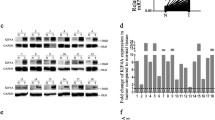
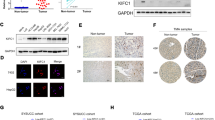
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the tumor with the second highest mortality rate worldwide. Recent research data show that KIF11, a member of the kinesin family (KIF), plays an important role in the progression of various tumors. However, its expression and molecular mechanism in HCC remain elusive. Here, we evaluated the potential role of KIF11 in HCC. The effect of KIF11 was evaluated using the hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines, LM3 and Huh7, after genetic or pharmacological treatment. Evaluating the role of KIF11 in the xenograft animal models using its specific inhibitor. The role of KIF11 was systematically evaluated using specimens obtained from the aforementioned animal and cell models after various in vivo and in vitro experiments. The clinicopathological analysis showed that KIF11 was expressed at high levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell experiments in vitro showed that KIF11 deficiency significantly slowed the proliferation of liver tumor cells. And in the experiment using liver cancer cells overexpressing OCT4, overexpression of OCT4 substantially increased the proliferation of tumor cells compared with tumor cells with KIF11 knockdown alone. Both in vitro cell experiment and in vivo xenotransplantation tumor experiment showed that monastrol, an inhibitor of KIF11, could effectively delay the proliferation and migration of tumor cells. Based on these results, KIF11 is expressed at high levels in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumor proliferation in an OCT4-dependent manner. KIF11 may become a therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma, and its inhibitor monastrol may become a clinical antitumor drug.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF (2003) Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:3983–3988. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0530291100
Asbaghi Y, Thompson LL, Lichtensztejn Z, McManus KJ (2017) KIF11 silencing and inhibition induces chromosome instability that may contribute to cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 56:668–680. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22471
Barasch J (2001) Genes and proteins involved in mesenchymal to epithelial transition. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 10:429–436. https://doi.org/10.1097/00041552-200105000-00021
Bobylev I, Peters D, Vyas M et al (2017) Kinesin-5 blocker monastrol protects against bortezomib-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. Neurotox Res 32:555–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9760-7
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Diefenbach RJ, Mackay JP, Armati PJ, Cunningham AL (1998) The C-terminal region of the stalk domain of ubiquitous human kinesin heavy chain contains the binding site for kinesin light chain. Biochemistry 37:16663–16670. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi981163r
Dyrskjøt L, Kruhøffer M, Thykjaer T, Marcussen N, Jensen JL, Møller K, Ørntoft TF (2004) Gene expression in the urinary bladder: a common carcinoma in situ gene expression signature exists disregarding histopathological classification. Cancer Res 64:4040–4048. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-03-3620
Garcia-Saez I, Skoufias DA (2021) Eg5 targeting agents: from new anti-mitotic based inhibitor discovery to cancer therapy and resistance. Biochem Pharmacol 184:114364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114364
Herr W, Sturm RA, Clerc RG et al (1988) The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev 2:1513–1516. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513
Hu ZD, Jiang Y, Sun HM, Wang JW, Zhai LL, Yin ZQ, Yan J (2021) KIF11 promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with liver cancers. Biomed Res Int 2021:2676745. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2676745
Jerabek S, Merino F, Schöler HR, Cojocaru V (2014) OCT4: dynamic DNA binding pioneers stem cell pluripotency. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839:138–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.10.001
Jungwirth G, Yu T, Cao J et al (2021) KIF11 inhibitors filanesib and ispinesib inhibit meningioma growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett 506:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2021.02.016
Kehler J, Tolkunova E, Koschorz B et al (2004) Oct4 is required for primordial germ cell survival. EMBO Rep 5:1078–1083. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400279
Lawrence CJ, Dawe RK, Christie KR et al (2004) A standardized kinesin nomenclature. J Cell Biol 167:19–22. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200408113
Liang C, Xu Y, Ge H, Li G, Wu J (2018) Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of OCT4 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther 11:47–57. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S151390
Liu X, Gong H, Huang K (2013) Oncogenic role of kinesin proteins and targeting kinesin therapy. Cancer Sci 104:651–656. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12138
Masanas M, Masiá N, Suárez-Cabrera L et al (2021) The oral KIF11 inhibitor 4SC-205 exhibits antitumor activity and potentiates standard and targeted therapies in primary and metastatic neuroblastoma models. Clin Transl Med 11:e533. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.533
Miki H, Setou M, Kaneshiro K, Hirokawa N (2001) All kinesin superfamily protein, KIF, genes in mouse and human. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:7004–7011. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.111145398
Mohiuddin IS, Wei SJ, Kang MH (2020) Role of OCT4 in cancer stem-like cells and chemotherapy resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Basis Dis 1866:165432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.03.005
Nakagawa M, Koyanagi M, Tanabe K et al (2008) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells without Myc from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nat Biotechnol 26:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1374
