Abstract
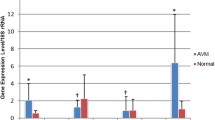
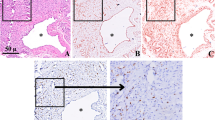
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are congenital abnormal vessels that shunt blood directly from the arterial to the venous system without a capillary bed. The underlying pathology of AVMs is not fully understood. The objective of the study was to determine the association between the expression patterns of tissue factor (TF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in AVMs with clinical and pathological findings. Eighteen cases of sporadic AVM with operative specimens were included in this study. The expression of messenger RNA (mRNA) of TF and IL-6 was assayed, and association with clinical factors was investigated. The distribution of TF and IL-6 was examined with immunofluorescence. The mRNA expression of TF was significantly higher in AVM specimens than in control tissues (P = 0.002) and significantly higher in the symptomatic group than in the asymptomatic group (P = 0.037). The mRNA expression of IL-6 was likewise significantly higher in AVM specimens than in control tissues (P = 0.038). Examination of immunostained sections indicated that TF+ cells were also positive for IL-6 and were distributed around normal endothelial cells and pericytes. Moreover, TF+/IL-6+ cells also expressed CD31, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), and platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFR-beta). These results suggest that TF is elevated in AVMs and that it mediates symptomatic events. IL-6 is associated with the angiogenic activity of TF, and both are present in the same abnormal endothelial cells and pericytes. These factors may have interactive effects and may serve in a prognostic role for AVMs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecassis IJ, DS X, Batjer HH, Bendok BR (2014) Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review. Neurosurg Focus 37:E7. doi:10.3171/2014.6.FOCUS14250
Aberg M, Siegbahn A (2013) Tissue factor non-coagulant signaling—molecular mechanisms and biological consequences with a focus on cell migration and apoptosis. J Thromb Haemost 11:817–825. doi:10.1111/jth.12156
Aki S, Yoshioka K, Okamoto Y, Takuwa N, Takuwa Y (2015) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase class II alpha-isoform PI3K-C2alpha is required for transforming growth factor beta-induced Smad signaling in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 290:6086–6105. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.601484
Al-Shahi Salman R, White PM, Counsell CE, du Plessis J, van Beijnum J, Josephson CB, Wilkinson T, Wedderburn CJ, Chandy Z, St George EJ, Sellar RJ, Warlow CP (2014) Outcome after conservative management or intervention for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations. JAMA 311:1661–1669. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3200
Amin-Hanjani S (2014) ARUBA results are not applicable to all patients with arteriovenous malformation. Stroke 45:1539–1540. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.002696
Aoki Y, Jaffe ES, Chang Y, Jones K, Teruya-Feldstein J, Moore PS, Tosato G (1999) Angiogenesis and hematopoiesis induced by Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded interleukin-6. Blood 93:4034–4043
Arderiu G, Pena E, Aledo R, Badimon L (2012) Tissue factor-Akt signaling triggers microvessel formation. J Thromb Haemost 10:1895–1905. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04848.x
Arderiu G, Pena E, Aledo R, Juan-Babot O, Badimon L (2011) Tissue factor regulates microvessel formation and stabilization by induction of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:2607–2615. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.233536
Bach RR (1988) Initiation of coagulation by tissue factor. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 23:339–368
Bugge TH, Xiao Q, Kombrinck KW, Flick MJ, Holmback K, Danton MJ, Colbert MC, Witte DP, Fujikawa K, Davie EW, Degen JL (1996) Fatal embryonic bleeding events in mice lacking tissue factor, the cell-associated initiator of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:6258–6263
Carmeliet P, Mackman N, Moons L, Luther T, Gressens P, Van Vlaenderen I, Demunck H, Kasper M, Breier G, Evrard P, Muller M, Risau W, Edgington T, Collen D (1996) Role of tissue factor in embryonic blood vessel development. Nature 383:73–75. doi:10.1038/383073a0
Cavalcanti DD, Kalani MY, Martirosyan NL, Eales J, Spetzler RF, Preul MC (2012) Cerebral cavernous malformations: from genes to proteins to disease. J Neurosurg 116:122–132. doi:10.3171/2011.8.jns101241
