Abstract
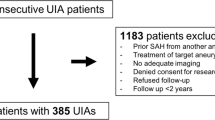
With the widespread use of imaging techniques, the possibility that an asymptomatic unruptured intracranial aneurysm (UIA) is detected has increased significantly. There is no established consensus regarding follow-up, duration, and frequency of such imaging surveillance. The objectives of this study include assessing the growth rate and rupture risk of small (less than 7mm) UIAs, identifying associated risk factors and providing an aneurysm surveillance protocol in appropriately selected patients. Systematic searches of Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Central were undertaken from database inception to March 2020 for published studies reporting the growth and rupture risks of small UIAs. Twenty-one studies reporting 8428 small UIAs were included in our meta-analysis. The pooled mean age was 61 years (95% CI: 55–67). The mean follow-up period for growth and rupture ranged from 11 to 108 months, with the pooled mean follow-up period across 14 studies being 42 months (95% CI: 33–51). Pooled overall growth rate was 6.0% (95% CI: 3.8–8.7). Pooled growth rates for aneurysms < 5mm and < 3 mm were 5.2% (95% CI: 3.0–7.9) and 0.8% (95% CI: 0.0–6.1), respectively. Pooled overall rupture rate was 0.4% (95% CI: 0.2–0.7). From the meta-regression analysis, having multiple aneurysms, smoking, hypertension, and personal history of SAH did not significantly predict growth, and a personal history of SAH, smoking, hypertension, and multiple aneurysms were not statistically significant predictors of rupture. Our findings suggest that small UIAs have low growth and rupture rates and very small UIAs have little or no risk for rupture. In the setting of incidental small UIAs, patients with multiple and/or posterior circulation aneurysms require more regular radiological monitoring.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Juvela S, Poussa K, Porras M (2001) Factors affecting formation and growth of intracranial aneurysms: a long-term follow-up study. Stroke 32:485–491
Wermer MJ, van der Schaaf IC, Algra A, Rinkel GJ (2007) Risk of rupture of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in relation to patient and aneurysm characteristics: an updated meta-analysis. Stroke 38:1404–1410
Rinkel GJ, Djibuti M, Algra A, van Gijn J (1998) Prevalence and risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review. Stroke 29:251–256
Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston J, Meissner I, Brown RD, Piepgras DG, Forbes GS, Thielen K, Nichols D, O'Fallon WM, Peacock J, Jaeger L, Kassell NF, Kongable-Beckman GL, Torner JC, Investigators, I. S. o. U. I. A. (2003) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 362:103–110
Thompson BG, Brown RD, Amin-Hanjani S, Broderick JP, Cockroft KM, Connolly ES, Duckwiler GR, Harris CC, Howard VJ, Johnston SC, Meyers PM, Molyneux A, Ogilvy CS, Ringer AJ, Torner J, American Heart Association Stroke Council, C. u. o. C. a. S. N., and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, Association, A. H. & Association, A. S (2015) Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 46:2368–2400
Raaymakers TW, Rinkel GJ, Limburg M, Algra A (1998) Mortality and morbidity of surgery for unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a meta-analysis. Stroke 29:1531–1538
Investigators, I. S. o. U. I. A (1998) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms--risk of rupture and risks of surgical intervention. N Engl J Med 339:1725–1733
Yamaki VN, Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Lanzino G (2016) Endovascular Treatment of Very Small Intracranial Aneurysms: Meta-Analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:862–867
Guresir E, Vatter H, Schuss P, Platz J, Konczalla J, de Rochement Rdu M, Berkefeld J, Seifert V (2013) Natural history of small unruptured anterior circulation aneurysms: a prospective cohort study. Stroke 44:3027–3031
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535
Cohen J (1960) A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas 20:37–47
Grainge, M. Excluding small studies from a systematic review or meta-analysis. Presented at: CSG Annual Meeting 2015; March 12-18, 2015; Dresden, Germany. https://skin.cochrane.org/sites/skin.cochrane.org/files/public/uploads/CSG-COUSIN_March%202015_M%20Grainge.pdf. Accessed February 1, 2020.
