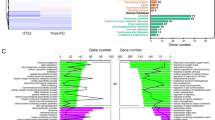
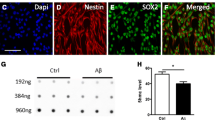
Abstract
N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C), a significant modified nucleoside, participates in the development of many diseases. Messenger RNAs (mRNAs) contain most of the information of the genome and are the molecules that transmit information from genes to proteins. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease in which fibrillar amyloid plaques are present. However, it remains unknown how mRNA ac4C modification affects the development of AD. In the current study, ac4C-modified mRNAs were comprehensively analyzed in AD mice by ac4C-RIP-seq and RNA-seq. Next, a protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed to examine the relationships between the genes with differential ac4C modification levels and their RNA expression levels. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) acquired above were subjected to Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis to further analyze the molecular mechanisms in AD. In total, 3312 significant ac4C peaks were found on 2512 mRNAs, 1241 of which were hyperacetylated and 1271 of which were hypoacetylated. In addition, 956 mRNAs with differential expression were found, including 520 upregulated mRNAs and 436 downregulated mRNAs. Overall, 134 mRNAs with simultaneous changes at the ac4C levels as well as RNA expression levels were identified via joint analysis. Then, through PPI network construction and functional enrichment analysis, 37 key mRNAs were screened, which were predominantly enriched in GABAergic synapses and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. The significant difference in the abundance of mRNA ac4C modification indicates that this modification is associated with AD progression, which may provide insight for more investigations of the potential mechanisms.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used and/or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Alam W, Tayara H, Chong KT (2020) XG-ac4C: identification of N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) in mRNA using eXtreme gradient boosting with electron-ion interaction pseudopotentials. Sci Rep 10:20942. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77824-2
Arango D, Sturgill D, Alhusaini N, Dillman AA, Sweet TJ, Hanson G, Hosogane M, Sinclair WR, Nanan KK, Mandler MD, Fox SD, Zengeya TT, Andresson T, Meier JL, Coller J, Oberdoerffer S (2018) Acetylation of Cytidine in mRNA Promotes Translation Efficiency. Cell 175:1872–1886 e1824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.030
Atmoko W, Raharja PAR, Birowo P, Hamid A, Taher A, Rasyid N (2021) Genetic polymorphisms as prognostic factors for recurrent kidney stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 16:e0251235. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0251235
Baglietto-Vargas D, Sanchez-Mejias E, Navarro V, Jimenez S, Trujillo-Estrada L, Gomez-Arboledas A, Sanchez-Mico M, Sanchez-Varo R, Vizuete M, Davila JC, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Vitorica J, Gutierrez A (2017) Dual roles of Abeta in proliferative processes in an amyloidogenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 7:10085. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10353-7
Bazazzadegan N, Dehghan Shasaltaneh M, Saliminejad K, Kamali K, Banan M, Nazari R, Riazi GH, Khorram Khorshid HR (2017) Effects of Ectoine on Behavior and Candidate Genes Expression in ICV-STZ Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv Pharm Bull 7:629–636. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2017.075
Broly M, Polevoda BV, Awayda KM, Tong N, Lentini J, Besnard T, Deb W, O’Rourke D, Baptista J, Ellard S, Almannai M, Hashem M, Abdulwahab F, Shamseldin H, Al-Tala S, Alkuraya FS, Leon A, van Loon RLE, Ferlini A, Sanchini M, Bigoni S, Ciorba A, van Bokhoven H, Iqbal Z, Al-Maawali A, Al-Murshedi F, Ganesh A, Al-Mamari W, Lim SC, Pais LS, Brown N, Riazuddin S, Bezieau S, Fu D, Isidor B, Cogne B, O’Connell MR (2022) THUMPD1 bi-allelic variants cause loss of tRNA acetylation and a syndromic neurodevelopmental disorder. Am J Hum Genet 109:587–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.02.001
Chenfei Z, Haizhen Y, Jie X, Na Z, Bo X (2022) Effects of aerobic exercise on hippocampal SUMOylation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neurosci Lett 767:136303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136303
Daneshmand P, Saliminejad K, Dehghan Shasaltaneh M, Kamali K, Riazi GH, Nazari R, Azimzadeh P, Khorram Khorshid HR (2016) Neuroprotective Effects of Herbal Extract (Rosa canina, Tanacetum vulgare and Urtica dioica) on Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 8:120–125
