Abstract
Background
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) of the brain allows quantitative measurement of tissue mechanics. Multiple studies are exploring possible applications in normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) in clinical and paraclinical contexts. This is of great interest in neurological surgery due to challenges related to diagnosis and prediction of treatment effects. In this scoping review, we present a topical overview and discuss the current literature, with particular attention to clinical implications and current challenges.
Methods
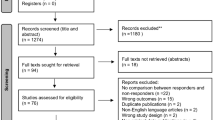
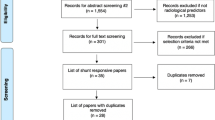
The protocol was based on the PRISMA extension for scoping reviews. After a systematic database search (PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science), the articles were screened for relevance. Thirty articles were subject to detailed screening, and key technical and clinical data items were extracted. The inclusion criteria included the use of MRE on human subjects with NPH.
Results
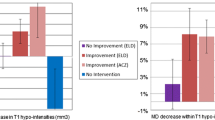
Seven articles were included in the final study. These studies had various objectives including the role of MRE in the assessment of regional elastic changes in NPH, shunt effect, and evaluation of NPH symptoms. MRE revealed patterns of mechanical changes in NPH that differed from other dementias. Regional MRE changes were associated with specific NPH signs and symptoms. Neurosurgical shunting caused partial normalization in tissue scaffold parameters. The studies were highly heterogeneous in technical aspects and design.
Conclusion
MRE studies in NPH are still limited by few participants, variable cohorts, inconsistent methodologies, and technical challenges, but the approach shows great potential for future clinical application.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ammar A, Abbas F, Al Issawi W, Fakhro F, Batarfi L, Hendam A et al (2017) Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus syndrome: is it understood? The Comprehensive Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Theory (CiNPHT). Springer International Publishing, Cham , pp 67–8
Arani A, Min H-K, Fattahi N, Wetjen NM, Trzasko JD, Manduca A et al (2018) Acute pressure changes in the brain are correlated with MR elastography stiffness measurements: initial feasibility in an in vivo large animal model. Magn Reson Med 79(2):1043–1051
Arani A, Murphy MC, Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Lake DS, Kruse SA et al (2015) Measuring the effects of aging and sex on regional brain stiffness with MR elastography in healthy older adults. Neuroimage 111:59–64
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005) Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26(3):839–851
Bertalan G, Klein C, Schreyer S, Steiner B, Kreft B, Tzschätzsch H et al (2020) Biomechanical properties of the hypoxic and dying brain quantified by magnetic resonance elastography. Acta Biomater 101:395–402
Bilston LE (2018) Soft tissue rheology and its implications for elastography: challenges and opportunities. NMR Biomed 31(10):e3832
Bohnen NI, Minoshima S, Giordani B, Frey KA, Kuhl DE (1999) Motor correlates of occipital glucose hypometabolism in Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Neurology 52(3):541–546
Cai W, Wang H, Huang W, Chung Y-C, Zhang L, Zou C et al (2011) Performance evaluation of a prototype pneumatic driver for MR elastography by MR elastography. In: 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics (BMEI), vol 4. China Institute of Electricals and Electronics Engineers, Shanghai, pp 430–443. https://doi.org/10.1109/BMEI.2011.6098350
Clayton EH, Genin GM, Bayly PV (2012) Transmission, attenuation and reflection of shear waves in the human brain. J R Soc Interface 9(76):2899–2910
Delgorio PL, Hiscox LV, Daugherty AM, Sanjana F, Pohlig RT, Ellison JM et al (2021) Effect of aging on the viscoelastic properties of hippocampal subfields assessed with high-resolution MR elastography. Cereb Cortex 31:2799–2811
ElSheikh M, Arani A, Perry A, Boeve BF, Meyer FB, Savica R et al (2017) MR elastography demonstrates unique regional brain stiffness patterns in dementias. Am J Roentgenol 209(2):403–408
