Abstract
Objective
Subsequent microvascular decompression (MVD) might be affected by the previous two-isocentre gamma knife radiosurgery (GKS) due to the tissue changes caused by its higher dose radiation and larger treatment volume. This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of MVD as a second step treatment after two-isocentre GKS.
Methods
Between December 2016 and May 2019, data from 19 consecutive trigeminal neuralgia (TN) patients who experienced MVD after failed two-isocentre GKS were collected. The clinical characteristics, intraoperative findings, surgical outcomes and complications were reviewed and compared with 158 patients who underwent MVD as an initial treatment.
Results
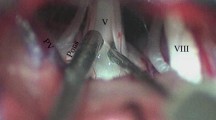
Fifteen patients (78.9%) achieved complete pain relief (Barrow Neurological Institute, BNI class I) immediately after surgery and nine patients (47.4%) maintained complete pain relief at the last follow-up, which was similar to patients who underwent initial MVD. The median follow-up period was 36 months. The incidence of new or worsened facial numbness showed no statistical significance between the groups. During surgery, trigeminal nerve atrophy was noted in 9 patients (47.4%), thickened arachnoid in 3 patients (15.8%), atherosclerotic plaque in 3 patients (15.8%) and neurovascular adhesion in 1 patient (5.3%).
Conclusions
MVD remains an effective and safe rescue therapy for patients who elect the minimally invasive treatment with two-isocentre GKS for the first time, without an increased risk of facial numbness.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alpert TE, Chung CT, Mitchell LT, Hodge CJ, Montgomery CT, Bogart JA, Kim DY, Bassano DA, Hahn SS (2005) Gamma knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia: improved initial response with two isocenters and increasing dose. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):185–188. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.102.s_supplement.0185
Barker FG 2nd, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1996) The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med 334(17):1077–1083. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199604253341701
Chen JC (2012) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia in patients with and without prior stereotactic radiosurgery. World Neurosurg 78(1–2):149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2011.09.029
Cheng J, Liu W, Hui X, Lei D, Zhang H (2017) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia in patients with failed gamma knife surgery: Analysis of efficacy and safety. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 161:88–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2017.08.017
Flickinger JC, Pollock BE, Kondziolka D, Phuong LK, Foote RL, Stafford SL, Lunsford LD (2001) Does increased nerve length within the treatment volume improve trigeminal neuralgia radiosurgery? A prospective double-blind, randomized study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51(2):449–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(01)01606-6
Hu YS, Lee CC, Guo WY, Lin CJ, Yang HC, Wu HM, Liu KD, Chung WY (2019) Trigeminal nerve atrophy predicts pain recurrence after gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery for classical trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 84(4):927–934. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyy122
Huang CF, Chuang JC, Tu HT, Chou MC (2006) Microsurgical outcomes after failed repeated Gamma Knife surgery for refractory trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 105(Suppl):117–119. https://doi.org/10.3171/sup.2006.105.7.117
Kanner AA, Neyman G, Suh JH, Weinhous MS, Lee SY, Barnett GH (2004) Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: comparing the use of a 4-mm versus concentric 4- and 8-mm collimators. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 82(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1159/000076661
Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC (2002) Stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Clin J Pain 18(1):42–47. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002508-200201000-00007
Leal PR, Barbier C, Hermier M, Souza MA, Cristino-Filho G, Sindou M (2014) Atrophic changes in the trigeminal nerves of patients with trigeminal neuralgia due to neurovascular compression and their association with the severity of compression and clinical outcomes. J Neurosurg 120(6):1484–1495. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.2.Jns131288
Leal PRL, Barbier C, Hermier M, Souza MA, Cristino G, Sindou M (2014) Atrophic changes in the trigeminal nerves of patients with trigeminal neuralgia due to neurovascular compression and their association with the severity of compression and clinical outcomes. J Neurosurg 120(6):1484–1495. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.2.Jns131288
Lee JK, Choi HJ, Ko HC, Choi SK, Lim YJ (2012) Long term outcomes of gamma knife radiosurgery for typical trigeminal neuralgia-minimum 5-year follow-up. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 51(5):276–280. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.51.5.276
Li P, Wang W, Liu Y, Zhong Q, Mao B (2012) Clinical outcomes of 114 patients who underwent gamma-knife radiosurgery for medically refractory idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Clin Neurosci 19(1):71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2011.03.020
Linskey ME, Ratanatharathorn V, Penagaricano J (2008) A prospective cohort study of microvascular decompression and Gamma Knife surgery in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 109(Suppl):160–172. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS/2008/109/12/S25
Maesawa S, Salame C, Flickinger JC, Pirris S, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2001) Clinical outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 94(1):14–20. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.94.1.0014
Maher CO, Pollock BE (2000) Radiation induced vascular injury after stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: case report. Surg Neurol 54(2):189–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-3019(00)00266-4
Massager N, Lorenzoni J, Devriendt D, Desmedt F, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2004) Gamma knife surgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia performed using a far-anterior cisternal target and a high dose of radiation. J Neurosurg 100(4):597–605. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2004.100.4.0597
