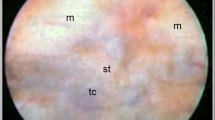
Abstract
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) is a hydrocephalus treatment procedure that involves opening the Liliequist membrane (LM). However, LM anatomy has not been well-studied neuroendoscopically, because approach angles differ between descriptive and microsurgical anatomical explorations. Discrepancies in ETV efficacy, especially among children age 2 and younger, may be due to incomplete LM opening. The objective of this study was to characterize the LM anatomically from a neuroendoscopic perspective to better understand the impact of anatomical features during LM ostomy and the ETV success rate. Additionally, the ETV success score was tested to predict patient outcome after the intraoperatively difficult opening of LM. Fifty-four patients who underwent ETV were prospectively analyzed with a mean follow-up of 53.1 months (1–90 months). The ETV technical parameters of difficulty were validated by seven expert neurosurgeons. The pediatric population (44) of this study represents the majority of patients (81.4%). The overall ETV success rate was 68.5%. Anomalies on the IIIVT floor resulted in an increased rate of ETV failure. The IIIVT was anomalous, and LM was thick in 33.3% of cases. Fenestration of LM was difficult in 39% of cases, and the LM and TC were opened separately in 55.6% of cases. The endoscopic third ventriculostomy success score (ETVSS) accurately predicted the level of difficulty opening the LM (p = 0.012), and the group with easy opening presented greater durability in ETV success. Neurosurgeons should be aware of the difficulty level of the overture of LM during ETV and its impact on long-term ETV effectiveness.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data not available
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Anik I, Ceylan S, Koc K, Anik Y, Etus V, Genc H (2011) Membranous structures affecting the success of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in adult aqueductus sylvii stenosis. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 54:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1277172
Anik I, Ceylan S, Koc K, Tugasaygi M, Sirin G, Gazioglu N, Sam B (2011) Microsurgical and endoscopic anatomy of Liliequist's membrane and the prepontine membranes: cadaveric study and clinical implications. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 153:1701–1711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-0978-5
Beems T, Grotenhuis JA (2002) Is the success rate of endoscopic third ventriculostomy age-dependent? An analysis of the results of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in young children. Childs Nerv Syst 18:605–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-002-0652-6
Bowes AL, King-Robson J, Dawes WJ, James G, Aquilina K (2017) Neuroendoscopic surgery in children: does age at intervention influence safety and efficacy? A single-center experience. J Neurosurg Pediatr 20:324–328. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.4.PEDS16488
Brasil AV, Schneider FL (1993) Anatomy of Liliequist’s membrane. Neurosurgery 32:956–960 discussion 960-951
Breimer GE, Sival DA, Brusse-Keizer MG, Hoving EW (2013) An external validation of the ETVSS for both short-term and long-term predictive adequacy in 104 pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 29:1305–1311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2122-8
Brockmeyer D, Abtin K, Carey L, Walker ML (1998) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: an outcome analysis. Pediatr Neurosurg 28:236–240. https://doi.org/10.1159/000028657
Buxton N, Vloeberghs M, Punt J (1998) Liliequist’s membrane in minimally invasive endoscopic neurosurgery. Clin Anat 11:187–190. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-2353(1998)11:3<187::AID-CA6>3.0.CO;2-Q
Cartmill M, Jaspan T, McConachie N, Vloeberghs M (2001) Neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy in dysmorphic brains. Childs Nerv Syst 17:391–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003810000438
Cinalli G, Sainte-Rose C, Chumas P, Zerah M, Brunelle F, Lot G, Pierre-Kahn A, Renier D (1999) Failure of third ventriculostomy in the treatment of aqueductal stenosis in children. J Neurosurg 90:448–454. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1999.90.3.0448
Connor DE Jr, Nanda A (2017) Bengt Liliequist: life and accomplishments of a true renaissance man. J Neurosurg 126:645–649. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.12.JNS131770
Costa Val JA (2009) Minicraniotomy for endoscopic third ventriculostomy in babies: technical note with a 7-year-segment analysis. Childs Nerv Syst 25:357–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0748-8
Costa Val JA, Scaldaferri PM, Furtado LM, de Souza Baptista G (2012) Third ventriculostomy in infants younger than 1 year old. Childs Nerv Syst 28:1233–1235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1740-x
Dezena R (2018) Endoscopic views of the membrane of Liliequist. J Bras Neurocirurgia 26:320–323. https://doi.org/10.22290/jbnc.v26i4.1373
Durnford AJ, Kirkham FJ, Mathad N, Sparrow OC (2011) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of childhood hydrocephalus: validation of a success score that predicts long-term outcome. J Neurosurg Pediatr 8:489–493. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.8.PEDS1166