Chand HS, Ness SA, Kisiel W (2006) Identification of a novel human tissue factor splice variant that is upregulated in tumor cells. Int J Cancer 118:1713–1720. doi:10.1002/ijc.21550
Chen L, Zhao Y, Chen Z, Tee M, Mao Y, LF Z (2009) Multiple dynamic cavernous malformations in a girl: long-term follow-up. Surg Neurol 72:728–732. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2009.04.002
Chen Y, Pawlikowska L, Yao JS, Shen F, Zhai W, Achrol AS, Lawton MT, Kwok PY, Yang GY, Young WL (2006) Interleukin-6 involvement in brain arteriovenous malformations. Ann Neurol 59:72–80. doi:10.1002/ana.20697
Dorfleutner A, Hintermann E, Tarui T, Takada Y, Ruf W (2004) Cross-talk of integrin alpha3beta1 and tissue factor in cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 15:4416–4425. doi:10.1091/mbc.E03-09-0640
Flex A, Gaetani E, Pola R, Santoliquido A, Aloi F, Papaleo P, Dal Lago A, Pola E, Serricchio M, Tondi P, Pola P (2002) The −174 G/C polymorphism of the interleukin-6 gene promoter is associated with peripheral artery occlusive disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 24:264–268
Gaudino M, Andreotti F, Zamparelli R, Di Castelnuovo A, Nasso G, Burzotta F, Iacoviello L, Donati MB, Schiavello R, Maseri A, Possati G (2003) The −174 G/C interleukin-6 polymorphism influences postoperative interleukin-6 levels and postoperative atrial fibrillation. Is atrial fibrillation an inflammatory complication? Circulation 108(Suppl 1):II195–II199. doi:10.1161/01.cir.0000087441.48566.0d
Giannarelli C, Alique M, Rodriguez DT, Yang DK, Jeong D, Calcagno C, Hutter R, Millon A, Kovacic JC, Weber T, Faries PL, Soff GA, Fayad ZA, Hajjar RJ, Fuster V, Badimon JJ (2014) Alternatively spliced tissue factor promotes plaque angiogenesis through the activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor signaling. Circulation 130:1274–1286. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.006614
Haas SL, Jesnowski R, Steiner M, Hummel F, Ringel J, Burstein C, Nizze H, Liebe S, Lohr JM (2006) Expression of tissue factor in pancreatic adenocarcinoma is associated with activation of coagulation. World J Gastroenterol 12:4843–4849
Hobbs JE, Zakarija A, Cundiff DL, Doll JA, Hymen E, Cornwell M, Crawford SE, Liu N, Signaevsky M, Soff GA (2007) Alternatively spliced human tissue factor promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a pancreatic cancer tumor model. Thromb Res 120(Suppl 2):S13–S21
Josephson CB, Bhattacharya JJ, Counsell CE, Papanastassiou V, Ritchie V, Roberts R, Sellar R, Warlow CP, Al-Shahi Salman R (2012) Seizure risk with AVM treatment or conservative management: prospective, population-based study. Neurology 79:500–507
Josephson CB, Sauro K, Wiebe S, Clement F, Jette N (2016) Medical vs invasive therapy in AVM-related epilepsy: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 86:64–71. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000002240
Kofler NM, Cuervo H, MK U, Murtomaki A, Kitajewski J (2015) Combined deficiency of Notch1 and Notch3 causes pericyte dysfunction, models CADASIL, and results in arteriovenous malformations. Sci Rep 5:16449. doi:10.1038/srep16449
Leblanc GG, Golanov E, Awad IA, Young WL (2009) Biology of vascular malformations of the brain. Stroke 40:e694–e702. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.563692
Lee CZ, Young WL (2005) Management of brain arteriovenous malformations. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 18:484–489. doi:10.1097/01.aco.0000182568.47927.f5
Li X, Wang R, Wang X, Xue X, Ran D, Wang S (2013) Relevance of IL-6 and MMP-9 to cerebral arteriovenous malformation and hemorrhage. Mol Med Rep 7:1261–1266. doi:10.3892/mmr.2013.1332
Mackman N (2007) Alternatively spliced tissue factor—one cut too many? Thromb Haemost 97:5–8
Maddaluno L, Rudini N, Cuttano R, Bravi L, Giampietro C, Corada M, Ferrarini L, Orsenigo F, Papa E, Boulday G, Tournier-Lasserve E, Chapon F, Richichi C, Retta SF, Lampugnani MG, Dejana E (2013) EndMT contributes to the onset and progression of cerebral cavernous malformations. Nature 498:492–496. doi:10.1038/nature12207
Mohr JP, Parides MK, Stapf C, Moquete E, Moy CS, Overbey JR, Al-Shahi Salman R, Vicaut E, Young WL, Houdart E, Cordonnier C, Stefani MA, Hartmann A, von Kummer R, Biondi A, Berkefeld J, Klijn CJ, Harkness K, Libman R, Barreau X, Moskowitz AJ (2014) Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): a multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet 383:614–621. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62302-8
