Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a highly heterogeneous malignant tumor associated with a poor prognosis, is a common cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with a limited survival benefit for patients despite ongoing therapeutic breakthroughs. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a severe infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is a global pandemic and a serious threat to human health. The increased susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and a poor prognosis in patients with cancer necessitate the exploration of the potential link between the two. No studies have investigated the relationship of COVID-19 genes with the prognosis and tumor development in patients with HCC. We screened prognosis-related COVID-19 genes in HCC, performed molecular typing, developed a stable and reliable COVID-19 genes signature for predicting survival, characterized the immune microenvironment in HCC patients, and explored new molecular therapeutic targets. Datasets of HCC patients, including RNA sequencing data and clinical information, were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC), and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases. Prognosis-related COVID-19 genes were identified by univariate Cox analysis. Molecular typing of HCC was performed using the consensus non-negative matrix factorization method (cNMF), followed by the analysis of survival, tumor microenvironment, and pathway enrichment for each subtype. Prognostic signatures were constructed using LASSO-Cox regression models, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to validate the predictive performance of the signature. The same approach was used for the test and external validation sets. Seven software packages were applied to determine the abundance of immune infiltration in HCC patients and investigate its relationship with the risk scores. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was used to explore the potential mechanisms by which the COVID-19 genes affect hepatocarcinogenesis and prognosis. Three types of machine learning methods were combined to identify the most critical genes in the signature and localize their expression at the single cell level. We identified 53 prognosis-related COVID-19 genes and classified HCC into two molecular subtypes (C1, C2) by using the NMF method. The prognosis of C2 was significantly better than that of C1, and the two subtypes differed remarkably in terms of the tumor immune microenvironment and biological functions. The 17 COVID-19 genes were screened using the LASSO regression method to develop a 17 COVID-19 genes signature, which demonstrated a good predictive performance for 1-, 2- and 3-year OS of patients with HCC. The risk score as an independent prognostic factor for HCC has better predictive accuracy than traditional clinical variables. Patients in the TCGA cohort were categorized by risk score into the high- and low-risk groups, with the high-risk group mainly enriched in the immune modulation-related pathways and the low-risk group mainly enriched in the metabolism-related pathways, suggesting that the COVID-19 genes may affect disease progression and prognosis by regulating the tumor immune microenvironment and metabolism in HCC. NOL10 was identified as the most critical gene in the signature and hypothesized to be a potential therapeutic target for HCC. Objectively, the COVID-19 genes signature developed in this study, as an independent prognostic factor in HCC patients, is closely associated with the prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment of HCC patients and indicates that they may regulate the development of HCC in multiple ways, providing us with new perspectives for understanding the molecular mechanisms of HCC and finding effective therapeutic targets.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets involved in this study can all be found in online databases, which are all freely available to the public. There are six databases involved in this study, including the TCGA database (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/), the ICGC database (https://dcc.icgc.org/releases/current/Projects/LIRI-JP), the GSE14520 dataset (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE14520), the HPA database (https://www.proteinatlas.org/), the CPTAC database (https://proteomics.cancer.gov/programs/cptac), and the TISCH database (http://tisch1.comp-genomics.org/home/).
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- COVID-19:
-
corona virus disease 2019
- SARS-CoV-2:
-
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- ICGC:
-
International Cancer Genome Consortium
- GEO:
-
Gene Expression Omnibus
- cNMF:
-
consensus nonnegative matrix factorization
- ROC:
-
receiver operating characteristic
- GSEA:
-
gene set enrichment analysis
- OS:
-
overall survival
- TCGA-LIHC:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- HPA:
-
Human Protein Atlas
- PRCG:
-
prognosis-related COVID-19 genes
- KM:
-
Kaplan–Meier
- GSVA:
