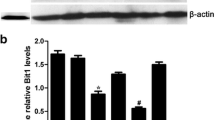
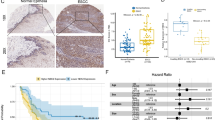
Abstract
Kinesin family member 23 (KIF23) serves as a tumor-promoting gene with prognostic values in various tumors. However, the role of KIF23 in esophageal carcinoma (ESCA) progression is largely unknown. The overlapping differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in GSE12452, GSE17351, and GSE20347 datasets were identified via GEO2R tool and Venn diagram software. KIF23 expression was analyzed using GSE12452, GSE17351, and GSE20347 datasets, GEPIA database, and qRT-PCR. Cell proliferation was assessed by CCK-8 and EdU incorporation assays. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) analysis was performed to investigate the pathways associated with the regulatory mechanisms of KIF23 in ESCA. The expression of E-cadherin, vimentin, N-cadherin, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and alternation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway were detected by western blot analysis. We identified two overlapping upregulated DEGs, among which KIF23 was selected for subsequent experiments. KIF23 was overexpressed in ESCA samples and cells, and knockdown of KIF23 retarded cell proliferation in ESCA cells. Besides, KIF23 knockdown suppressed epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process in ESCA cells, as evidenced by the increase of E-cadherin expression and the reduction of vimentin, N-cadherin, and MMP-9 expression. GSEA analysis suggested that Wnt signaling pathway was the significant pathway related to KIF23. Moreover, we demonstrated that KIF23 silencing inhibited the Wnt/β‐catenin pathway in ESCA cells. Activation of Wnt/β‐catenin pathway by SKL2001 reversed the effects of KIF23 silencing on cell proliferation and EMT in ESCA cells. In conclusion, KIF23 knockdown inhibited the proliferation and EMT in ESCA cells through blockage of Wnt/β‐catenin pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abnet CC, Arnold M, Wei WQ (2018) Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology 154(2):360–373. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.023
Anastas JN, Moon RT (2013) WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 13(1):11–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3419
Barrett T, Suzek TO, Troup DB, Wilhite SE, Ngau WC, Ledoux P, Rudnev D, Lash AE, Fujibuchi W, Edgar R (2005) NCBI GEO: mining millions of expression profiles–database and tools. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D562-566. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki022
Cao LJ, Zhang YJ, Dong SQ, Li XZ, Tong XT, Chen D, Wu ZY, Zheng XH, Xue WQ, Jia WH, Zhang JB (2021) ATAD2 interacts with C/EBPβ to promote esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 40(1):109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-01905-x
Chaw SY, Abdul Majeed A, Dalley AJ, Chan A, Stein S, Farah CS (2012) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) biomarkers–E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC and vimentin–in oral squamous cell carcinogenesis and transformation. Oral Oncol 48(10):997–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.05.011
Chen T, You Y, Jiang H, Wang ZZ (2017) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): a biological process in the development, stem cell differentiation, and tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol 232(12):3261–3272. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25797
Chen W, Wang F, Zhang J, Li C, Hong L (2022) LINC01087 indicates a poor prognosis of glioma patients with preoperative MRI. Funct Integr Genomics 22(1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-021-00812-w
D’Avino PP, Giansanti MG, Petronczki M (2015) Cytokinesis in animal cells. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7(4):a015834. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a015834
Davis S, Meltzer PS (2007) GEOquery: a bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics 23(14):1846–1847. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm254
Deng F, Zhou K, Cui W, Liu D, Ma Y (2015) Clinicopathological significance of wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(3):3045–3053
Du F, Liu H, Lu Y, Zhao X, Fan D (2017) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: liaison between cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Crit Rev Oncog 22(3–4):275–282. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevOncog.2018024855
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ (2003) Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 349(23):2241–2252. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra035010
Fischer M, Grundke I, Sohr S, Quaas M, Hoffmann S, Knörck A, Gumhold C, Rother K (2013) p53 and cell cycle dependent transcription of kinesin family member 23 (KIF23) is controlled via a CHR promoter element bound by DREAM and MMB complexes. PLoS One 8(5):e63187. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063187
Huang H (2018) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a cancer biomarker and MMP-9 biosensors: recent advances. Sensors 18(10):3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103249
Huber MA, Kraut N, Beug H (2005) Molecular requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17(5):548–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2005.08.001
Iltzsche F, Simon K, Stopp S, Pattschull G, Francke S, Wolter P, Hauser S, Murphy DJ, Garcia P, Rosenwald A, Gaubatz S (2017) An important role for Myb-MuvB and its target gene KIF23 in a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 36(1):110–121. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.181
Isakson P, Lystad AH, Breen K, Koster G, Stenmark H, Simonsen A (2013) TRAF6 mediates ubiquitination of KIF23/MKLP1 and is required for midbody ring degradation by selective autophagy. Autophagy 9(12):1955–1964. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.26085
Jian W, Deng XC, Munankarmy A, Borkhuu O, Ji CL, Wang XH, Zheng WF, Yu YH, Zhou XQ, Fang L (2021) KIF23 promotes triple negative breast cancer through activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Gland Surg 10(6):1941–1950. https://doi.org/10.21037/gs-21-19
Kahn M (2014) Can we safely target the WNT pathway? Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(7):513–532. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4233
Kato T, Wada H, Patel P, Hu HP, Lee D, Ujiie H, Hirohashi K, Nakajima T, Sato M, Kaji M, Kaga K, Matsui Y, Tsao MS, Yasufuku K (2016) Overexpression of KIF23 predicts clinical outcome in primary lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 92:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.11.018
Kong D, Li Y, Wang Z, Sarkar FH (2011) Cancer stem cells and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-phenotypic cells: are they cousins or twins? Cancers 3(1):716–729. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers30100716