Mouchtouris N, Jabbour PM, Starke RM, Hasan DM, Zanaty M, Theofanis T, Ding D, Tjoumakaris SI, Dumont AS, Ghobrial GM, Kung D, Rosenwasser RH, Chalouhi N (2015) Biology of cerebral arteriovenous malformations with a focus on inflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35:167–175. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2014.179
Novakovic RL, Lazzaro MA, Castonguay AC, Zaidat OO (2013) The diagnosis and management of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurol Clin 31:749–763. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2013.03.003
Ott I, Weigand B, Michl R, Seitz I, Sabbari-Erfani N, Neumann FJ, Schomig A (2005) Tissue factor cytoplasmic domain stimulates migration by activation of the GTPase Rac1 and the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. Circulation 111:349–355
Rangel-Castilla L, Russin JJ, Martinez-Del-Campo E, Soriano-Baron H, Spetzler RF, Nakaji P (2014) Molecular and cellular biology of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a review of current concepts and future trends in treatment. Neurosurg Focus 37:E1. doi:10.3171/2014.7.FOCUS14214
Ruf W, Dorfleutner A, Riewald M (2003) Specificity of coagulation factor signaling. J Thromb Haemost 1:1495–1503
Schmidt A, Brixius K, Bloch W (2007) Endothelial precursor cell migration during vasculogenesis. Circ Res 101:125–136. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.148932
Schulz GB, Wieland E, Wustehube-Lausch J, Boulday G, Moll I, Tournier-Lasserve E, Fischer A (2015) Cerebral cavernous malformation-1 protein controls DLL4-Notch3 signaling between the endothelium and pericytes. Stroke 46:1337–1343. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007512
Sure U, Butz N, Schlegel J, Siegel AM, Wakat JP, Mennel HD, Bien S, Bertalanffy H (2001) Endothelial proliferation, neoangiogenesis, and potential de novo generation of cerebrovascular malformations. J Neurosurg 94:972–977. doi:10.3171/jns.2001.94.6.0972
Tian H, Mythreye K, Golzio C, Katsanis N, Blobe GC (2012) Endoglin mediates fibronectin/alpha5beta1 integrin and TGF-beta pathway crosstalk in endothelial cells. EMBO J 31:3885–3900. doi:10.1038/emboj.2012.246
Toomey JR, Kratzer KE, Lasky NM, Stanton JJ, GJ B Jr (1996) Targeted disruption of the murine tissue factor gene results in embryonic lethality. Blood 88:1583–1587
van den Berg YW, van den Hengel LG, Myers HR, Ayachi O, Jordanova E, Ruf W, Spek CA, Reitsma PH, Bogdanov VY, Versteeg HH (2009) Alternatively spliced tissue factor induces angiogenesis through integrin ligation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:19497–19502. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905325106
Whitehead KJ, Smith MC, Li DY (2013) Arteriovenous malformations and other vascular malformation syndromes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3:a006635. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a006635
Yasuda M, Okada E, Nagai Y, Tamura A, Ishikawa O (2010) Reactive proliferation of endothelial cells and pericytes associated with arteriovenous malformation. J Dermatol 37:363–366. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2010.00788.x
Yoshioka K, Yoshida K, Cui H, Wakayama T, Takuwa N, Okamoto Y, Du W, Qi X, Asanuma K, Sugihara K, Aki S, Miyazawa H, Biswas K, Nagakura C, Ueno M, Iseki S, Schwartz RJ, Okamoto H, Sasaki T, Matsui O, Asano M, Adams RH, Takakura N, Takuwa Y (2012) Endothelial PI3K-C2alpha, a class II PI3K, has an essential role in angiogenesis and vascular barrier function. Nat Med 18:1560–1569. doi:10.1038/nm.2928
Zhou F, Xue M, Qin D, Zhu X, Wang C, Zhu J, Hao T, Cheng L, Chen X, Bai Z, Feng N, Gao SJ, Lu C (2013) HIV-1 Tat promotes Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) vIL-6-induced angiogenesis and tumorigenesis by regulating PI3K/PTEN/AKT/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. PLoS One 8:e53145. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053145
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This work was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI grant number 25462226 (to O.H.) as well as the RR&D Service of Department of Veterans Affairs (B7335R, B9260L), the NMSS [RG2135], and the CT Stem Cell Research Program (12-SCB-Yale-05).
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of Sapporo Medical University Hospital, and all subjects signed informed consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noshiro, S., Mikami, T., Kataoka-Sasaki, Y. et al. Biological relevance of tissue factor and IL-6 in arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurg Rev 40, 359–367 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0780-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0780-1