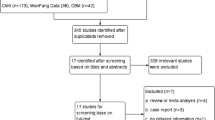
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to present a meta-analysis on the safety and efficacy of different endovascular modalities when treating vertebral artery dissections, since ideal treatment remains controversial. We performed a meta-analysis of 39 retrospective studies involving different treatment modalities for vertebral artery dissections in adults and obtained weighted pooled proportional outcome and mortality ratios with a random effects model. Overall, 75.11 % (confidence interval (CI) 68.89–80.84, I 2 66.89 %) had excellent outcomes, 10.10 % (CI 6.83–15.56, I 2 65.64 %) had good outcomes, and 13.70 % (CI 9.64–18.35, I 2 60.33 %) had poor outcomes. Postoperative complications occurred in 10.52 % (CI 6.87–14.84, I 2 62.48 %), with 2.73 % (CI 1.64–4.10, I 2 0.0 %) exhibiting vasospasm, 3.03 % (CI 1.88–4.46, I 2 0.0 %) experiencing postoperative rebleeding, and 6.31 % (CI 3.57–9.76, I 2 60.92 %) showing ischemia. Overall mortality was 8.69 % (CI 6.13–11.64, I 2 33.76 %). When compared to these overall ratios, different treatment modality subgroups did not differ significantly, except for the proximal occlusion group, with poor outcome ratio = 26.96 % (difference 13.26, CI 0.02–30.04, p = 0.0403) and mortality ratio = 21.36 % (difference 12.67, CI 0.94–28.86, p = 0.0189). Different endovascular treatment modalities are comparatively safe and effective in the management of vertebral artery dissection. Their reduced operative time, minimal invasiveness, and overall safety render them a suitable option for intervention-amenable dissections.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn J, Chung S, Lee B, Kim S, Yoon P, Joo J et al (2005) Treatment of spontaneous arterial dissections with stent placement for preservation of the parent artery. Acta Neurochir 147:265–273
Ahn J, Han I, Kim T, Yoon P, Lee Y, Lee B et al (2006) Endovascular treatment of intracranial vertebral artery dissections with stent placement or stent-assisted coiling. AJNR 27:1514–1521
Albuquerque F, Fiorella D, Han P, Deshmukh V, Kim L, McDougall C (2005) Endovascular management of intracranial vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. Neurosurg Focus 18:E3
Ali M, Amenta P, Starke R, Jabbour P, Gonzalez L, Tjoumakaris S et al (2012) Intracranial vertebral artery dissections: evolving perspectives. Interv Neuroradiol 18:469–483
Ansari S, Thompson B, Gemmete J, Gandhi D (2008) Endovascular treatment of distal cervical and intracranial dissections with the neuroform stent. Neurosurgery 62:636–646
Anxionnat R, Ferreira de Melo-Neto J, Bracard S, Lacour J, Pinelli C, Civit T et al (2003) Treatment of hemorrhagic intracranial dissections. Neurosurgery 53:289–301
Brandt T, Morcher M, Hausser I (2005) Association of cervical artery dissection with connective tissue abnormalities in skin and arteries. Front Neurol Neurosci 20:16–29
Brandt T, Orberk E, Weber R, Werner I, Busse O, Müller B et al (2001) Pathogenesis of cervical artery dissections: association with connective tissue abnormalities. Neurology 57:24–30
Brott T, Halperin J, Abbara S, Bacharach J, Barr J, Bush R et al (2011) 2011 ASA/ACCF/AHA/AAN/AANS/ACR/ASNR/CNS/SAIP/SCAI/SIR/SNIS/SVM/SVS guideline on the management of patients with extracranial carotid and vertebral artery disease: executive summary. J Neuro Interv Surg 3:100–130
Chandra A, Suliman A, Angle N (2007) Spontaneous dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries: the 10-year UCSD Experience. Ann Vasc Surg 21:178–185
Endo H, Matsumoto Y, Kondo R, Sato K, Fujimura M, Inoue T et al (2013) Medullary infarction as a poor prognostic factor after internal coil trapping of a ruptured vertebral artery dissection. J Neurosurg 118:131–139
Flis C, Jäger H, Sidhu P (2007) Carotid and vertebral artery dissections: clinical aspects, imaging features and endovascular treatment. Eur Radiol 17:820–834
Fusco M, Harrigan M (2007) Cerebrovascular dissections—a review. Part I: spontaneous dissections. Neurosurgery 68:242–257
Gui L, Shi G, Li G, Fan W, Huang H, Zhou Z et al (2010) Spontaneous vertebral artery dissection: report of 16 cases. Neurol India 58:869–874
Halbach V, Higashida R, Dowd C, Fraser K, Smith T, Teitelbaum G et al (1993) Endovascular treatment of vertebral artery dissections and pseudoaneurysms. J Neurosurg 79:183–191
