Abstract
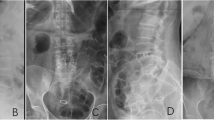
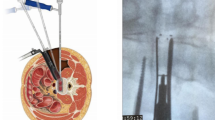
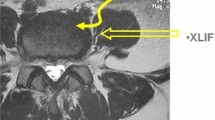
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of OLIF (oblique lumbar interbody fusion) in the treatment of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis with sagittal imbalance. Fifty-nine patients were included in our analysis. Included patients were divided into 2 groups according to the surgical techniques: PLIF (posterior lumbar interbody fusion) (n = 31) and OLIF + PSF (OLIF combined with posterior spinal fixation) (n = 28). Perioperative radiographic parameters, complications, and clinical outcome from each group were assessed and compared. The operation time for both groups was 165.1 min in the OLIF group and 182.1 min in the PLIF group (P < 0.05). The intraoperative blood loss was 190.6 ml in the OLIF group and 356.3 ml in the PLIF group (P < 0.05). The number of intraoperative and postoperative complications for both groups was 7 in the OLIF group and 11 in the PLIF group. Significant clinical improvement was observed in VAS scores and ODI when comparing preoperative evaluation and final follow-up. The preoperative SVA (the distance from the posterosuperior corner of S1body to the C7 plumb line), PI (pelvic incidence), LL (lumbar lordosis), PI-LL mismatch, DH (disc height), and lumbar Cobb angles of both groups were similar. The postoperative and final follow-up SVA, LL, PI-LL mismatch, and disc height were improved in both groups, and a statistical difference was found between both groups (P < 0.05). An improvement of SVA, LL, PI-LL mismatch, and disc height at the OLIF group was better than that found at the PLIF group. An improvement in radiographic and clinical outcomes for the OLIF group was better than that seen for the PLIF group. Then, OLIF had a more curative effect in lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis with sagittal imbalance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold PM, Anderson KK, McGuire RA Jr (2012) The lateral transpsoas approach to the lumbar and thoracic spine: A review. Surg Neurol Int (Suppl 3):S198-S215.
Bae J, Theologis AA, Strom R, Tay B, Burch S, Berven S et al (2018) Comparative analysis of 3 surgical strategies for adult spinal deformity with mild to moderate sagittal imbalance. J Neurosurg Spine 28:40–49
Baghdadi YM, Larson AN, Dekutoski MB, Cui Q, Sebastian AS, Armitage BM et al (2014) Sagittal balance and spinopelvic parameters after lateral lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative scoliosis: a case-control study. Spine 39:E166–E173
Berjano P, Balsano M, Buric J, Petruzzi M, Lamartina C (2012) Direct lateral access lumbar and thoracolumbar fusion: preliminary results. Eur Spine J 21(Suppl 1):S37–S42
Boos N, Marchesi D, Zuber K, Aebi M (1993) Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis by reduction and pedicular fixation. A 4–6-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 18:1655–1661
Cho JY, Goh TS, Son SM, Kim DS, Lee JS (2019) Comparison of anterior approach and posterior approach to instrumented interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis: a meta-analysis. World Neurosurg 129:286–293
Dahdaleh NS, Smith ZA, Snyder LA, Graham RB, Fessler RG, Koski TR (2014) Lateral transpsoas lumbar interbody fusion: outcomes and deformity correction. Neurosurg Clin N Am 25:353–360
Dakwar E, Cardona RF, Smith DA, Uribe JS (2010) Early outcomes and safety of the minimally invasive, lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach for adult degenerative scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus 28(3):E8
Dakwar E, Vale FL, Uribe JS (2011) Trajectory of the main sensory and motor branches of the lumbar plexus outside the psoas muscle related to the lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach. J Neurosurg Spine 14:290–295
Fredrickson BE, Baker D, McHolick WJ, Yuan HA, Lubicky JP (1984) The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66(5):699–707
Freudenberger C, Lindley EM, Beard DW, Reckling WC, Williams A, Burger EL et al (2009) Posterior versus anterior lumbar interbody fusion with anterior tension band plating: retrospective analysis. Orthopedics 32(7):492
Fujibayashi S, Hynes RA, Otsuki B, Kimura H, Takemoto M, Matsuda S (2015) Effect of indirect neural decompression through oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease. Spine 40(3):E175–E182
Goyal N, Wimberley DW, Hyatt A, Zeiller S, Vaccaro AR, Hilibrand AS et al (2009) Radiographic and clinical outcomes after instrumented reduction and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion of mid and high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 22:321–327
Gragnaniello C, Seex K (2016) Anterior to psoas (ATP) fusion of the lumbar spine: evolution of a technique facilitated by changes in equipment. J Spine Surg 2(4):256
Guérin P, Obeid I, Bourghli A, Masquefa T, Luc S, Gille O et al (2012) The lumbosacral plexus: anatomic considerations for minimally invasive retroperitoneal transpsoas approach. Surg Radiol Anat 34:151–157
Hassanzadeh H, Jain A, El Dafrawy MH, Ain MC, Mesfin A, Skolasky RL et al (2013) Three-column osteotomies in the treatment of spinal deformity in adult patients 60 years old and older: outcome and complications. Spine 38:726–731