Etus V, Solakoglu S, Ceylan S (2011) Ultrastructural changes in the Liliequist membrane in the hydrocephalic process and its implications for the endoscopic third ventriculostomy procedure. Turk Neurosurg 21:359–366. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.4171-11.0
Froelich SC, Abdel Aziz KM, Cohen PD, van Loveren HR, Keller JT (2008) Microsurgical and endoscopic anatomy of Liliequist’s membrane: a complex and variable structure of the basal cisterns. Neurosurgery 63:ONS1–ONS8; discussion ONS8-9. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000335004.22628.ee
Fukuhara T, Vorster SJ, Luciano MG (2000) Risk factors for failure of endoscopic third ventriculostomy for obstructive hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 46:1100–1109; discussion 1109-1111. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200005000-00015
Furtado LMF, da Costa Val Filho JA, Dos Santos Junior EC (2021) External validation of the ETV success score in 313 pediatric patients: a Brazilian single-center study. Neurosurg Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01461-6
Furtado LMF, da Costa Val Filho JA, Holliday JB, da Silva Costa J, de Matos MA, Nascimento VAM, Ramos Cavalcanti T (2020) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in patients with myelomeningocele after shunt failure. Childs Nerv Syst 36:3047–3052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04596-5
Fushimi Y, Miki Y, Ueba T, Kanagaki M, Takahashi T, Yamamoto A, Haque TL, Konishi J, Takahashi JA, Hashimoto N, Konishi J (2003) Liliequist membrane: three-dimensional constructive interference in steady state MR imaging. Radiology 229:360–365; discussion 365. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2292021507
Hellwig D, Giordano M, Kappus C (2013) Redo third ventriculostomy. World Neurosurg 79:S22 e13–S22 e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2012.02.006
Hopf NJ, Grunert P, Fries G, Resch KD, Perneczky A (1999) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: outcome analysis of 100 consecutive procedures. Neurosurgery 44:795–804; discussion 804-796. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199904000-00062
Inoue K, Seker A, Osawa S, Alencastro LF, Matsushima T, Rhoton AL Jr (2009) Microsurgical and endoscopic anatomy of the supratentorial arachnoidal membranes and cisterns. Neurosurgery 65:644–664; discussion 665. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000351774.81674.32
Koch D, Wagner W (2004) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in infants of less than 1 year of age: which factors influence the outcome? Childs Nerv Syst 20:405–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-0958-7
Kulkarni AV, Drake JM, Mallucci CL, Sgouros S, Roth J, Constantini S, Canadian Pediatric Neurosurgery Study G (2009) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of childhood hydrocephalus. J Pediatr 155:254–259 e251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.02.048
Kulkarni AV, Riva-Cambrin J, Holubkov R, Browd SR, Cochrane DD, Drake JM, Limbrick DD, Rozzelle CJ, Simon TD, Tamber MS, Wellons JC 3rd, Whitehead WE, Kestle JR, Hydrocephalus Clinical Research N (2016) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children: prospective, multicenter results from the hydrocephalus clinical research network. J Neurosurg Pediatr 18:423–429. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.4.PEDS163
Kulkarni AV, Sgouros S, Constantini S, Investigators I (2016) International Infant hydrocephalus study: initial results of a prospective, multicenter comparison of endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) and shunt for infant hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 32:1039–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3095-1
Labidi M, Lavoie P, Lapointe G, Obaid S, Weil AG, Bojanowski MW, Turmel A (2015) Predicting success of endoscopic third ventriculostomy: validation of the ETV success score in a mixed population of adult and pediatric patients. J Neurosurg 123:1447–1455. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.12.JNS141240
Liliequist B (1956) The anatomy of the subarachnoid cisterns. Acta radiol 46:61–71. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016925609170813
Lu J, Zhu X (2005) Microsurgical anatomy of the interpeduncular cistern and related arachnoid membranes. J Neurosurg 103:337–341. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.103.2.0337
Matsuno H, Rhoton AL Jr, Peace D (1988) Microsurgical anatomy of the posterior fossa cisterns. Neurosurgery 23:58–80. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198807000-00012
Mortazavi MM, Rizq F, Harmon O, Adeeb N, Gorjian M, Hose N, Modammadirad E, Taghavi P, Rocque BG, Tubbs RS (2015) Anatomical variations and neurosurgical significance of Liliequist's membrane. Childs Nerv Syst 31:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2590-5
Naftel RP, Reed GT, Kulkarni AV, Wellons JC (2011) Evaluating the children’s hospital of Alabama endoscopic third ventriculostomy experience using the endoscopic third ventriculostomy success score: an external validation study. J Neurosurg Pediatr 8:494–501. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.8.PEDS1145
Pavez A, Salazar C, Rivera R, Contreras J, Orellana A, Guzman C, Iribarren O, Hernandez H, Elzo J, Moraga D (2006) Description of endoscopic ventricular anatomy in myelomeningocele. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 49:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-932193
