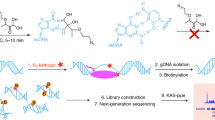
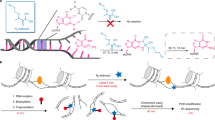
Abstract
Transcription initiates the formation of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) regions within the genome, delineating transcription bubbles, a highly dynamic genomic process. Kethoxal-assisted single-stranded DNA sequencing (KAS-seq) utilizing N3-kethoxal has emerged as a potent tool for mapping specific guanine positions in ssDNA on a genome-wide scale. However, the original KAS-seq method required the costly Accel-NGS Methyl-seq DNA library kit. This study introduces an optimized iteration of the KAS-seq technique, referred to as adapter-tagged KAS-seq (atKAS-seq), incorporating an adapter tagging strategy. This modification involves integrating sequencing adapters via complementary strand synthesis using random N9 tagging. Additionally, by harnessing the potential of ascorbic acid (ASC), recognized for inducing global epigenetic changes, we employed the atKAS-seq methodology to elucidate critical pathways influenced by short-term, high-dose ASC treatment. Our findings underscore that atKAS-seq enables rapid and precise analyses of transcription dynamics and enhancer activities concurrently. This method offers a streamlined, cost-efficient, and low-input approach, affirming its utility in probing intricate genomic regulatory mechanisms.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper and/or the Supplementary Materials. All sequencing data generated in publication have been deposited in NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and are accessible through GEO Series accession number: GSE237843 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE237843).
References
Bensberg M, Rundquist O, Selimovic A, Lagerwall C, Benson M, Gustafsson M, Vogt H, Lentini A, Nestor CE (2021) TET2 as a tumor suppressor and therapeutic target in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2110758118
Blaschke K, Ebata KT, Karimi MM, Zepeda-Martínez JA, Goyal P, Mahapatra S, Tam A, Laird DJ, Hirst M, Rao A, Lorincz MC, Ramalho-Santos M (2013) Vitamin C induces Tet-dependent DNA demethylation and a blastocyst-like state in ES cells. Nature 500:222–226. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12362
Broemer M, Meier P (2009) Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 19:130–140
Carlson MFS, Pages H, Li N (2013) org. hs. eg. db: Genome wide annotation for human. R package version 3.3. https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/data/annotation/html/org.Hs.eg.db.html
Core LJ, Waterfall JJ, Lis JT (2008) Nascent RNA sequencing reveals widespread pausing and divergent initiation at human promoters. Science 322:1845–1848. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1162228
Ewels P, Magnusson M, Lundin S, Käller M (2016) MultiQC: summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 32:3047–3048. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw354
Fattahi F, Saeednejad Zanjani L, Habibi Shams Z, Kiani J, Mehrazma M, Najafi M, Madjd Z (2021) High expression of DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 (DDIT4) is associated with advanced pathological features in the patients with colorectal cancer. Sci Rep 11:13626. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92720-z
Feng J, Liu T, Qin B, Zhang Y, Liu XS (2012) Identifying ChIP-seq enrichment using MACS. Nat Protoc 7:1728–1740. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.101
Gene Ontology (2015) Gene Ontology Consortium: going forward. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D1049-1056. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1179
He YF, Li BZ, Li Z, Liu P, Wang Y, Tang Q, Ding J, Jia Y, Chen Z, Li L, Sun Y, Li X, Dai Q, Song CX, Zhang K, He C, Xu GL (2011) Tet-mediated formation of 5-carboxylcytosine and its excision by TDG in mammalian DNA. Science 333:1303–1307. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1210944
He W, Yin X, Xu C, Liu X, Huang Y, Yang C, Xu Y, Hu L (2023) Ascorbic Acid Reprograms Epigenome and Epitranscriptome by Reducing Fe(III) in the Catalytic Cycle of Dioxygenases. ACS Chem Biol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.3c00567
Ito S, Shen L, Dai Q, Wu SC, Collins LB, Swenberg JA, He C, Zhang Y (2011) Tet proteins can convert 5-methylcytosine to 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine. Science 333:1300–1303. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1210597
Jiang S (2020) Tet2 at the interface between cancer and immunity. Commun Biol 3:667. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01391-5
Karolchik D, Hinrichs AS, Kent WJ (2012) The UCSC Genome Browser. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics Chapter 1:1.4.1–1.4.33. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi0104s40
Klose RJ, Kallin EM, Zhang Y (2006) JmjC-domain-containing proteins and histone demethylation. Nat Rev Genet 7:715–727. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1945
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R (2009) The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li W, Zhang T, Sun M, Shi Y, Zhang XJ, Xu GL, Ding J (2021) Molecular mechanism for vitamin C-derived C(5)-glyceryl-methylcytosine DNA modification catalyzed by algal TET homologue CMD1. Nat Commun 12:744. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21061-2