Fattahi N, Arani A, Perry A, Meyer F, Manduca A, Glaser K et al (2016) MR elastography demonstrates increased brain stiffness in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Am J Neuroradiol 37(3):462–467
Freimann FB, Streitberger KJ, Klatt D, Lin K, McLaughlin J, Braun J et al (2012) Alteration of brain viscoelasticity after shunt treatment in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neuroradiology 54(3):189–196
Gallia GL, Rigamonti D, Williams MA (2006) The diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2(7):375–381
Gerischer LM, Fehlner A, Koebe T, Prehn K, Antonenko D, Grittner U et al (2018) Combining viscoelasticity, diffusivity and volume of the hippocampus for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage Clin 18:485–493
Griffiths D, Derbyshire S, Stenger A, Resnick N (2005) Brain control of normal and overactive bladder. J Urol 174(5):1862–1867
Hetzer S, Birr P, Fehlner A, Hirsch S, Dittmann F, Barnhill E et al (2018) Perfusion alters stiffness of deep gray matter. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38(1):116–125
Hiscox LV, Johnson CL, Barnhill E, McGarry MDJ, Huston J, Van Beek EJR et al (2016) Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) of the human brain: technique, findings and clinical applications. Phys Med Biol 61(24):R401–R437
Hiscox LV, Johnson CL, McGarry MDJ, Marshall H, Ritchie CW, van Beek EJR et al (2020) Mechanical property alterations across the cerebral cortex due to Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Commun 2(1):fcz049
Hiscox LV, Johnson CL, McGarry MDJ, Perrins M, Littlejohn A, van Beek EJR et al (2018) High-resolution magnetic resonance elastography reveals differences in subcortical gray matter viscoelasticity between young and healthy older adults. Neurobiol Aging 65:158–167
Hiscox LV, Johnson CL, McGarry MDJ, Schwarb H, van Beek EJR, Roberts N et al (2020) Hippocampal viscoelasticity and episodic memory performance in healthy older adults examined with magnetic resonance elastography. Brain Imaging Behav 14(1):175–185
Huston J, Murphy MC, Boeve BF, Fattahi N, Arani A, Glaser KJ et al (2016) Magnetic resonance elastography of frontotemporal dementia. J Magn Reson Imaging 43(2):474–478
Jahn K, Zwergal A, Schniepp R (2010) Gait disturbances in old age. Dtsch Aerztebl Online 107(17):306–316
Manduca A, Bayly PJ, Ehman RL, Kolipaka A, Royston TJ, Sack I et al (2021) MR elastography: principles, guidelines, and terminology. Magn Reson Med 85(5):2377–2390
Manduca A, Oliphant TE, Dresner MA, Mahowald JL, Kruse SA, Amromin E et al (2001) Magnetic resonance elastography: non-invasive mapping of tissue elasticity. Med Image Anal 5(4):237–254
Mariappan YK, Glaser KJ, Ehman RL (2010) Magnetic resonance elastography: a review. Clin Anat 23(5):497–511
McGarry M, Van Houten E, Solamen L, Gordon-Wylie S, Weaver J, Paulsen K (2019) Uniqueness of poroelastic and viscoelastic nonlinear inversion MR elastography at low frequencies. Phys Med Biol 64(7):075006
McGarry MDJ, Johnson CL, Sutton BP, Georgiadis JG, Van Houten EEW, Pattison AJ et al (2015) Suitability of poroelastic and viscoelastic mechanical models for high and low frequency MR elastography. Med Phys 42(2):947–957
Mori K (2001) Management of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: a multi-institutional study conducted in Japan. J Neurosurg 95(6):970–973
Murphy MC, Cogswell PM, Trzasko JD, Manduca A, Senjem ML, Meyer FB et al (2020) Identification of normal pressure hydrocephalus by disease-specific patterns of brain stiffness and damping ratio. Invest Radiol 55(4):200–208
Murphy MC, Huston J, Ehman RL (2019) MR elastography of the brain and its application in neurological diseases. Neuroimage 187:176–183
Murphy MC, Huston J, Jack CR, Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Felmlee JP et al (2011) Decreased brain stiffness in Alzheimer’s disease determined by magnetic resonance elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging 34(3):494–498
Murphy MC, Huston J, Jack CR, Glaser KJ, Senjem ML, Chen J et al (2013) Measuring the characteristic topography of brain stiffness with magnetic resonance elastography. PLoS One 8(12):e81668
