gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. J Neurosurg 110:540–542. https://doi.org/10.3171/2008.9.JNS08860
Patro SN, Iancu D, Al Mansoori T, Lesiuk H, Vassilyadi M (2018) Endovascular glue embolization of a radiation-induced lenticulostriate artery pseudoaneurysm in a pediatric patient with optic pathway glioma: case report and review of literature. Interv Neuroradiol 24(5):499–508. https://doi.org/10.1177/1591019918773303
Pereira P, Cerejo A, Cruz J, Vaz R (2002) Intracranial aneurysm and vasculopathy after surgery and radiation therapy for craniopharyngioma: case report. Neurosurgery 50(4):885–888. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200204000-00042
Pesce A, Palmieri M, Zancana G, Salvati M, Santoro A, Raco A, Frati A (2020) Radiation-induced brain aneurysms: institutional experience and state of the art in the contemporary literature. World Neurosurg 135:339–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.09.157
Sciubba DM, Gallia GL, Recinos P, Garonzik IM, Clatterbuck RE (2006) Intracranial aneurysm following radiation therapy during childhood for a brain tumor. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 105((2)(Suppl)):134–139. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2006.105.2.134
Stone HB, Coleman CN, Anscher MS, McBride WH (2003) Effects of radiation on normal tissue: consequences and mechanisms. Lancet Oncol 4(9):529–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(03)01191-4
Sunderland G, Hassan F, Bhatnagar P, Mitchell P, Jayakrishnan V, Forster D, Mendelow AD (2014) Development of anterior inferior cerebellar artery pseudoaneurysm after gamma knife surgery for vestibular schwannoma. A case report and review of the literature. Br J Neurosurg 28(4):536–538. https://doi.org/10.3109/02688697.2013.847168
Takao T, Fukuda M, Kawaguchi T, Nishino K, Ito Y, Tanaka R, Sato M (2006) Ruptured intracranial aneurysm following gamma knife surgery for acoustic neuroma. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:1317–8; discussion 1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-006-0912-4
Tamura M, Kogo K, Masuo O, Oura Y, Matsumoto H, Fujita K, Nakao N, Uematsu Y, Itakura T, Chernov M, Hayashi M, Muragaki Y, Iseki H (2013) Formation and rupture of the internal carotid artery aneurysm after multiple courses of intensity-modulated radiation therapy for management of the skull base Ewing sarcoma/PNET: case report. J Neurol Surg Rep 74:111–117. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1358379
Twitchell S, Karsy M, Guan J, Couldwell WT, Taussky P (2018) Sequelae and management of radiation vasculopathy in neurosurgical patients. J Neurosurg:1–9. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.12.JNS172635
Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL et al (2007) Incidental findings on brain MRI in the general population. N Engl J Med 357(18):1821–1828. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa070972
Vogel TD, Kulwin CG, DeNardo AJ, Payner TD, Boaz JC, Fulkerson DH (2011) Tumor bleeding from a de novo aneurysm associated with optic glioma. J Neurosurg Pediatr 7:633–636. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.3.PEDS10562
Wagner MW, Dewan MC, Dmytriw AA, Ramaswamy V, Taylor MD, Muthusami P (2021) Radiation-induced intracranial aneurysm presenting with acute hemorrhage in a child treated for medulloblastoma. Childs Nerv Syst 37(4):1387–1389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04853-7
Wooding T, Phatouros C (2018) Progressive spontaneous resolution of an anterior communicating artery berry aneurysm following radiation treatment for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Neuroradiol 28(2):289–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0611-y
Wu YH, Lin SS, Chen HH, Chang FC, Liang ML, Wong TT, Yen SH, Chen YW (2016) Radiotherapy-related intracranial aneurysm: case presentation of a 17-year male and a meta-analysis based on individual patient data. Childs Nerv Syst 32(9):1641–1652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3144-9
Yamaguchi S, Kato T, Takeda M, Ikeda H, Kitamura K (2009) Ruptured distal anterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm following stereotactic irradiation for vestibular schwannoma: case report. Neurol Med Chir 49:202–205. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.49.202
Yoon WS, Lee KS, Jeun SS, Hong YK (2011) De novo aneurysm after treatment of glioblastoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 50(5):457–459. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2011.50.5.457
Yucesoy K, Feiz-Erfan I, Spetzler RF, Han PP, Coons S (2004) Anterior communicating artery aneurysm following radiation therapy for optic glioma: report of a case and review of the literature. Skull Base 14:169–173. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-832263
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
- Substantial contributions to conception and design: SS, SM, HS, NK.
- Acquisition and analysis and interpretation of data: SS, SM, HS, YA.
- Drafting a significant portion of the manuscript or figures: SS, SM.
- Supervisor: RS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki. This study was approved by the institutional review board of Tosei General Hospital.
Consent to participate
All experiments were performed in accordance with relevant named guidelines and regulations and informed consent was obtained from the patient’s families.
Consent for publocation
All authors consent to the submission of the manuscript in Neurosurgical Review. All authors guarantee that the research findings have not been previously published.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinoda, S., Muraoka, S., Shimizu, H. et al. The prognosis and treatment effectiveness of de novo aneurysm formation after radiation therapy for brain tumor. Neurosurg Rev 45, 2995–3002 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-022-01820-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-022-01820-5