-
gene set variation analysis
- HLA:
-
human leukocyte antigens
- LASSO:
-
least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- DCA:
-
decision curve analysis
- AUC:
-
area under curve
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- GO:
-
gene ontology
- CPTAC:
-
Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium
- TISCH:
-
tumor immune single-cell hub
- LSECs:
-
liver sinusoidal endothelial cells
References
Alpalhão M, Ferreira JA, Filipe P (2020) Persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection and the risk for cancer. Med Hypotheses 143:109882
Aran D, Hu Z, Butte AJ (2017) xCell: digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol 18:1–14
Bai D-S, Wu C, Yang L-X, Zhang C, Zhang P-F, He Y-Z, Cai J-B, Song Z-J, Dong Z-R, Huang X-Y (2016) UBAP2 negatively regulates the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cell by ubiquitinating and degradating Annexin A2. Oncotarget 7(22):32946
Basit S, Al-Harbi KM, Alhijji SAM, Albalawi AM, Alharby E, Eldardear A, Samman MI (2016) CIT, a gene involved in neurogenic cytokinesis, is mutated in human primary microcephaly. Hum Genet 135:1199–1207
Becht E, Giraldo NA, Lacroix L, Buttard B, Elarouci N, Petitprez F, Selves J, Laurent-Puig P, Sautès-Fridman C, Fridman WH (2016) Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol 17(1):1–20
Bhandari S, Li R, Simón-Santamaría J, McCourt P, Johansen SD, Smedsrød B, Martinez-Zubiaurre I, Sørensen KK (2020) Transcriptome and proteome profiling reveal complementary scavenger and immune features of rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and liver macrophages. BMC Mol Cell Biol 21(1):1–25
Boroughs LK, DeBerardinis RJ (2015) Metabolic pathways promoting cancer cell survival and growth. Nat Cell Biol 17(4):351–359
Chen W, Yang Z, Chen Y (2022) A novel oxidative phosphorylation-associated gene signature for prognosis prediction in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Dis Markers 2022:3594901
Dai M, Liu D, Liu M, Zhou F, Li G, Chen Z, Zhang Z, You H, Wu M, Zheng Q et al (2020) Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2: a multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak. Cancer Discover 10(6):783–791
Désert R, Rohart F, Canal F, Sicard M, Desille M, Renaud S, Turlin B, Bellaud P, Perret C, Clément B (2017) Human hepatocellular carcinomas with a periportal phenotype have the lowest potential for early recurrence after curative resection. Hepatol 66(5):1502–1518
Donnarumma G, Paoletti I, Fusco A, Perfetto B, Buommino E, de Gregorio V, Baroni A (2016) β-defensins: work in progress. In: Donelli G (ed) Advances in Microbiology, Infectious Diseases and Public Health. Springer
Du H, Pang M, Hou X, Yuan S, Sun L (2017) PLOD2 in cancer research. Biomed Pharmacother 90:670–676
Erola P, Martin R, Gaunt TR (2022) The network of SARS-CoV-2-cancer molecular interactions and pathways. BioRxiv:2022–2004
Evangelou K, Havaki S, Kotsinas A (2014) E2F transcription factors and digestive system malignancies: how much do we know? World J Gastroenterol: WJG 20(29):10212
Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim T-Y, Kudo M, Breder V, Merle P, Kaseb AO (2020) Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 382(20):1894–1905
Finotello F, Mayer C, Plattner C, Laschober G, Rieder D, Hackl H, Krogsdam A, Loncova Z, Posch W, Wilflingseder D (2019) Molecular and pharmacological modulators of the tumor immune contexture revealed by deconvolution of RNA-seq data. Genome Med 11(1):1–20
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2010) Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Software 33(1):1–22
Gajewski TF, Woo S-R, Zha Y, Spaapen R, Zheng Y, Corrales L, Spranger S (2013) Cancer immunotherapy strategies based on overcoming barriers within the tumor microenvironment. Curr Opin Immunol 25(2):268–276
Gao B, Wang Y, Lu S (2023) Construction and validation of a novel signature based on epithelial-mesenchymal transition–related genes to predict prognosis and immunotherapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma by comprehensive analysis of the tumor microenvironment. Funct Integr Genom 23(1):6
Gao Q, Zhu H, Dong L, Shi W, Chen R, Song Z, Huang C, Li J, Dong X, Zhou Y (2019) Integrated proteogenomic characterization of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell 179(2):561–577
Geisslinger F, Vollmar AM, Bartel K (2020) Cancer patients have a higher risk regarding COVID-19–and vice versa? Pharmaceuticals 13(7):143
Ghosh SK, McCormick TS, Weinberg A (2019) Human beta defensins and cancer: contradictions and common ground. Front Oncol 9:341
Gracia-Sancho J, Caparrós E, Fernández-Iglesias A, Francés R (2021) Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver diseases. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(6):411–431
Hammoutene A, Rautou P-E (2019) Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 70(6):1278–1291
Han HJ, Nwagwu C, Anyim O, Ekweremadu C, Kim S (2021) COVID-19 and cancer: from basic mechanisms to vaccine development using nanotechnology. Int Immunopharmacol 90:107247