Narayan G, Bourdon V, Chaganti S et al (2007) Gene dosage alterations revealed by cDNA microarray analysis in cervical cancer: identification of candidate amplified and overexpressed genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 46:373–384. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.20418
Pandian J, Panneerpandian P, Sekar BT, Selvarasu K, Ganesan K (2022) OCT4-mediated transcription confers oncogenic advantage for a subset of gastric tumors with poor clinical outcome. Funct Integr Genomics 22:1345–1360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00894-0
Patra SK (2020) Roles of OCT4 in pathways of embryonic development and cancer progression. Mech Ageing Dev 189:111286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2020.111286
Pesce M, Schöler HR (2000) Oct-4: control of totipotency and germline determination. Mol Reprod Dev 55:452–457. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1098-2795(200004)55:4<452::Aid-mrd14>3.0.Co;2-s
Petrick JL, Florio AA, Loomba R, McGlynn KA (2020a) Have incidence rates of liver cancer peaked in the United States? Cancer 126:3151–3155. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32794
Petrick JL, Florio AA, Znaor A et al (2020b) International trends in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, 1978-2012. Int J Cancer 147:317–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32723
Rath O, Kozielski F (2012) Kinesins and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 12:527–539. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3310
Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A et al (2006) X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer. Cancer Cell 9:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2006.01.013
Schöler HR, Ciesiolka T, Gruss P (1991) A nexus between Oct-4 and E1A: implications for gene regulation in embryonic stem cells. Cell 66:291–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(91)90619-a
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE, Hawkins C, Squire J, Dirks PB (2003) Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 63:5821–5828
Taniwaki M, Takano A, Ishikawa N et al (2007) Activation of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:6624–6631. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-07-1328
Thankamony AP, Murali R, Karthikeyan N et al (2020) Targeting the Id1-Kif11 axis in triple-negative breast cancer using combination therapy. Biomolecules 10:1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091295
Valery PC, Laversanne M, Clark PJ, Petrick JL, McGlynn KA, Bray F (2018) Projections of primary liver cancer to 2030 in 30 countries worldwide. Hepatology 67:600–611. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29498
Venere M, Horbinski C, Crish JF et al (2015) The mitotic kinesin KIF11 is a driver of invasion, proliferation, and self-renewal in glioblastoma. Sci Transl Med 7:304ra143. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aac6762
Wang G, Zhou H, Gu Z, Gao Q, Shen G (2018) Oct4 promotes cancer cell proliferation and migration and leads to poor prognosis associated with the survivin/STAT3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 40:979–987. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6491
Wei D, Rui B, Qingquan F et al (2021) KIF11 promotes cell proliferation via ERBB2/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in gallbladder cancer. Int J Biol Sci 17:514–526. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.54074
Wernig M, Meissner A, Cassady JP, Jaenisch R (2008) c-Myc is dispensable for direct reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell 2:10–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2007.12.001
Wordeman L (2010) How kinesin motor proteins drive mitotic spindle function: lessons from molecular assays. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21:260–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.01.018
Xie F, Wang J, Zhang B (2023) RefFinder: a web-based tool for comprehensively analyzing and identifying reference genes. Funct Integr Genomics 23:125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-0
Zhang X, El-Serag HB, Thrift AP (2020) Sex and race disparities in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States examined through age-period-cohort analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 29:88–94. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-19-1052
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Meifu Chen from the People’s Hospital of Hunan Province for his donation of some reagents on this subject. At the same time, we also thank Dr. Jun He from Xiangya Second Hospital.
Funding
This research project is funded by the Hunan Provincial Innovation Platform and Talent Plan-2020 Hunan Young Talents (2020RC3062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ contributed to the conception of the current research and was responsible for completing some figures and manuscripts. In addition, JZ also completed the experimental part. XQ, ZW, DL, and YJ participated in the data processing and revised the manuscript. The corresponding author (KL) ensures the feasibility of the experiment and the authenticity of the data on the premise of obtaining the consent of all the authors. All authors participated in this article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Approval to obtain experimental tissues from patients with cholangiocarcinoma and normal controls was obtained under informed consent. This study was reviewed and approved by the ethics committee of the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University ((2022) Clinical Study Review No. 095).
Animal ethics
The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the ethics committee of the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wei, Z., Qi, X. et al. Kinesin family member 11 promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via the OCT4 pathway. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 284 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01209-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01209-7