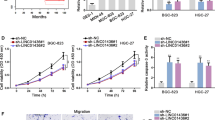
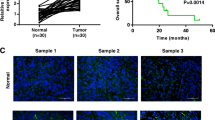
Abstract
Long noncoding RNAs play important roles in the occurrence and development of many malignant cancers. This study focuses on the effects of LINC01087 on gastric cancer and its underlying mechanism. In the present study, LINC01087 and CAAP1 were found to be upregulated, and miR-135a-5p was diminished in gastric cancer specimens and cells. Inhibition of LINC01087 resulted in cell proliferation inhibition and induced cell apoptosis through the intrinsic apoptosis signaling pathway, as evidenced by the activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9. An investigation of the signaling pathway revealed that the effects on proliferation and apoptosis following LINC01087 knockdown were mediated by suppression of CAAP1. Furthermore, application of a miR-135a-5p inhibitor or overexpression of CAAP1 could attenuate the apoptotic effect achieved by LINC01087 inhibition, confirming the involvement of miR-135a-5p/CAAP1 signaling in the occurrence of gastric cancer. In conclusion, the LINC01087/miR-135a-5p/CAAP1 axis modulates gastric cancer tumorigenesis and pathogenesis and presents new insight into gastric cancer targeted therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Barreto SG, Windsor JA (2016) Redefining early gastric cancer. Surg Endosc 30:24–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4184-z
Bridges MC, Daulagala AC, Kourtidis A (2021) LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J Cell Biol 220:e202009045. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202009045
Cable J, Heard E, Hirose T et al (2021) Noncoding RNAs: biology and applications-a Keystone Symposia report. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1506:118–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.14713
Chaudhary AK, Na D, Lee EY (2015) Rapid and high-throughput construction of microbial cell-factories with regulatory noncoding RNAs. Biotechnol Adv 33:914–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.05.009
Chen W, Wang F, Zhang J, Li C, Hong L (2022) LINC01087 indicates a poor prognosis of glioma patients with preoperative MRI. Funct Integr Genomics 22:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-021-00812-w
Chen Z, Li Y, Tan B et al (2020) Progress and current status of molecule-targeted therapy and drug resistance in gastric cancer. Drugs Today (Barc) 56:469–482. https://doi.org/10.1358/dot.2020.56.7.3112071
De Palma FDE, Carbonnier V, Salvatore F, Kroemer G, Pol JG, Maiuri MC (2022) Systematic investigation of the diagnostic and prognostic impact of LINC01087 in human cancers. Cancers (Basel) 14:5980. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235980
Diao H, Xu X, Zhao B, Yang G (2021) miR-135a-5p inhibits tumor invasion by targeting ANGPT2 in gallbladder cancer. Mol Med Rep 24:528. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.12167
Dykes IM, Emanueli C (2017) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation by long non-coding RNA. Genom Proteom Bioinform 15:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2016.12.005
Naorem LD, Prakash VS, Muthaiyan M, Venkatesan A (2020) Comprehensive analysis of dysregulated lncRNAs and their competing endogenous RNA network in triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Biol Macromol 145:429–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.196
Pan J, Xu X, Wang G (2020) lncRNA ZFAS1 is involved in the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer cells through competitively binding to miR-135a-5p. Cancer Manag Res 12:1135–1149. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s237439
She JK, Fu DN, Zhen D, Gong GH, Zhang B (2020) LINC01087 is highly expressed in breast cancer and regulates the malignant behavior of cancer cells through miR-335-5p/Rock1. Onco Targets Ther 13:9771–9783. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s255994
Thrift AP, El-Serag HB (2020) Burden of gastric cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:534–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.045
Tian YH, Jia LW, Liu ZF, Chen YH (2021) LINC01087 inhibits glioma cell proliferation and migration, and increases cell apoptosis via miR-384/Bcl-2 axis. Aging (Albany NY) 13:20808–20819. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203478
Tripathi R, Aier I, Chakraborty P, Varadwaj PK (2020) Unravelling the role of long non-coding RNA - LINC01087 in breast cancer. Noncoding RNA Res 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncrna.2019.12.002
Venerito M, Link A, Rokkas T, Malfertheiner P (2016) Gastric cancer - clinical and epidemiological aspects. Helicobacter 1:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/hel.12339
Yin Y, Huang J, Shi H et al (2022) LINC01087 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of thyroid cancer cells by upregulating PPM1E. J Oncol 2022:7787378. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7787378
Zhang H, Wang M, Lang Z, Liu H, Liu J, Ma L (2022) MiR-135a-5p suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating BAG3. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 77:100115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinsp.2022.100115
Zhang HM, Li H, Wang GX et al (2020) MKL1/miR-5100/CAAP1 loop regulates autophagy and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Neoplasia 22:220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2020.03.001
Zhang J, Xiao F, Qiang G et al (2021) Novel lncRNA panel as for prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma based on ceRNA network mechanism. Comput Math Methods Med 2021:8020879. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8020879
Zhao RR, Mao XR, Wang XF, Zheng Y, Wang YP, Zhou YN (2022) Role of annexin A family in tumorigenesis and chemoresistance of gastric cancer. Neoplasma 69:251–263. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2021_210629n872
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DZ designed the study. KZ, CD, and DZ performed the experiments and drafted the manuscript. QL and CD analyzed the data. DZ and KZ revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures involving human participants were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional and National Research Committee, and with the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethical Committee of Soochow Medical University. Verbal informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the present study.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, KX., Ding, C., Liu, QH. et al. Knockdown of LINC01087 inhibits gastric cancer malignant behavior by regulating the miR-135a-5p/CAAP1 axis. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 248 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01157-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01157-2