Du B, Zhang Y, Liang M, Du Z, Li H, Fan C, Zhang H, Jiang Y, Bi X (2021) N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and its clinical relevance in cognitive dysfunctions. Aging (Albany NY) 13:20716–20737. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203457
Donaghy PC, Cockell SJ, Martin-Ruiz C, Coxhead J, Kane J, Erskine D, Koss D, Taylor JP, Morris CM, O’Brien JT, Thomas AJ (2022) Blood mRNA Expression in Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia With Lewy Bodies. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 30:964–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jagp.2022.02.003
Drummond E, Pires G, MacMurray C, Askenazi M, Nayak S, Bourdon M, Safar J, Ueberheide B, Wisniewski T (2020) Phosphorylated tau interactome in the human Alzheimer’s disease brain. Brain 143:2803–2817. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awaa223
Fan C, Ma Y, Chen S, Zhou Q, Jiang H, Zhang J, Wu F (2021) Comprehensive Analysis of the Transcriptome-Wide m6A Methylation Modification Difference in Liver Fibrosis Mice by High-Throughput m6A Sequencing. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:767051. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.767051
Fei X, Cai Y, Lin F, Huang Y, Liu T, Liu Y (2021) Amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells repair mouse corneal cold injury by promoting mRNA N4-acetylcytidine modification and ETV4/JUN/CCND2 signal axis activation. Hum Cell 34:86–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00442-7
Feigerlova E, Battaglia-Hsu SF (2017) Role of post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA stability in renal pathophysiology: focus on chronic kidney disease. FASEB J 31:457–468. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201601087RR
Garcia JD, Gookin SE, Crosby KC, Schwartz SL, Tiemeier E, Kennedy MJ, Dell'Acqua ML, Herson PS, Quillinan N, Smith KR (2021) Stepwise disassembly of GABAergic synapses during pathogenic excitotoxicity. Cell Rep 37:110142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110142
Good TJ, Villafuerte J, Ryan JD, Grady CL, Barense MD (2020) Resting State BOLD Variability of the Posterior Medial Temporal Lobe Correlates with Cognitive Performance in Older Adults with and without Risk for Cognitive Decline. eNeuro 7. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0290-19.2020
Guo S, Wang J, Xu H, Rong W, Gao C, Yuan Z, Xie F, Bi K, Zhang Z, Li Q (2019) Classic Prescription, Kai-Xin-San, Ameliorates Alzheimer’s Disease as an Effective Multitarget Treatment: From Neurotransmitter to Protein Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:9096409. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9096409
Guven G, Bilgic B, Samanci B, Gurvit H, Hanagasi H, Donmez C, Aslan R, Lohmann E, Erginel-Unaltuna N (2020) Peripheral TREM2 mRNA levels in early and late-onset Alzheimer disease’s patients. Mol Biol Rep 47:5903–5909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05661-7
Hao H, Liu W, Miao Y, Ma L, Yu B, Liu L, Yang C, Zhang K, Chen Z, Yang J, Zheng Z, Zhang B, Deng F, Gong P, Yuan J, Hu Z, Guan W (2022) N4-acetylcytidine regulates the replication and pathogenicity of enterovirus 71. Nucleic Acids Res 50:9339–9354. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac675
Heinz S, Benner C, Spann N, Bertolino E, Lin YC, Laslo P, Cheng JX, Murre C, Singh H, Glass CK (2010) Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell 38:576–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.05.004
Jin G, Xu M, Zou M, Duan S (2020) The Processing, Gene Regulation, Biological Functions, and Clinical Relevance of N4-Acetylcytidine on RNA: A Systematic Review. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 20:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.01.037
Jung YJ, Park YS, Yoon KJ, Kong YY, Park JW, Nam HG (2009) Molecule-level imaging of Pax6 mRNA distribution in mouse embryonic neocortex by molecular interaction force microscopy. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e10. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn965
Kamagata E, Kudo T, Kimura R, Tanimukai H, Morihara T, Sadik MG, Kamino K, Takeda M (2009) Decrease of dynamin 2 levels in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease alters Abeta metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:691–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.12.147
Kim D, Paggi JM, Park C, Bennett C, Salzberg SL (2019) Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat Biotechnol 37:907–915. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0201-4