Hamada J, Kai Y, Morioka M, Yano S, Todaka T, Ushio Y (2003) Multimodal treatment of ruptured dissecting aneurysms of the vertebral artery during the acute stage. J Neurosurg 99:960–966
Hassan A, Zacharatos H, Souslian F, Suri M, Qureshi A (2012) Long-term clinical and angiographic outcomes in patients with cervico-cranial dissections treated with stent placement: a meta-analysis of case series. J Neurotrauma 29:1342–1353
Huang Y, Chen Y, Wang Y, Tu Y, Jeng J, Liu H (2009) Cervicocranial arterial dissection: experience of 73 patients in a single center. Surg Neurol S2:20–27
Iihara K, Sakai N, Murao K, Sakai H, Higashi T, Kogure S et al (2002) Dissecting aneurysms of the vertebral artery: a management strategy. J Neurosurg 97:259–267
Jin S, Kwon D, Choi C, Ahn J, Kwun B (2009) Endovascular strategies for vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms. AJNR 30:1518–1524
Joo J, Ahn J, Chung Y, Han I, Chung S, Yoon P et al (2005) Treatment of intra- and extracranial arterial dissections using stents and embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28:595–602
Kai Y, Hamada J, Morioka M, Ohmori Y, Watanabe M, Hirano T et al (2012) Dissecting aneurysms of the vertebral artery—angiographic patterns at the dissecting site on balloon test occlusion. Neuroradiology 5:857–862
Kai Y, Hamada J, Morioka M, Todaka T, Mizuno T, Ushio Y (2003) Endovascular coil trapping for ruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms by using double microcatheters technique in the acute stage. Acta Neurochir 145:447–451
Kashiwazaki D, Ushikoshi S, Asano T, Kuroda S, Houkin K (2013) Long-term clinical and radiological results of endovascular internal trapping in vertebral artery dissection. Neuroradiology 55:201–206
Kim B, Kim S, Kim D, Shin Y, Suh S, Kim D et al (2011) Outcomes and prognostic factors of intracranial unruptured vertebrobasilar artery dissection. Neurology 76:1735–1741
Kim C, Son Y, Paek S, Han M, Kim J, Chung Y et al (2006) Clinical analysis of vertebrobasilar dissection. Acta Neurochir 148:395–404
Kocaeli H, Chaalala C, Andaluz N, Zuccarello M (2009) Spontaneous intradural vertebral artery dissection: a single-center experience and review of the literature. Skull Base 19:209–218
Kudo T, Iihara K, Satow T, Murao K, Miyamoto S (2007) Incidence of ischemic complications after endovascular treatment for ruptured dissecting vertebral artery aneurysms. Interv Neuroradiol 13:157–162
Kurata A, Yamada M, Ohmomo T, Hirayama H, Suzuki S, Miyasaka Y et al (2001) The efficacy of coil embolization at the dissection site of ruptured dissecting vertebral artery aneurysms. Interv Neuroradiol 7:73–82
Lee J, Kim T, Joo S, Yoon W, Choi H (2010) Endovascular treatment of ruptured dissecting vertebral artery aneurysms—long-term follow-up results, benefits of early embolization and predictors of outcome. Acta Neurochir 152:1455–1465
Lee Y, Ahn J, Han I, Chung Y, Hong C, Joo J (2007) Therapeutic endovascular treatments for traumatic vertebral artery injuries. J Trauma 62:886–891
Luo C, Chang C, Teng M, Chang F (2005) Endovascular treatment of ruptured vertebral dissecting aneurysms with electrodetachable coils. J Chin Med Assoc 68:578–584
Lv X, Jiang C, Li Y, Wu Z (2010) Clinical outcomes of ruptured and unruptured vertebral artery-posterior inferior cerebellar artery complex dissecting aneurysms after endovascular embolization. AJNR 31:1232–1236
Lylyk P, Cohen J, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Miranda C (2001) Combined endovascular treatment of dissecting vertebral artery aneurysms by using stents and coils. J Neurosurg 94:427–432
Malek A, Halbach V, Phatouros C, Meyers P, Dowd C, Higashida R (2000) Endovascular treatment of a ruptured intracranial dissecting vertebral aneurysm in a kickboxer. J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care 48
Manabe H, Hatayama T, Hasegawa S, Islam S, Suzuki S (2000) Coil embolisation for ruptured vertebral artery dissection distal to the origin of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Neuroradiology 42:384–387
Mangiafico S, Padolecchia R, Cellerini M, Puglioli M, Villa G, Nistri M (2003) Rebleeding and ischemia after acute endovascular treatment of ruptured dissecting subarachnoid vertebral artery aneurysms. Interv Neuroradiol 9:205–212
Mas J, Bousser M, Hasboun D, Laplane D (1987) Extracranial vertebral artery dissections: a review of 13 cases. Stroke 18:1037–1047