Morbidini-Gaffney S, Chung CT, Alpert TE, Newman N, Hahn SS, Shah H, Mitchell L, Bassano D, Darbar A, Bajwa SA, Hodge C (2006) Doses greater than 85 Gy and two isocenters in gamma knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia: updated results. J Neurosurg 105(Suppl):107–111. https://doi.org/10.3171/sup.2006.105.7.107
O’Connor MM, Mayberg MR (2000) Effects of radiation on cerebral vasculature: a review. Neurosurgery 46(1):138–149. discussion 150–131. https://doi.org/10.1093/neurosurgery/46.1.138
Park YS, Kim JP, Chang WS, Kim HY, Park YG, Chang JW (2011) Gamma knife radiosurgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia as primary vs. secondary treatment option. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113(6):447–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.01.006
Pollock BE, Schoeberl KA (2010) Prospective comparison of posterior fossa exploration and stereotactic radiosurgery dorsal root entry zone target as primary surgery for patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 67(3):633–638. discussion 638–639. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000377861.14650.98
Régis J, Metellus P, Hayashi M, Roussel P, Donnet A, Bille-Turc F (2006) Prospective controlled trial of gamma knife surgery for essential trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 104(6):913–924. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.104.6.913
Régis J, Tuleasca C, Resseguier N, Carron R, Donnet A, Yomo S, Gaudart J, Levivier M (2016) The very long-term outcome of radiosurgery for classical trigeminal neuralgia. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 94(1):24–32. https://doi.org/10.1159/000443529
Sekula RF Jr, Frederickson AM, Jannetta PJ, Bhatia S, Quigley MR (2010) Microvascular decompression after failed gamma knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a safe and effective rescue therapy? J Neurosurg 113(1):45–52. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.1.JNS091386
Shetter AG, Zabramski JM, Speiser BL (2005) Microvascular decompression after gamma knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia: intraoperative findings and treatment outcomes. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):259–261. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.102.s_supplement.0259
Somaza S, Montilla EM, Mora MC (2019) Gamma knife radiosurgery on the trigeminal ganglion for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: Results and review of the literature. Surg Neurol Int 10:89. https://doi.org/10.25259/SNI-134-2019
Spina A, Mortini P, Alemanno F, Houdayer E, Iannaccone S (2017) Trigeminal neuralgia: toward a multimodal approach. World Neurosurg 103:220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.03.126
The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version) (2013) Cephalalgia 33(9):629–808. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102413485658
Tuleasca C, Regis J, Sahgal A, De Salles A, Hayashi M, Ma L, Martinez-Alvarez R, Paddick I, Ryu S, Slotman BJ, Levivier M (2018) Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review. J Neurosurg 130(3):733–757. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.9.JNS17545
Tyler-Kabara EC, Kassam AB, Horowitz MH, Urgo L, Hadjipanayis C, Levy EI, Chang YF (2002) Predictors of outcome in surgically managed patients with typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia: comparison of results following microvascular decompression. J Neurosurg 96(3):527–531. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.96.3.0527
Xu Z, Schlesinger D, Moldovan K, Przybylowski C, Sun X, Lee CC, Yen CP, Sheehan J (2014) Impact of target location on the response of trigeminal neuralgia to stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 120(3):716–724. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.10.Jns131596
Zakrzewska JM, Akram H (2011) Neurosurgical interventions for the treatment of classical trigeminal neuralgia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 9:CD007312. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007312.pub2
Zhang X, Li P, Zhang S, Gong F, Yang S, Wang W (2014) Effect of radiation dose on the outcomes of gamma knife treatment for trigeminal neuralgia: a multi-factor analysis. Neurol India 62(4):400–405. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.141272
Zhao H, Fan SQ, Wang XH, Zhang X, Tang YD, Zhu J, Zhou P, Li ST (2018) Evaluation of microvascular decompression as rescue therapy for trigeminal neuralgia in patients with failed gamma knife surgery. World Neurosurg 116:e86–e91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.063
Zhao H, Fan SQ, Wang XH, Zhang X, Tang YD, Zhu J, Zhou P, Li ST (2018) Evaluation of microvascular decompression as rescue therapy for trigeminal neuralgia in patients with failed gamma knife surgery. World Neurosurgery 116:E86–E91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.063
Zhao H, Shen Y, Yao D, Xiong N, Abdelmaksoud A, Wang H (2018) Outcomes of two-isocenter gamma knife radiosurgery for patients with typical trigeminal neuralgia: pain response and quality of life. World Neurosurg 109:e531–e538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.10.014
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my gratitude to the department of radiology for providing the valuable image data and surgeons for providing the intraoperative videos.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: Jia-jing Wang and Song-shan Chai. Data acquisition and analysis: Jia-jing Wang and Zhen Zhao. Writing the first draft: Jia-jing Wang and Zhen Zhao. Revision: Yi-hao Wang and Wei Xiang. Supervision: Wei Xiang. Read and approved final version: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study received full approval from the ethics committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology and informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent for participation was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Jj., Zhao, Z., Chai, Ss. et al. Microvascular decompression as a second step treatment for trigeminal neuralgia in patients with failed two-isocentre gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurg Rev 45, 783–791 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01587-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01587-1