Kitagishi Y, Nakanishi A, Ogura Y, Matsuda S (2014) Dietary regulation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3beta pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 6:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt265
Knock E, Matsuzaki S, Takamura H, Satoh K, Rooke G, Han K, Zhang H, Staniszewski A, Katayama T, Arancio O, Fraser PE (2018) SUMO1 impact on Alzheimer disease pathology in an amyloid-depositing mouse model. Neurobiol Dis 110:154–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2017.11.015
Lee MY, Lee J, Hyeon SJ, Cho H, Hwang YJ, Shin JY, McKee AC, Kowall NW, Kim JI, Stein TD, Hwang D, Ryu H (2020) Epigenome signatures landscaped by histone H3K9me3 are associated with the synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Aging Cell 19:e13153. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13153
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W (2014) featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30:923–930. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656
Liu Z, Qin G, Mana L, Huang S, Wang Y, Wang P (2020) Shenzhiling Oral Liquid Protects STZ-Injured Oligodendrocyte through PI3K/Akt-mTOR Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020:4527283. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4527283
Lu W, Bromley-Coolidge S, Li J (2017) Regulation of GABAergic synapse development by postsynaptic membrane proteins. Brain Res Bull 129:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.07.004
Luo TT, Dai CQ, Wang JQ, Wang ZM, Yang Y, Zhang KL, Wu FF, Yang YL, Wang YY (2020) Drp1 is widely, yet heterogeneously, distributed in the mouse central nervous system. Mol Brain 13:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-020-00628-y
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Ma LZ, Huang YY, Wang ZT, Li JQ, Hou XH, Shen XN, Ou YN, Dong Q, Tan L, Yu JT, Initiative ADN (2019a) Metabolically healthy obesity reduces the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in elders: a longitudinal study. Aging (Albany NY) 11:10939–10951. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102496
Ma G, Liu M, Du K, Zhong X, Gong S, Jiao L, Wei M (2019b) Differential Expression of mRNAs in the Brain Tissues of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Based on GEO Expression Profile and Its Clinical Significance. Biomed Res Int 2019:8179145. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8179145
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. Embnet J 17:10–12. https://doi.org/10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Meng J, Cui X, Rao MK, Chen Y, Huang Y (2013) Exome-based analysis for RNA epigenome sequencing data. Bioinformatics 29:1565–1567. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt171
von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt S, Bork P, Snel B (2003) STRING: a database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 31:258–261. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg034
Natale S, Esteban Masferrer M, Deivasigamani S, Gross CT (2021) A role for cerebral cortex in the suppression of innate defensive behaviour. Eur J Neurosci 54:6044–6059. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.15426
Nistico R, Ferraina C, Marconi V, Blandini F, Negri L, Egebjerg J, Feligioni M (2014) Age-related changes of protein SUMOylation balance in the AbetaPP Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Pharmacol 5:63. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2014.00063
Panes JD, Godoy PA, Silva-Grecchi T, Celis MT, Ramirez-Molina O, Gavilan J, Munoz-Montecino C, Castro PA, Moraga-Cid G, Yevenes GE, Guzman L, Salisbury JL, Trushina E, Fuentealba J (2020) Changes in PGC-1alpha/SIRT1 Signaling Impact on Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Amyloid-Beta Peptide Toxicity Model. Front Pharmacol 11:709. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00709
Rodin RE, Dou Y, Kwon M, Sherman MA, D’Gama AM, Doan RN, Rento LM, Girskis KM, Bohrson CL, Kim SN, Nadig A, Luquette LJ, Gulhan DC, Brain Somatic Mosaicism N, Park PJ, Walsh CA (2021) The landscape of somatic mutation in cerebral cortex of autistic and neurotypical individuals revealed by ultra-deep whole-genome sequencing. Nat Neurosci 24:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-00765-6
Shafik AM, Zhang F, Guo Z, Dai Q, Pajdzik K, Li Y, Kang Y, Yao B, Wu H, He C, Allen EG, Duan R, Jin P (2021) N6-methyladenosine dynamics in neurodevelopment and aging, and its potential role in Alzheimer’s disease. Genome Biol 22:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-020-02249-z
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Suresh Babu S, Joladarashi D, Jeyabal P, Thandavarayan RA, Krishnamurthy P (2015) RNA-stabilizing proteins as molecular targets in cardiovascular pathologies. Trends Cardiovasc Med 25:676–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2015.02.006