Murphy MC, Jones DT, Jack CR, Glaser KJ, Senjem ML, Manduca A et al (2016) Regional brain stiffness changes across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. Neuroimage Clin 10:283–90
Murphy MC, Manduca A, Trzasko JD, Glaser KJ, Huston J, Ehman RL (2018) Artificial neural networks for stiffness estimation in magnetic resonance elastography. Magn Reson Med 80(1):351–360
Muthupillai R, Ehman RL (1996) Magnetic resonance elastography. Nat Med 2(5):601–603
Muthupillai R, Lomas DJ, Rossman PJ, Greenleaf JF, Manduca A, Ehman RL (1995) Magnetic resonance elastography by direct visualization of propagating acoustic strain waves. Science 269(5232):1854–1857
Perry A, Graffeo CS, Fattahi N, ElSheikh MM, Cray N, Arani A et al (2017) Clinical correlation of abnormal findings on magnetic resonance elastography in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. World Neurosurg 99:695-700.e1
Sack I, Jöhrens K, Würfel J, Braun J (2013) Structure-sensitive elastography: on the viscoelastic powerlaw behavior of in vivo human tissue in health and disease. Soft Matter 9(24):5672
Skalický P, Mládek A, Vlasák A, De Lacy P, Beneš V, Bradáč O (2020) Normal pressure hydrocephalus—an overview of pathophysiological mechanisms and diagnostic procedures. Neurosurg Rev 43(6):1451–1464
Solamen LM, McGarry MDJ, Fried J, Weaver JB, Lollis SS, Paulsen KD (2020) Poroelastic mechanical properties of the brain tissue of normal pressure hydrocephalus patients during lumbar drain treatment using intrinsic actuation MR elastography. Acad Radiol 28(4):457–466
Streitberger KJ, Wiener E, Hoffmann J, Freimann FB, Klatt D, Braun J et al (2011) In vivo viscoelastic properties of the brain in normal pressure hydrocephalus. NMR Biomed 24(4):385–392
Svensson SF, De Arcos J, Darwish OI, Fraser‐Green J, Storås TH, Holm S et al (2021) Robustness of MR elastography in the healthy brain: repeatability, reliability, and effect of different reconstruction methods. J Magn Reson Imaging 53(5):1510–1521. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.27475
Svensson SF, Nordhoy W, Lovland G, Sinkus R, De Arcos JR, Darwish O et al (2019) In vivo assessment of stiffness, viscosity and perfusion - in healthy subjects and brain cancer patients. Neuroradiology 61(1):S72–S73
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D et al (2018) PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med 169(7):467–473
Weaver JB, Pattison AJ, McGarry MD, Perreard IM, Swienckowski JG, Eskey CJ et al (2012) Brain mechanical property measurement using MRE with intrinsic activation. Phys Med Biol 57(22):7275–7287
Wuerfel E, Brandt A, Schregel K, Paul F, Sack I, Wuerfel J (2013) Correlation of cerebral magnetic resonance elastography with cognitive performance in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 19(7):974–975
Yin Z, Romano AJ, Manduca A, Ehman RL, Huston J (2018) Stiffness and beyond: what MR elastography can tell us about brain structure and function under physiologic and pathologic conditions. Top Magn Reson Imaging 27(5):305–318
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Alioune Badara Diop and ADA Arkitektur for their assistance with the graphical design.
Furthermore, we wish to thank MD-PhD Claire Gudex—medial writer—for contributing with proofreading and document editing.
Funding
The study was supported by the Lundbeck Foundation through the pregraduate neurosurgical scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JSA-D: main author, database search, screening
CBP: writing, proofreading, commenting, and supervising
BH: writing, proofreading, commenting, and supervising
UJ: writing, proofreading, and commenting
SM: writing, proofreading, and commenting
FH: writing, proofreading, and commenting
BJ: writing, proofreading, and commenting
FRP: writing, screening, proofreading, commenting, and main supervisor
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The authors hereby consent to the publication according to the terms of Neurosurgical Review. Patient consent is not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aunan-Diop, J.S., Pedersen, C.B., Halle, B. et al. Magnetic resonance elastography in normal pressure hydrocephalus—a scoping review. Neurosurg Rev 45, 1157–1169 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01669-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01669-0