Qi ST, Fan J, Zhang XA, Pan J (2011) Reinvestigation of the ambient cistern and its related arachnoid membranes: an anatomical study. J Neurosurg 115:171–178. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.2.JNS101365
Resch KD, Perneczky A, Tschabitscher M, Kindel S (1994) Endoscopic anatomy of the ventricles. Acta Neurochir Suppl 61:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6908-7_10
Romero Adel C, Aguiar PH, Borchartt TB, Conci A (2011) Quantitative ventricular neuroendoscopy performed on the third ventriculostomy: anatomic study. Neurosurgery 68:347–354; discussion 353-344. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e318211449a
Romero L, Ros B, Ibanez G, Rius F, Gonzalez L, Arraez M (2014) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: can we predict success during surgery? Neurosurg Rev 37:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-013-0494-6
Salvador SF, Oliveira J, Pereira J, Barros H, Vaz R (2014) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the management of hydrocephalus: outcome analysis of 168 consecutive procedures. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 126:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.08.037
Shen W, Syed HR, Gandhoke G, Garcia R, Pundy T, Tomita T (2018) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children with a fiber optic neuroendoscopy. Childs Nerv Syst 34:837–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3679-4
Sherrod BA, Iyer RR, Kestle JRW (2020) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for pediatric tumor-associated hydrocephalus. Neurosurg Focus 48:E5. https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.10.FOCUS19725
Siomin V, Weiner H, Wisoff J, Cinalli G, Pierre-Kahn A, Saint-Rose C, Abbott R, Elran H, Beni-Adani L, Ouaknine G, Constantini S (2001) Repeat endoscopic third ventriculostomy: is it worth trying? Childs Nerv Syst 17:551–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003810100475
Sufianov AA, Sufianova GZ, Iakimov IA (2009) Microsurgical study of the interpeduncular cistern and its communication with adjoining cisterns. Childs Nerv Syst 25:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0746-x
Vinas FC, Panigrahi M (2001) Microsurgical anatomy of the Liliequist’s membrane and surrounding neurovascular territories. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 44:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-15999
Vulcu S, Eickele L, Cinalli G, Wagner W, Oertel J (2015) Long-term results of endoscopic third ventriculostomy: an outcome analysis. J Neurosurg 123:1456–1462. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.11.JNS14414
Wagner W, Koch D (2005) Mechanisms of failure after endoscopic third ventriculostomy in young infants. J Neurosurg 103:43–49. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2005.103.1.0043
Wang SS, Zheng HP, Zhang FH, Wang RM (2011) Microsurgical anatomy of Liliequist’s membrane demonstrating three-dimensional configuration. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 153:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0823-2
Yadav YR, Parihar V, Pande S, Namdev H, Agarwal M (2012) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy. J Neurosci Rural Pract 3:163–173. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-3147.98222
Yasargil MG, Kasdaglis K, Jain KK, Weber HP (1976) Anatomical observations of the subarachnoid cisterns of the brain during surgery. J Neurosurg 44:298–302. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1976.44.3.0298
Zhang XA, Qi ST, Huang GL, Long H, Fan J, Peng JX (2012) Anatomical and histological study of Liliequist's membrane: with emphasis on its nature and lateral attachments. Childs Nerv Syst 28:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1599-2
Acknowledgements
To the neurosurgeons who participated in the face validity
Prof. Alexandre Giannetti - Hospital das Clínicas, Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte - Brazil
Dr. Arthur da Cunha - Hospital da Restauração, Recife - Brazil
Prof. Hamilton Matushita - Hospital das Clínicas, University of São Paulo - USP of São Paulo - Brazil
Prof. Jorge Bizzi - Hospital das Clínicas, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul - Brazil
Prof. Ricardo Santos de Oliveira - Hospital das Clínicas, University of São Paulo – USP of Ribeirão Preto
Prof. Roberto Dezena - Hospital das Clínicas, Federal University of the Triângulo Mineiro - Brazil
Prof. Samuel Zymberg - Hospital São Paulo - Universidade Federal de São Paulo - Federal University of São Paulo, São Paulo - Brazil
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: José Aloysio da Costa Val FilhoMethodology: José Aloysio da Costa Val FilhoFormal analysis and investigation: José Aloysio da Costa Val FilhoWriting - original draft preparation: Leopoldo Mandic Ferreira Furtado, Guaracy de Macedo Machado Filho, and Fernando Levi Alencar MacielWriting - review and editing: Leopoldo Mandic Ferreira Furtado, José Aloysio da Costa Val FilhoSupervision: Sebastião Nataniel da Silva Gusmão
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the ethical board with protocol number 1.515.461.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Costa Val Filho, J.A., da Silva Gusmão, S.N., Furtado, L.M.F. et al. The role of the Liliequist membrane in the third ventriculostomy. Neurosurg Rev 44, 3375–3385 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01508-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01508-2