Isaacs RE, Hyde J, Goodrich JA, Rodgers WB, Phillips FM (2010) A prospective, nonrandomized, multicenter evaluation of extreme lateral interbody fusion for the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis: perioperative outcomes and complications. Spine 35(26 Suppl):S322–S330
Jun S, Hua RZ, Lu TJ, Xiang C, Dong XS (2010) A radiographic assessment of the ability of the extreme lateral interbody fusion procedure to indirectly decompress the neural elements. Spine 35(26 Suppl):S331–S337
Kasliwal MK, Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Saulle D, Lenke LG, Polly DW Jr et al (2012) Short-term complications associated with surgery for high-grade spondylolisthesis in adults and pediatric patients: a report from the Scoliosis Research Society Morbidity and Mortality database. Neurosurgery 71:109–116
Kim KT, Jo DJ, Lee SH, Seo EM (2018) Oblique retroperitoneal approach for lumbar interbody fusion from L1 to S1 in adult spinal deformity. Neurosurg Rev 41(1):355–363
Knight RQ, Schwaegler P, Hanscom D, Roh J (2009) Direct lateral lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative conditions: early complication profile. J Spinal Disord Tech 22:34–37
Kwon BK, Hilibrand AS, Malloy K, Savas PE, Silva MT, Albert TJ et al (2005) A critical analysis of the literature regarding surgical approach and outcome for adult low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(Suppl):S30–S40
Labelle H, Roussouly P, Chopin D, Berthonnaud E, Hresko T, O’Brien M (2008) Spino-pelvic alignment after surgical correction for developmental spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 17:1170–1176
Lafage V, Schwab F, Patel A, Hawkinson N, Farcy JP (2009) Pelvic tilt and truncal inclination: two key radiographic parameters in the setting of adults with spinal deformity. Spine 34:E599–E606
Lin GX, Akbary K, Kotheeranurak V, Quillo-Olvera J, Jo HJ, Yang XW et al (2018) Clinical and radiologic outcomes of direct versus indirect decompression with lumbar interbody fusion: a matched-pair comparison analysis. World Neurosurg 119:e898–e909
Longo UG, Loppini M, Romeo G, Maffulli N, Denaro V (2014) Evidence-based surgical management of spondylolisthesis: reduction or arthrodesis in situ. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96:53–58
Mummaneni PV, Bisson EF, Kerezoudis P, Glassman S, Foley K, Slotkin JR et al (2017) Minimally invasive versus open fusion for grade I degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: analysis of the quality outcomes Database. Neurosurg Focus 43(2):E11
Park P, Foley KT (2008) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with reduction of spondylolisthesis: technique and outcomes after a minimum of 2 years’ follow-up. Neurosurg Focus 25(2):E16
Petraco DM, Spivak JM, Cappadona JG, Kummer FJ, Neuwirth MG (1996) An anatomic evaluation of L5 nerve stretch in spondylolisthesis reduction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 21:1133–1139
Roland M, Fairbank J (2000) The Roland-Morris disability questionnaire and the Oswestry disability questionnaire. Spine 25(24):3115–3124
Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S, Hostin R, Shaffrey CI, Smith JS et al (2013) Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting of adult spinal deformity: a prospective multicenter analysis. Spine 38:E803–E812
Suk S-II, Lee C-K, Kim W-J, Lee J-H, Cho K-J, Kim H-G (1997) Adding posterior lumbar inter-body fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine 22(2):210–220
Tempel ZJ, Gandhoke GS, Bonfield CM, Okonkwo DO, Kanter AS (2014) Radiographic and clinical outcomes following combined lateral lumbar interbody fusion and posterior segmental stabilization in patients with adult degenerative scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus 36(5):E11
Than KD, Wang AC, Rahman SU, Wilson TJ, Valdivia JM, Park P et al (2011) Complication avoidance and management in anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurg Focus 31(4):E6
Vaccaro AR, Kepler CK, Rihn JA, Suzuki H, Ratliff JK, Harrop JS et al (2012) Anatomical relationships of the anterior blood vessels to the lower lumbar intervertebral discs: analysis based on magnetic resonance imaging of patients in the prone position. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94:1088–1094
Wang MY, Cummock MD, Yu Y, Trivedi RA (2010) An analysis of the differences in the acute hospitalization charges following minimally invasive versus open posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine 12:694–699
Wood KB, Devine J, Fischer D, Dettori JR, Janssen M (2010) Vascular injury in elective anterior lumbosacral surgery. Spine 35(9 Suppl):S66–S75
Woods KR, Billys JB, Hynes RA (2017) Technical description of oblique lateral interbody fusion at L1-L5 (OLIF25) and at L5-S1 (OLIF51) and evaluation of complication and fusion rates. Spine J 17(4):545
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine Investigational Review Board (IRB) for the Protection of Human Subjects.
Informed consent
All subjects gave informed consent prior to participation in conformity with procedures approved by the Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine Investigational Review Board (IRB).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, Ms., Seo, EM. Efficacy and radiographic analysis of oblique lumbar interbody fusion in treating lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis with sagittal imbalance. Neurosurg Rev 44, 2181–2189 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01390-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01390-4