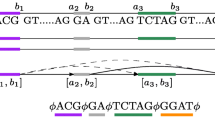
Abstract
Background: Although the events associated with alternative splicing (AS), alternative polyadenylation (APA) and alternative transcription initiation (ATI) can be identified by many approaches based on isoform sequencing (Iso-Seq), these analyses are generally independent of each other and the links between these events are still rarely mentioned. However, an interdependency analysis can be achieved because the transcriptional start site, splice sites and polyA site could be simultaneously included in a long, full-length read from Iso-Seq. Results: We create ASAPA pipeline that enables streamlined analysis for a robust detection of potential links among AS, ATI and APA using Iso-Seq data. We tested this pipeline using Arabidopsis data and found some interesting results: some adjacent introns tend to be simultaneously spliced or retained; coupling between AS and ATI or APA is limited to the initial or terminal intron; and ATI and APA are potentially linked in some special cases. Conclusion: Our pipeline enables streamlined analysis for a robust detection of potential links among AS, ATI and APA using Iso-Seq data, which is conducive to a better understanding of transcription landscape generation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdel-Ghany SE, Hamilton M, Jacobi JL, Ngam P, Devitt N, Schilkey F, Ben-Hur A, Reddy ASN (2016) A survey of the sorghum transcriptome using single-molecule long reads. Nat Commun 7. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11706
Anvar SY, Allard G, Tseng E, Sheynkman GM, de Klerk E, Vermaat M, Yin RH, Johansson HE, Ariyurek Y, den Dunnen JT, Turner SW, ‘t Hoen PAC (2018) Full-length mRNA sequencing uncovers a widespread coupling between transcription initiation and mRNA processing. Genome Biol 19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1418-0
Ardui S, Ameur A, Vermeesch JR, Hestand MS (2018) Single molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing comes of age: applications and utilities for medical diagnostics. Nucleic Acids Res 46:2159–2168. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky066
Au KF, Sebastiano V, Afshar PT, Durruthy JD, Lee L, Williams BA, H van Bakel, Schadt EE, Reijo-Pera RA, Underwood JG, Wong WH (2013) Characterization of the human ESC transcriptome by hybrid sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1320101110
Barash Y, Calarco JA, Gao W, Pan Q, Wang X, Shai O, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ (2010) Deciphering the splicing code. Nature 465:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09000
Bentley DL (2014) Coupling mRNA processing with transcription in time and space. Nat Rev Genet 15:163–175. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3662
Braunschweig U, Barbosa-Morais NL, Pan Q, Nachman EN, Alipanahi B, Gonatopoulos-Pournatzis T, Frey B, Irimia M, Blencowe BJ (2014) Widespread intron retention in mammals functionally tunes transcriptomes. Genome Res 24:1774–1786. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.177790.114
Chowdhury HA, Bhattacharyya DK, Kalita JK (2018) Differential expression analysis of RNA-seq reads: overview, taxonomy and tools. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcbb.2018.2873010
Dvinge H, Bradley RK (2015) Widespread intron retention diversifies most cancer transcriptomes. Genome Med 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-015-0168-9
Foissac S, Sammeth M (2007) ASTALAVISTA: dynamic and flexible analysis of alternative splicing events in custom gene datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W297–W299. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm311
Gao Y, Wang H, Zhang H, Wang Y, Chen J, Gu L, Hancock J (2018) PRAPI: post-transcriptional regulation analysis pipeline for Iso-Seq. Bioinformatics 34:1580–1582. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx830
Hilgers V (2015) Alternative polyadenylation coupled to transcription initiation: insights from ELAV-mediated 3′ UTR extension. RNA Biol 12:918–921. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1060393
Hsin J-P, Manley JL (2012) The RNA polymerase II CTD coordinates transcription and RNA processing. Genes Dev 26:2119–2137. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.200303.112
Jin Z, Lv X, Sun Y, Fan Z, Xiang G, Yao Y (2021) Comprehensive discovery of salt-responsive alternative splicing events based on Iso-Seq and RNA-seq in grapevine roots. Environmental and experimental botany 192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104645
Li H, Birol I (2018) Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 34:3094–3100. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty191
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R (2009) The sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Middleton R, Gao D, Thomas A, Singh B, Au A, Wong JJL, Bomane A, Cosson B, Eyras E, Rasko JEJ, Ritchie W (2017) IRFinder: assessing the impact of intron retention on mammalian gene expression. Genome Biol 18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1184-4
Movassat M, Crabb TL, Busch A, Yao C, Reynolds DJ, Shi Y, Hertel KJ (2016) Coupling between alternative polyadenylation and alternative splicing is limited to terminal introns. RNA Biol 13:646–655. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1191727
Pimentel H, Parra M, Gee SL, Mohandas N, Pachter L, Conboy JG (2016) A dynamic intron retention program enriched in RNA processing genes regulates gene expression during terminal erythropoiesis. Nucleic Acids Res 44:838–851. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1168
Rigo F, Martinson HG (2008) Functional coupling of last-intron splicing and 3’-end processing to transcription in vitro: the poly(A) signal couples to splicing before committing to cleavage. Mol Cell Biol 28:849–862. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01410-07
Steijger T, Abril JF, Engström PG, Kokocinski F, Hubbard TJ, Guigó R, Harrow J, Bertone P (2013) Assessment of transcript reconstruction methods for RNA-seq. Nat Methods 10:1177–1184. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2714
Thorvaldsdottir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP (2013) Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform 14:178–192. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbs017
Trincado JL, Entizne JC, Hysenaj G, Singh B, Skalic M, Elliott DJ, Eyras E (2018) SUPPA2: fast, accurate, and uncertainty-aware differential splicing analysis across multiple conditions. Genome Biol 19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1417-1
Ule J, Blencowe BJ (2019) Alternative Splicing Regulatory networks: functions, mechanisms, and evolution. Mol Cell 76:329–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.017
Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Zhang L, Mayr C, Kingsmore SF, Schroth GP, Burge CB (2008) Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 456:470–476. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07509
Wong JJL, Schmitz U (2022) Intron retention: importance, challenges, and opportunities. Trends Genet 38:789–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2022.03.017
Zhang R, Kuo R, Coulter M, Calixto CPG, Entizne JC, Guo W, Marquez Y, Milne L, Riegler S, Matsui A, Tanaka M, Harvey S, Gao Y, Wießner-Kroh T, Paniagua A, Crespi M, Denby K, Hur Ab, Huq E, Jantsch M, Jarmolowski A, Koester T, Laubinger S, Li QQ, Gu L, Seki M, Staiger D, Sunkar R, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Tu S-L, Wachter A, Waugh R, Xiong L, Zhang X-N, Conesa A, Reddy ASN, Barta A, Kalyna M, Brown JWS (2022) A high-resolution single-molecule sequencing-based Arabidopsis transcriptome using novel methods of Iso-Seq analysis. Genome Biol 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-022-02711-0
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32072537,31872068), fruit industry technology system of Shandong Province (SDAIT-06-03), and Agriculture Improved Variety Project of Shandong Province (2020LZGC008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.W., Y.Y. and Z.J. conceived the research. Z.J., F.W. and L.Y. designed the pipeline. Z.J., F.W. and S.W. tested the procedure. F.W., Z.J. and Z.F. analyzed the result. F.W., Z.J. and Y.Y. wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Jin, Z., Wang, S. et al. ASAPA: a bioinformatic pipeline based on Iso-Seq that identifies the links among alternative splicing, alternative transcription initiation and alternative polyadenylation. Funct Integr Genomics 24, 67 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-024-01332-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-024-01332-z