Nyaga VN, Arbyn M, Aerts M (2014) Metaprop: a Stata command to perform meta-analysis of binomial data. Archives Public Health 72:39
Higgins JPT, G. S. (2011) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0, The Cochrane Collaboration.
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 315:629–634
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ, Group GW (2008) GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 336:924–926
Asari S, Ohmoto T (1993) Natural history and risk factors of unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 95:205–214
Brinjikji W, Pereira VM, Khumtong R, Kostensky A, Tymianski M, Krings T, Radovanovich I (2018) PHASES and ELAPSS scores are associated with aneurysm growth: a study of 431 unruptured intracranial aneurysms. World Neurosurg 114:e425–e432
Broderick JP, Brown RD Jr, Sauerbeck L, Hornung R, Huston J 3rd, Woo D, Anderson C, Rouleau G, Kleindorfer D, Flaherty ML, Meissner I, Foroud T, Moomaw EC, Connolly ES, Investigators FIAS (2009) Greater rupture risk for familial as compared to sporadic unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 40:1952–1957
Byoun HS, Huh W, Oh CW, Bang JS, Hwang G, Kwon OK (2016) Natural history of unruptured intracranial aneurysms : a retrospective single center analysis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 59:11–16
Chien A, Liang F, Sayre J, Salamon N, Villablanca P, Vinuela F (2013) Enlargement of small, asymptomatic, unruptured intracranial aneurysms in patients with no history of subarachnoid hemorrhage: the different factors related to the growth of single and multiple aneurysms. J Neurosurg 119:190–197
Ferns SP, Sprengers MES, Van Rooij WJJ, Van Den Berg R, Velthuis BK, De Kort GAP, Sluzewski M, Van Zwam WH, Rinkel GJE, Majoie CBLM (2011) De novo aneurysm formation and growth of untreated aneurysms: a 5-year MRA follow-up in a large cohort of patients with coiled aneurysms and review of the literature. Stroke 42:313–318
Gondar R, Gautschi OP, Cuony J, Perren F, Jagersberg M, Corniola MV, Schatlo B, Molliqaj G, Morel S, Kulcsar Z, Mendes Pereira V, Rufenacht D, Schaller K, Bijlenga P (2016) Unruptured intracranial aneurysm follow-up and treatment after morphological change is safe: observational study and systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87:1277–1282
Huang H, O'Neill AH, Chandra RV, Lai LT (2020) Asymptomatic intracranial aneurysms in the elderly: long-term clinical and radiologic follow-up of 193 consecutive patients. World Neurosurg 133:e600–e608
Ikawa F, Morita A, Tominari S, Nakayama T, Shiokawa Y, Date I, Nozaki K, Miyamoto S, Kayama T, Arai H (2020) Rupture risk of small unruptured cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 132:69–78
Inagawa T (1991) Follow-up study of unruptured aneurysms arising from the C3 and C4 segments of the internal carotid artery. Surg Neurol 36:99–105
Irazabal MV, Huston J 3rd, Kubly V, Rossetti S, Sundsbak JL, Hogan MC, Harris PC, Brown RD Jr, Torres VE (2011) Extended follow-up of unruptured intracranial aneurysms detected by presymptomatic screening in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:1274–1285
Jeon JS, Ahn JH, Huh W, Son YJ, Bang JS, Kang HS, Sohn CH, Oh CW, Kwon OK, Kim JE (2014) A retrospective analysis on the natural history of incidental small paraclinoid unruptured aneurysm. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85:289–294
Matsubara S, Hadeishi H, Suzuki A, Yasui N, Nishimura H (2004) Incidence and risk factors for the growth of unruptured cerebral aneurysms: observation using serial computerized tomography angiography. J Neurosurg 101:908–914
Sonobe M, Yamazaki T, Yonekura M, Kikuchi H (2010) Small unruptured intracranial aneurysm verification study: SUAVe study, Japan. Stroke 41:1969–1977