Tantai J, Pan X, Hu D (2016) RNF4-mediated SUMOylation is essential for NDRG2 suppression of lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 7:26837–26843. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8663
Tsai K, Jaguva Vasudevan AA, Martinez Campos C, Emery A, Swanstrom R, Cullen BR (2020) Acetylation of Cytidine Residues Boosts HIV-1 Gene Expression by Increasing Viral RNA Stability. Cell Host Microbe 28:306–312 e306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.011
Wang C, Ju Y, Zou Q, Lin C (2021) DeepAc4C: A convolutional neural network model with hybrid features composed of physicochemical patterns and distributed representation information for identification of N4-acetylcytidine in mRNA. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btab611
Wang G, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zou J, Zhong J, Zheng Z, Zhou X, Zheng Y, Chen B, Liu C (2022) NAT10-mediated mRNA N4-acetylcytidine modification promotes bladder cancer progression. Clin Transl Med 12:e738. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.738
Wang M, Wang S, Li Y, Cai G, Cao M, Li L (2020a) Integrated analysis and network pharmacology approaches to explore key genes of Xingnaojing for treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Behav 10:e01610. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1610
Wang S, Su W, Zhong C, Yang T, Chen W, Chen G, Liu Z, Wu K, Zhong W, Li B, Mao X, Lu J (2020b) An Eight-CircRNA Assessment Model for Predicting Biochemical Recurrence in Prostate Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:599494. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.599494
Wilson CA, Fouda S, Sakata S (2020) Effects of optogenetic stimulation of basal forebrain parvalbumin neurons on Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Sci Rep 10:15456. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72421-9
Wu Y, Jiang D, Zhang H, Yin F, Guo P, Zhang X, Bian C, Chen C, Li S, Yin Y, Bockler D, Zhang J, Han Y (2022) N1-Methyladenosine (m1A) Regulation Associated With the Pathogenesis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Through YTHDF3 Modulating Macrophage Polarization. Front Cardiovasc Med 9:883155. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.883155
Ye X, Zhao L, Kang J (2019) Expression and significance of PTEN and Claudin-3 in prostate cancer. Oncol Lett 17:5628–5634. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10212
Yu M, Chen X, Liu J, Ma Q, Zhuo Z, Chen H, Zhou L, Yang S, Zheng L, Ning C, Xu J, Gao T, Hou ST (2019) Gallic acid disruption of Abeta1-42 aggregation rescues cognitive decline of APP/PS1 double transgenic mouse. Neurobiol Dis 124:67–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.11.009
Zeng L, Jiang HL, Ashraf GM, Li ZR, Liu R (2021) MicroRNA and mRNA profiling of cerebral cortex in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease by RNA sequencing. Neural Regen Res 16:2099–2108. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.308104
Zhang H, Su Y, Sun Z, Chen M, Han Y, Li Y, Dong X, Ding S, Fang Z, Li W, Li W (2021) Ginsenoside Rg1 alleviates Aβ deposition by inhibiting NADPH oxidase 2 activation in APP/PS1 mice. J Ginseng Res 45:665–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2021.03.003
Zhao W, Zhou Y, Cui Q, Zhou Y (2019) PACES: prediction of N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) modification sites in mRNA. Sci Rep 9:11112. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47594-7
Funding
This study was supported by the Major Science and Technology Project of Anhui Province (No. 201903a07020016) and the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province (No. GXXT-2020–025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanzhen Ma wrote the entire manuscript; Yongzhong Wang and Weizu Li revised the manuscript language and diagrams; Chang Fan participated in some statistical analysis work; Hui Jiang corrected the article; and Wenming Yang revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and Consent to participate
The animal experiment was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University (LLSC20210753).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Fan, C., Wang, Y. et al. Comprehensive analysis of mRNAs in the cerebral cortex in APP/PS1 double-transgenic mice with Alzheimer's disease based on high-throughput sequencing of N4-acetylcytidine. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 267 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01192-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01192-z