Li J, Ying J, Fan Y, Wu L, Ying Y, Chan AT, Srivastava G, Tao Q (2010) WNT5A antagonizes WNT/β-catenin signaling and is frequently silenced by promoter CpG methylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 10(6):617–624. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.10.6.12609
Li T, Li Y, Gan Y, Tian R, Wu Q, Shu G, Yin G (2019a) Methylation-mediated repression of MiR-424/503 cluster promotes proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells through targeting the hub gene KIF23. Cell Cycle 18(14):1601–1618. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1624112
Li XL, Ji YM, Song R, Li XN, Guo LS (2019b) KIF23 promotes gastric cancer by stimulating cell proliferation. Dis Markers 2019:9751923. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9751923
Li N, Yu Y, Wang B (2020) Downregulation of AAA-domain-containing protein 2 restrains cancer stem cell properties in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via blockade of the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 319(1):C93-c104. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00133.2019
Li S, Zhang Y, He Z, Xu Q, Li C, Xu B (2022) Knockdown of circMYOF inhibits cell growth, metastasis, and glycolysis through miR-145-5p/OTX1 regulatory axis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Funct Integr Genomics 22(4):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00862-8
Liljeholm M, Irvine AF, Vikberg AL, Norberg A, Month S, Sandström H, Wahlin A, Mishima M, Golovleva I (2013) Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia type III (CDA III) is caused by a mutation in kinesin family member, KIF23. Blood 121(23):4791–4799. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-10-461392
Lucanus AJ, Yip GW (2018) Kinesin superfamily: roles in breast cancer, patient prognosis and therapeutics. Oncogene 37(7):833–838. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.406
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Kohno S, Nakao K (2010) MicroRNAs and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Digestion 82(3):138–144. https://doi.org/10.1159/000310918
Nislow C, Lombillo VA, Kuriyama R, McIntosh JR (1992) A plus-end-directed motor enzyme that moves antiparallel microtubules in vitro localizes to the interzone of mitotic spindles. Nature 359(6395):543–547. https://doi.org/10.1038/359543a0
Nusse R, Clevers H (2017) Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 169(6):985–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.016
Radisky ES, Radisky DC (2010) Matrix metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 15(2):201–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-010-9177-x
Shade A, Handelsman J (2012) Beyond the Venn diagram: the hunt for a core microbiome. Environ Microbiol 14(1):4–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02585.x
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(43):15545–15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Sung CO, Park CK, Kim SH (2011) Classification of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotypes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is strongly associated with patient prognosis. Mod Pathol 24(8):1060–1068. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2011.59
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2(6):442–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc822
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65(2):87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
Wang LD, Zhou FY, Li XM et al (2010) Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54. Nat Genet 42(9):759–763. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.648
Wang L, Wang Y, Bi J (2022a) In silico development and experimental validation of a novel 7-gene signature based on PI3K pathway-related genes in bladder cancer. Funct Integr Genomics 22(5):797–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00884-2
Wang S, Li W, Yang L, Yuan J, Wang L, Li N, Zhao H (2022b) CircPVT1 facilitates the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-143-3p/SLC7A11 axis through MAPK signaling pathway. Funct Integr Genomics 22(5):891–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00865-5
Wei SC, Fattet L, Yang J (2015) The forces behind EMT and tumor metastasis. Cell Cycle 14(15):2387–2388. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2015.1063296
Yoshida J, Ishikawa T (2019) Clinical significance of soluble forms of immune checkpoint molecules in advanced esophageal cancer. Med Oncol 36(7):60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-019-1285-x
Zhang DY, Lei JS, Sun WL, Wang DD, Lu Z (2020) Follistatin Like 5 (FSTL5) inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin Med J 133(15):1798–1804. https://doi.org/10.1097/cm9.0000000000000847
Zhong YB, Shan AJ, Lv W, Wang J, Xu JZ (2018) Long non-coding RNA LINC00675 inhibits tumorigenesis and EMT via repressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(23):8288–8297. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201812_16526
Zhou Z, Cheng Y, Jiang Y, Liu S, Zhang M, Liu J, Zhao Q (2018) Ten hub genes associated with progression and prognosis of pancreatic carcinoma identified by co-expression analysis. Int J Biol Sci 14(2):124–136. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.22619
Zhou P, Li Y, Li B, Zhang M, Liu Y, Yao Y, Li D (2019) NMIIA promotes tumor growth and metastasis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and EMT in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 38(27):5500–5515. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0806-6
Zhu C, Bossy-Wetzel E, Jiang W (2005) Recruitment of MKLP1 to the spindle midzone/midbody by INCENP is essential for midbody formation and completion of cytokinesis in human cells. Biochem J 389(2):373–381. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20050097
Zou JX, Duan Z, Wang J, Sokolov A, Xu J, Chen CZ, Li JJ, Chen HW (2014) Kinesin family deregulation coordinated by bromodomain protein ANCCA and histone methyltransferase MLL for breast cancer cell growth, survival, and tamoxifen resistance. Mol Cancer Res 12(4):539–549. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-13-0459
Funding
This study was funded by the Joint Construction Project of Henan Provincial Medical Science and Technology Program (No. LHGJ20200902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q.X. and X.L. conducted the experiments and drafted the manuscript. Y.L. and J.Y. analyzed the results and conducted the bioinformatics analysis. A.Y. conceived and designed this study. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have consented this study to publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Quanxiao Xu and Xianzhe Li are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Li, X., Li, Y. et al. Kinesin family member 23 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal carcinoma by inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 154 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01088-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01088-y