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Lyu R, Wu T, Zhu AC, West-Szymanski DC, Weng X, Chen M, He C (2022) KAS-seq: genome-wide sequencing of single-stranded DNA by N(3)-kethoxal-assisted labeling. Nat Protoc 17:402–420. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-021-00647-6
Lyu R, Wu T, Park G, He YY, Chen MJ, He C (2023) KAS-analyzer: a novel computational framework for exploring KAS-seq data. Bioinform Adv 3. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioadv/vbad121
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. Embnet J 17:10–12
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA (2010) The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.107524.110
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono H, Kanehisa M (1999) KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 27:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/27.1.29
Park WH, Kim SH (2012) MG132, a proteasome inhibitor, induces human pulmonary fibroblast cell death via increasing ROS levels and GSH depletion. Oncol Rep 27:1284–1291. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2012.1642
Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2010) BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26:841–842. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033
Ramírez F, Dündar F, Diehl S, Grüning BA, Manke T (2014) deepTools: a flexible platform for exploring deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W187-191. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku365
Tahiliani M, Koh KP, Shen Y, Pastor WA, Bandukwala H, Brudno Y, Agarwal S, Iyer LM, Liu DR, Aravind L, Rao A (2009) Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science 324:930–935. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1170116
Thaler R, Khani F, Sturmlechner I, Dehghani SS, Denbeigh JM, Zhou X, Pichurin O, Dudakovic A, Jerez SS, Zhong J, Lee JH, Natarajan R, Kalajzic I, Jiang YH, Deyle DR, Paschalis EP, Misof BM, Ordog T, van Wijnen AJ (2022) Vitamin C epigenetically controls osteogenesis and bone mineralization. Nat Commun 13:5883. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32915-8
Wagner GP, Kin K, Lynch VJ (2012) Measurement of mRNA abundance using RNA-seq data: RPKM measure is inconsistent among samples. Theory Biosci 131:281–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-012-0162-3
Wingett SW, Andrews S (2018) FastQ screen: a tool for multi-genome mapping and quality control. F1000Res 7:1338. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.15931.2
Wu T, Lyu R, You Q, He C (2020) Kethoxal-assisted single-stranded DNA sequencing captures global transcription dynamics and enhancer activity in situ. Nat Methods 17:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-0797-9
Wu T, Lyu R, He C (2022) spKAS-seq reveals R-loop dynamics using low-input materials by detecting single-stranded DNA with strand specificity. Sci Adv 8:eabq2166. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abq2166
Xue JH, Chen GD, Hao F, Chen H, Fang Z, Chen FF, Pang B, Yang QL, Wei X, Fan QQ, Xin C, Zhao J, Deng X, Wang BA, Zhang XJ, Chu Y, Tang H, Yin H, Ma W, Chen L, Ding J, Weinhold E, Kohli RM, Liu W, Zhu ZJ, Huang K, Tang H, Xu GL (2019) A vitamin-C-derived DNA modification catalysed by an algal TET homologue. Nature 569:581–585. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1160-0
Yin R, Mao SQ, Zhao B, Chong Z, Yang Y, Zhao C, Zhang D, Huang H, Gao J, Li Z, Jiao Y, Li C, Liu S, Wu D, Gu W, Yang YG, Xu GL, Wang H (2013) Ascorbic acid enhances Tet-mediated 5-methylcytosine oxidation and promotes DNA demethylation in mammals. J Am Chem Soc 135:10396–10403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja4028346
Young JI, Züchner S, Wang G (2015) Regulation of the Epigenome by Vitamin C. Annu Rev Nutr 35:545–564. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071714-034228
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16:284–287. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Acknowledgements
The authors extend sincere gratitude to Dr. Ruitu Lyu from the University of Chicago for invaluable guidance and instructions in data analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFA1100400) and from Natural science foundation of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (21ZR1480300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X. L. conducted the analysis of high-throughput sequencing data, generated the figures, and drafted the manuscript. W. H. conducted the experimental work. L. H. conceived and supervised the project, contributing significantly to manuscript writing, with input and contributions from all authors. All authors have reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., He, W. & Hu, L. Exploring transient global transcriptional changes induced by ascorbic acid revealed via atKAS-seq profiling. Funct Integr Genomics 24, 66 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-024-01349-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-024-01349-4