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J (2013) GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform 14:1–15
Hu X, Bao M, Huang J, Zhou L, Zheng S (2020) Identification and validation of novel biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 10:541479
IARC (n.d.)Latest global cancer data: cancer burden rises to 19.3 million new cases and 10.0 million cancer deaths in 2020. https://www.iarc.who.int/news-events/latest-global-cancer-data-cancer-burden-rises-to-19-3-million-new-cases-and-10-0-million-cancer-deaths-in-2020/
Jiang C, He ZL, Hu XH, Ma PY (2020) MiRNA-15a-3p inhibits the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by interacting with HMOX1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(24):12694–12700
Jiang F, Hu Y, Liu X, Wang M, Wu C (2022) Methylation pattern mediated by m 6 A regulator and tumor microenvironment invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:2930310
Jiang X, Wang G, Liu Y, Mei C, Yao Y, Wu X, Chen X, Ma W, Li K, Zhang Z (2021) A novel long non-coding RNA RP11-286H15. 1 represses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by promoting ubiquitination of PABPC4. Cancer Lett 499:109–121
Johnson WE, Li C, Rabinovic A (2007) Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 8(1):118–127
Jyotsana N, King MR (2020) The impact of COVID-19 on cancer risk and treatment. Cell Mol Bioeng 13:285–291
Kiatsurayanon C, Peng G, Niyonsaba F (2022) Opposing roles of antimicrobial peptides in skin cancers. Curr Pharm Des 28(3):248–258
Kumar D, Verma C, Dahiya S, Singh PK, Raboaca MS, Illés Z, Bakariya B (2021) Cardiac diagnostic feature and demographic identification (CDF-DI): an IoT enabled healthcare framework using machine learning. Sensors 21(19):6584
Li T, Fan J, Wang B, Traugh N, Chen Q, Liu JS, Li B, Liu XS (2017) TIMER: a web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res 77(21):e108–e110
Liang W, Guan W, Chen R, Wang W, Li J, Xu K, Li C, Ai Q, Lu W, Liang H (2020) Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol 21(3):335–337
Ling Y-M, Chen J-Y, Guo L, Wang C-Y, Tan W-T, Wen Q, Zhang S-D, Deng G-H, Lin Y, Kwok HF (2017) β-defensin 1 expression in HCV infected liver/liver cancer: an important role in protecting HCV progression and liver cancer development. Sci Rep 7(1):13404
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc J-F, De Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul J-L, Forner A (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359(4):378–390
Löbrich M, Jeggo PA (2007) The impact of a negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer induction. Nat Rev Cancer 7(11):861–869
Lohitesh K, Chowdhury R, Mukherjee S (2018) Resistance a major hindrance to chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: an insight. Cancer Cell Int 18:1–15
Ma J, Yin J, Qian Y, Wu Y (2020) Clinical characteristics and prognosis in cancer patients with COVID-19: a single center’s retrospective study. J Infect 81(2):318–356
Mao X, Xu J, Wang W, Liang C, Hua J, Liu J, Zhang B, Meng Q, Yu X, Shi S (2021) Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: new findings and future perspectives. Mol Cancer 20(1):1–30
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M, Alizadeh AA (2015) Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods 12(5):453–457
Ng CKY, Piscuoglio S, Terracciano LM (2017) Molecular classification of hepatocellular carcinoma: the view from metabolic zonation. Hepatology 66(5):1377–1380
Noda T, Yamamoto H, Takemasa I, Yamada D, Uemura M, Wada H, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Eguchi H, Tanemura M (2012) PLOD 2 induced under hypoxia is a novel prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Liver Int 32(1):110–118
Policard M, Jain S, Rego S, Dakshanamurthy S (2021) Immune characterization and profiles of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients reveals potential host therapeutic targets and SARS-CoV-2 oncogenesis mechanism. Virus Res 301:198464
Quint K, Agaimy A, Di Fazio P, Montalbano R, Steindorf C, Jung R, Hellerbrand C, Hartmann A, Sitter H, Neureiter D (2011) Clinical significance of histone deacetylases 1, 2, 3, and 7: HDAC2 is an independent predictor of survival in HCC. Virchows Archiv 459:129–139
Rajagopalan D, Jha S (2018) An epi (c) genetic war: pathogens, cancer and human genome. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Rev Cancer 1869(2):333–345
Rumgay H, Arnold M, Ferlay J, Lesi O, Cabasag CJ, Vignat J, Laversanne M, McGlynn KA, Soerjomataram I (2022) Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J Hepatol 77(6):1598–1606
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA: a Cancer J Clin 70(1):7–30
Simon N, Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2011) Regularization paths for Cox’s proportional hazards model via coordinate descent. J Stat Software 39(5):1–13
Starokadomskyy P, Gemelli T, Rios JJ, Xing C, Wang RC, Li H, Pokatayev V, Dozmorov I, Khan S, Miyata N (2016) DNA polymerase-α regulates the activation of type I interferons through cytosolic RNA: DNA synthesis. Nat Immunol 17(5):495–504