Mokri B, Houser O, Sandok B, Piepgras D (1988) Spontaneous dissections of the vertebral arteries. Neurology 38:880–885
Naito I, Iwai T, Sasaki T (2002) Management of intracranial vertebral artery dissections initially presenting without subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 51:930–938
Naito I, Takatama S, Shimaguchi H, Iwai T (2004) Endovascular treatment of vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms using stents. Interv Neuroradiol 10:181–186
Park K, Park J, Hwang S, Im S, Shin W, Kim B (2008) Vertebral artery dissection: natural history, clinical features and therapeutic considerations. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 44:109–115
Peluso J, van Rooij W, Sluzewski M, Beute G, Majoie C (2008) Endovascular treatment of symptomatic intradural vertebral dissecting aneurysms. AJNR 29:102–107
Pham M, Rahme R, Arnaout O, Hurley M, Bernstein R, Batjer H et al (2011) Endovascular stenting of extracranial carotid and vertebral artery dissections: a systematic review of the literature. Neurosurgery 68:856–866
Purkayastha S, Gupta K, Krishnamoorthy T, Bodhey N (2006) Endovascular treatment of ruptured posterior circulation dissecting aneurysms. J Neuroradiol 33:329–337
Rabinov J, Hellinger F, Morris P, Ogilvy C, Putman C (2003) Endovascular management of vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms. AJNR 24:1421–1428
Ramgren B, Cronqvist M, Romner B, Brandr L, Holtas S, Larsson E (2005) Vertebrobasilar dissection with subarachnoid hemorrhage: a retrospective study of 29 patients. Neuroradiology 47:97–104
Rubinstein S, Peerdeman S, van Tulder M, Riphagen I, Haldeman S (2005) A systematic review of the risk factors for cervical artery dissection. Stroke 36:1575–1580
Santos-Franco J, Zenteno M, Lee A (2008) Dissecting aneurysms of the vertebrobasilar system. A comprehensive review on natural history and treatment options. Neurosurg Rev 31:131–140
Sasaki O, Ogawa H, Koike T, Koizumi T, Tanaka R (1991) A clinicopathological study of dissecting aneurysms of the intracranial vertebral artery. J Neurosurg 75:874–882
Schievink W, Wijdicks E, Michels V (1998) Heritable connective tissue disorders in cervical artery dissections: a prospective study. Neurology 50:1166
Shah Q, Messé S (2007) Cervicocranial arterial dissection. Curr Treat Options Neurol 9:55–62
Shin Y, Kim B, Kim S, Suh S, Ryu C, Koh J et al (2012) Endovascular treatment of bilateral intracranial vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms presenting with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 70:ons75–ons81
Su W, Gou S, Ni S, Li G, Liu Y, Zhu S et al (2011) Management of ruptured and unruptured intracranial vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. J Clin Neurosci 18:1639–1644
Sugiu K, Tokunaga K, Watanabe K, Sasahara W, Ono S, Tamiya T et al (2005) Emergent endovascular treatment of ruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. Neuroradiology 47:158–164
Taha M, Sakaida H, Asakura F, Maeda M, Toma N, Yamamoto A et al (2010) Endovascular management of vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms: review of 25 patients. Turk Neurosurg 20:126–135
Thanvi B, Munshi S, Dawson S, Robinson T (2005) Carotid and vertebral artery dissection syndromes. Postgrad Med J 81:383–388
Touzé E, Randoux B, Méary E, Arquizan C, Meder J, Mas J (2001) Aneurysmal forms of cervical artery dissection. Stroke 32:418–423
Tsukahara T, Wada H, Satake K, Yaoita H, Takahashi A (1995) Proximal balloon occlusion for dissecting vertebral aneurysms accompanied by subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 36:914–920
Xu R, Liu W, Li J, Liu X, Hao D, Zhang T (2013) Endovascular intervention of intradural hemorrhage from ruptured spontaneous vertebral artery dissection. Neurosciences 18:46–51
Yamaura I, Tani E, Yokota M, Nakano A, Fukami M, Kaba K et al (1999) Endovascular treatment of ruptured dissecting aneurysms aimed at occlusion of the dissected site by using Gugliemi detachable coils. J Neurosurg 90:853–856
Yasui T, Komiyama M, Nishikawa M, Nakajima H (2000) Subarachnoid hemorrhage from vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms involving the origin of the posteroinferior cerebellar artery: report of two cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 46:196
Yoon W, Seo J, Kim T, Do H, Jayaraman M, Marks M (2007) Dissection of the V4 segment of the vertebral artery: clinicoradiologic manifestations and endovascular treatment. Eur Radiol 17:983–993
