Abstract
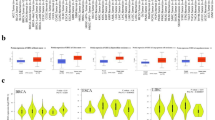
In recent years, the potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D (KCND) channels, particularly KCND2 (also known as Kv4.2), have been suggested to play a role in a variety of cancers, but their role in breast cancer has not yet been revealed. We analyzed RNA sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas database and the Genotype-Tissue Expression database to investigate the differential expression of KCND2 in breast cancer and normal breast tissue. In addition, we leveraged GO and KEGG analysis techniques to gain a better understanding of the potential functional enrichment of 500 genes related to KCND2. Our findings were validated using collected tissue samples and clinical data from hospitals showed that KCND2 is a crucial independent factor in the prognosis of breast cancer patients. The higher the expression of KCND2, the shorter the survival time of breast cancer patients. Colony formation assay confirmed that KCND2 promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells, whereas transwell assay and wound healing assay verified that KCND2 promoted breast cancer invasion and migration. In addition, 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) and flow cytometry revealed that KCND2 affected the cycle changes of breast cancer cells and contributed to the G1/S phase transition of breast cancer cells. Overall, our study demonstrates that KCND2 holds a promising potential as a significant target for breast cancer diagnosis and therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Some data used in this study were obtained from the publicly accessible websites (https://portal.gdc.com; https://www.genome.gov/Funded-Programs-Projects/Genotype-Tissue-Expression-Project ). Other data are available from Shengjie Yang on reasonable request.
References
Aran D, Hu Z, Butte AJ (2017) xCell: digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol 18(1):220. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1349-1
Borst J, Ahrends T, Bąbała N, Melief CJM, Kastenmüller W (2018) CD4(+) T cell help in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 18(10):635–647. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-018-0044-0
Britt KL, Cuzick J, Phillips K-A (2020) Key steps for effective breast cancer prevention. Nat Rev Cancer 20(8):417–436. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-020-0266-x
de Azevedo ALK, Carvalho TM, Mara CS, Giner IS, de Oliveira JC, Gradia DF et al (2023) Major regulators of the multi-step metastatic process are potential therapeutic targets for breast cancer management. Funct Integr Genomics 23(2):171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01097-x
Dehghani-Samani A, Madreseh-Ghahfarokhi S, Dehghani-Samani A (2019) Mutations of voltage-gated ionic channels and risk of severe cardiac arrhythmias. Acta Cardiol Sin 35(2):99–110. https://doi.org/10.6515/acs.201903_35(2).20181028a
Dolina JS, Van Braeckel-Budimir N, Thomas GD, Salek-Ardakani S (2021) CD8(+) T Cell Exhaustion in Cancer. Front Immunol 12:715234. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.715234
Frank-Hansen R, Larsen LA, Andersen P, Jespersgaard C, Christiansen M (2005) Mutations in the genes KCND2 and KCND3 encoding the ion channels Kv4.2 and Kv4.3, conducting the cardiac fast transient outward current (ITO,f), are not a frequent cause of long QT syndrome. Clin Chim Acta 351(1-2):95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cccn.2004.08.017
Frost FG, Cherukuri PF, Milanovich S, Boerkoel CF (2020) Pan-cancer RNA-seq data stratifies tumours by some hallmarks of cancer. J Cell Mol Med 24(1):418–430. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14746
Ganser K, Klumpp L, Bischof H, Lukowski R, Eckert F, Huber SM (2021) Potassium Channels in Cancer. Handb Exp Pharmacol 267:253–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2021_465
Gao K, Lin Z, Wen S, Jiang Y (2022) Potassium channels and epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand 146(6):699–707. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.13695
Hanker AB, Sudhan DR, Arteaga CL (2020) Overcoming endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 37(4):496–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.009
Izzi V, Davis MN, Naba A (2020) Pan-Cancer analysis of the genomic alterations and mutations of the matrisome. Cancers (Basel) 12(8):2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082046
Kuang Q, Purhonen P, Hebert H (2015) Structure of potassium channels. Cell Mol Life Sci 72(19):3677–3693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1948-5
Li B, Severson E, Pignon JC, Zhao H, Li T, Novak J et al (2016) Comprehensive analyses of tumor immunity: implications for cancer immunotherapy. Genome Biol 17(1):174. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1028-7
Li M, Zhao Y, Li H, Deng X, Sheng M (2023) Application value of circulating LncRNA in diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of breast cancer. Funct Integr Genomics 23(1):61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-00983-8
Loibl S, Poortmans P, Morrow M, Denkert C, Curigliano G (2021) Breast cancer. Lancet 397(10286):1750–1769. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32381-3
Lu X, Li K, Yang J (2021) Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 2 induces an aggressive phenotype in lung adenocarcinoma. Neoplasma 68(1):135–143. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2020_200629N667
Postma AV, Bezzina CR, de Vries JF, Wilde AA, Moorman AF, Mannens MM (2000) Genomic organisation and chromosomal localisation of two members of the KCND ion channel family, KCND2 and KCND3. Hum Genet 106(6):614–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000308
Sette A, Spadavecchia J, Landoulsi J, Casale S, Haye B, Crociani O et al (2013) Development of novel anti-Kv 11.1 antibody-conjugated PEG-TiO(2) nanoparticles for targeting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. J Nanopart Res 15(12):2111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2111-6
Sturm G, Finotello F, Petitprez F, Zhang JD, Baumbach J, Fridman WH et al (2019) Comprehensive evaluation of transcriptome-based cell-type quantification methods for immuno-oncology. Bioinform 35(14):i436–i445. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz363
Trayes KP, Cokenakes SEH (2021) Breast cancer treatment. Am Fam Physician 104(2):171–178
Wei H, Li Y, Du Y, Ma J (2018) KCND2 upregulation might be an independent indicator of poor survival in gastric cancer. Future Oncol 14(27):2811–2820. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2018-0418
Xie F, Wang J, Zhang B (2023) RefFinder: a web-based tool for comprehensively analyzing and identifying reference genes. Funct Integr Genomics 23(2):125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01055-7
Zheng X, Ma H, Dong Y, Fang M, Wang J, Xiong X et al (2023) Immune-related biomarkers predict the prognosis and immune response of breast cancer based on bioinformatic analysis and machine learning. Funct Integr Genomics 23(3):201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01124-x
Zhou T, Cai Z, Ma N, Xie W, Gao C, Huang M et al (2020) A novel ten-gene signature predicting prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:629. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00629
Funding
This work was funded by Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Project (Z211100002521011) and National Science and Technology Major Project (2017ZX09304026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SY and XW conceived and designed the experiments. SY, PZ, LQ, and YW completed cell experiments and collected relevant data. SY and YL analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors discussed and improved the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the he Ethics Committee of Beijing Shijitan Hospital (sjtky11-lx-2022 (052)) and Ethics Committee of Shandong Cancer Hospital (SDTHEC20110324). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary 1
Five-hundred genes list (Supplementary 1) which were most relevant to KCND2 (XLSX 23 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Zhou, P., Qi, L. et al. Promoting proliferation and tumorigenesis of breast cancer: KCND2’s significance as a prognostic factor. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 257 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01183-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01183-0