Sorenson TJ, Vine R, Lanzino G (2018) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms in patients over 80 years: natural history and management implications. Acta Neurochir 160:1773–1777
Teo M, St George EJ (2016) Radiologic surveillance of untreated unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a single surgeon’s experience. World Neurosurg 90:20–28
Villablanca JP, Duckwiler GR, Jahan R, Tateshima S, Martin NA, Frazee J, Gonzalez NR, Sayre J, Vinuela FV (2013) Natural history of asymptomatic unruptured cerebral aneurysms evaluated at CT angiography: growth and rupture incidence and correlation with epidemiologic risk factors. Radiology 269:258–265
Wermer MJH, Van Der Schaaf IC, Velthuis BK, Majoie CB, Albrecht KW, Rinkel GJE (2006) Yield of short-term follow-up CT/MR angiography for small aneurysms detected at screening. Stroke 37:414–418
Zylkowski J, Kunert P, Jaworski M, Rosiak G, Marchel A, Rowinski O (2015) Changes of size and shape of small, unruptured intracranial aneurysms in repeated computed tomography angiography studies. Wideochirurgia i Inne Techniki Maloinwazyjne 10:178–188
Brinjikji W, Zhu YQ, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Murad MH, Wang Z, Kallmes DF (2016) Risk factors for growth of intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:615–620
Backes D, Rinkel GJ, Laban KG, Algra A, Vergouwen MD (2016) patient- and aneurysm-specific risk factors for intracranial aneurysm growth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 47:951–957
Malhotra A, Wu X, Forman HP, Nardini HKG, Matouk CC, Gandhi D, Moore C, Sanelli P (2017) Growth and rupture risk of small unruptured intracranial aneurysms a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 167:26–33
Burns JD, Huston IJ, Layton KF, Piepgras DG, Brown RD Jr (2009) Intracranial aneurysm enlargement on serial magnetic resonance angiography: Frequency and risk factors. Stroke 40:406–411
Matsumoto K, Oshino S, Sasaki M, Tsuruzono K, Taketsuna S, Yoshimine T (2013) Incidence of growth and rupture of unruptured intracranial aneurysms followed by serial MRA. Acta Neurochir 155:211–216
Wermer MJ, van der Schaaf IC, Velthuis BK, Algra A, Buskens E, Rinkel GJ, Group AS (2005) Follow-up screening after subarachnoid haemorrhage: frequency and determinants of new aneurysms and enlargement of existing aneurysms. Brain 128:2421–2429
Aishima K, Shimizu T, Aihara M, Yoshimoto Y (2016) Lifetime effects of small unruptured intracranial aneurysms. World Neurosurg 95:434–440
Malhotra A, Wu X, Forman HP, Matouk CC, Gandhi D, Sanelli P (2018) Management of tiny unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a comparative effectiveness analysis. JAMA Neurol 75:27–34
Chmayssani M, Rebeiz JG, Rebeiz TJ, Batjer HH, Bendok BR (2011) Relationship of growth to aneurysm rupture in asymptomatic aneurysms <= 7 mm: a systematic analysis of the literature. Neurosurgery 68:1164–1171 discussion 1171
Juvela S, Poussa K, Lehto H, Porras M (2013) Natural history of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a long-term follow-up study. Stroke 44:2414–2421
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declarations
The authors have no personal, financial, or institutional interest in any of the drugs, materials, or devices described in this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable for this systematic review.
Informed consent
Not applicable for this systematic review.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 39 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K.S., Zhang, J.J.Y., Alalade, A.F. et al. Radiological surveillance of small unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of 8428 aneurysms. Neurosurg Rev 44, 2013–2023 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01420-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01420-1