Stine ZE, Walton ZE, Altman BJ, Hsieh AL, Dang CV (2015) MYC, metabolism, and cancer. Cancer Discover 5(10):1024–1039
Stingi A, Cirillo L (2021) SARS-CoV-2 infection and cancer: evidence for and against a role of SARS-CoV-2 in cancer onset. BioEssays 43(8):2000289
Sun D, Wang J, Han Y, Dong X, Ge J, Zheng R, Shi X, Wang B, Li Z, Ren P (2021) TISCH: a comprehensive web resource enabling interactive single-cell transcriptome visualization of tumor microenvironment. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):D1420–D1430
Sun Q, Zhang B, Hu Q, Qin Y, Xu W, Liu W, Yu X, Xu J (2018) The impact of cancer-associated fibroblasts on major hallmarks of pancreatic cancer. Theranostics 8(18):5072
Tamminga M, Hiltermann TJN, Schuuring E, Timens W, Fehrmann RSN, Groen HJM (2020) Immune microenvironment composition in non-small cell lung cancer and its association with survival. Clin Trans Immunol 9(6):e1142
Tang J-C, Liu J-H, Liu X-L, Liang X, Cai X-J (2015) Effect of fibulin-5 on adhesion, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via an integrin-dependent mechanism. World J Gastroenterol: WJG 21(39):11127
Tu K, Dou C, Zheng X, Li C, Yang W, Yao Y, Liu Q (2014) Fibulin-5 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by down-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression. BMC Cancer 14(1):1–9
Turley SJ, Cremasco V, Astarita JL (2015) Immunological hallmarks of stromal cells in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol 15(11):669–682
Van Veldhoven CM, Khan AE, Teucher B, Rohrmann S, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Tjønneland A, Overvad K, Vigl M, Boeing H, Benetou V (2011) Physical activity and lymphoid neoplasms in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC). Eur J Cancer 47(5):748–760
Wang H, Wu K, Sun Y, Li Y, Wu M, Qiao Q, Wei Y, Han Z-G, Cai B (2012) STC2 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and migration in vitro. BMB Rep 45(11):629–634
Wang H, Yu L, Cui Y, Huang J (2022) G protein subunit gamma 5 is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dis Markers 2022:1313359
Wang Y, Liu Y (2021) Gut-liver-axis: barrier function of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 36(10):2706–2714
White MK, Pagano JS, Khalili K (2014) Viruses and human cancers: a long road of discovery of molecular paradigms. Clin Microbiol Rev 27(3):463–481
Wu Y, Liu Z, Xu X (2020) Molecular subtyping of hepatocellular carcinoma: a step toward precision medicine. Cancer Commun 40(12):681–693
Xiong L, Luo Y, Yuan T, Lin W, Lin B, Wu C, Duan Y, Ou Y (2023) Prognostic 7-SLC-gene signature identified via weighted gene co-expression network analysis for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Oncol 2023:4364654
Xu T, Le TD, Liu L, Su N, Wang R, Sun B, Colaprico A, Bontempi G, Li J (2017) CancerSubtypes: an R/Bioconductor package for molecular cancer subtype identification, validation and visualization. Bioinformatics 33(19):3131–3133
Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martínez E, Vegesna R, Kim H, Torres-Garcia W, Treviño V, Shen H, Laird PW, Levine DA (2013) Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat Commun 4(1):2612
Zarei M, Bose D, Nouri-Vaskeh M, Tajiknia V, Zand R, Ghasemi M (2022) Long-term side effects and lingering symptoms post COVID-19 recovery. Rev Med Virol 32(3):e2289
Zhao Y, Zhang J, Wang S, Jiang Q, Xu K (2021) Identification and validation of a nine-gene amino acid metabolism-related risk signature in HCC. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:731790
Zhou J, Sun H, Wang Z, Cong W, Wang J, Zeng M, Zhou W, Bie P, Liu L, Wen T (2020) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (2019 edition). Liver Cancer 9(6):682–720
Zhu Y, Qi M (2020) Expression and prognostic roles of PABPC1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Surg 84:3–12
Zongyi Y, Xiaowu L (2020) Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 470:8–17
Acknowledgements
We express our appreciation for all the open public databases mentioned in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SG was responsible for the design of the study, collecting and processing data, and generating images, as well as the writing and submission of the paper. LZ contributed technical assistance. Corresponding author HW supervised this study throughout and reviewed the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All datasets used in this study have been previously published.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
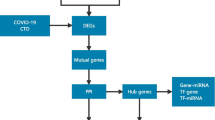
Supplementary Figure S1 The work-flow of the study. Schematic diagram of this study is shown in the work-flow. (JPG 2562 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, S., Zhang, L. & Wang, H. Characterizing the key genes of COVID-19 that regulate tumor immune microenvironment and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 262 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01184-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01184-z