Yoshimoto Y, Wakai S (1997) Unruptured intracranial vertebral artery dissection. Stroke 28:370–374
Youl B, Coutellier A, Dubois B, Leger J, Bousser M (1990) Three cases of spontaneous extracranial vertebral artery dissection. Stroke 21:618–625
Zhao W, Krings T, Alvarez H, Ozanne A, Holmin S, Lasjaunias P (2007) Management of spontaneous haemorrhagic intracranial vertebrobasilar dissection: review of 21 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir 149:585–596
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comments
Takuma Wakai and Hiroyuki Kinouchi, Yamanashi, Japan
The authors described the results of a meta-analysis on 39 studies regarding endovascular treatments for 637 patients with vertebral artery (VA) dissection and showed the efficacy and safety of these modalities. This paper is suggestive and has clinical relevance since the number of cases has been increased by the introduction of magnetic resonance imaging into a diagnostic tool in acute stroke and also endovascular treatment has been considered as an alternative therapy to open surgery in VA dissection especially in cases with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
This study provided detailed clinical outcomes and angiographic results in VA dissections treated by different endovascular techniques, including stenting, stent-assisted coiling, parent vessel occlusion by means of coiling or balloons, balloon-assisted coiling, and proximal occlusion. The majority of the lesions had an intracranial location, and the most common clinical presentation was SAH followed by ischemia and other symptoms. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery involvement was seen in about 15 %. This paper showed the superiority of endovascular treatments in VA dissections; however, only proximal occlusion could not achieve good clinical outcome and angiographic improvement compared to other treatments. Proximal occlusion was more likely to be applied to SAH patients, and as pointed out, this has been performed in technically complex lesions such as those involving branches or difficult to treat with coils or balloons. It has been known that the cure of VA dissention would be to eradicate the lesion from the arterial bloodstream by trapping with or without bypass. Therefore, proximal occlusion cannot preclude the dissection from being reruptured or regrown [1]. Recently, the pipeline embolization device was introduced as the flow-diverting device intended to exclude the aneurysm hemodynamically from the parent artery preserving blood flow through covered arterial branches [2–3]. This new device might achieve higher curability with less ischemic complications for the lesion involving branches. The reduced operative time, minimal invasiveness, and overall safety render endovascular treatment a suitable option for intervention-amenable dissections.
Meanwhile, unruptured VA dissections usually have a benign nature [4] and have a tendency to be treated with conservative therapy. This paper did not show any evidence revealing endovascular treatment is superior to conservative treatment. Further study is necessary to determine the suitable management for unruptured VA dissection.
References
1. Rabinov JD, Hellinger FR, Morris PP, Ogilvy CS, Putman CM (2003) Endovascular management of vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 24:1421–1428
2. Yeung TW, Lai V, Lau HY, Poon WL, Tan CB, Wong YC (2012) Long-term outcome of endovascular reconstruction with the pipeline embolization device in the management of unruptured dissecting aneurysms of the intracranial vertebral artery. J Neurosurg. 116:882–887
3. Cruz JP, O’Kelly C, Kelly M, Wong JH, Alshaya W, Martin A, et al (2013) Pipeline embolization device in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 34:271–276
4. Yoshimoto Y, Wakai S. (1997) Unruptured intracranial vertebral artery dissection. Clinical course and serial radiographic imagings. Stroke 28:370–374
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández-Durán, S., Ogilvy, C.S. Clinical outcomes of patients with vertebral artery dissection treated endovascularly: a meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 37, 569–577 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-014-0541-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-014-0541-y