Abstract
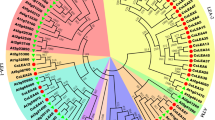
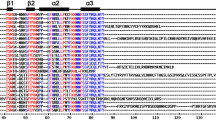
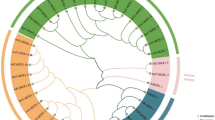
The tea plant is an important commercial horticulture crop cultivated worldwide. Yield and quality of this plant are influenced by abiotic stress. The bHLH family transcription factors play a pivotal role in the growth and development, including abiotic stress response, of plants. A growing number of bHLH proteins have been functionally characterized in plants. However, few studies have focused on the bHLH proteins in tea plants. In this study, 120 CsbHLH TFs were identified from tea plants using computational prediction method. Structural analysis detected 23 conservative residues, with over 50% identities in the bHLH domain. Moreover, 103 CsbHLH proteins were assumed to bind DNA and encompassed 98 E-Box binders and 85 G-Box binders. The CsbHLH proteins were grouped into 20 subfamilies based on phylogenetic analysis and a previous classification system. A survey of transcriptome profiling screened 22 and 39 CsbHLH genes that were upregulated under heat and drought stress. Nine CsbHLH genes were validated using qRT-PCR. Results were approximately in accordance with transcriptome data. These genes could be induced by one or more abiotic stresses.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- AIB:
-
ABA-inducible bHLH-type transcription factor
- bHLH:
-
Basic helix-loop-helix
- BLAST:
-
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
- BRs:
-
Brassinosteroids
- CBF:
-
C-repeat binding factor
- COE:
-
Collier/Olf-1/EBF
- FPKM:
-
Fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- HMM:
-
Hidden Markov model
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- MEGA:
-
Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis
- MEME:
-
Multiple Em for motif elicitation
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- NJ:
-
Neighbor-joining
- PAS:
-
Per-Arnt-Sim
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- RNA-Seq:
-
RNA sequencing
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
References
Abe H, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao T, Iwasaki T, Hosokawa D, Shinozaki K (1997) Role of Arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought-and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 9(10):1859–1868
Ahmad A, Niwa Y, Goto S, Ogawa T, Shimizu M, Suzuki A, Kobayashi K, Kobayashi H (2015) bHLH106 integrates functions of multiple genes through their G-box to confer salt tolerance on Arabidopsis. PLoS One 10(5):e0126872
Akula R, Ravishankar GA (2011) Influence of abiotic stress signals on secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Signal Behav 6(11):1720–1731
Atchley WR, Fitch WM (1997) A natural classification of the basic helix–loop–helix class of transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(10):5172–5176
Atchley WR, Terhalle W, Dress A (1999) Positional dependence, cliques, and predictive motifs in the bHLH protein domain. J Mol Evol 48(5):501–516
Bailey PC, Martin C, Toledo-Ortiz G, Quail PH, Huq E, Heim MA, Jakoby M, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2003) Update on the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 15(5):2497–2502
Capella-Gutiérrez S, Silla-Martínez JM, Gabaldón T (2009) trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25(15):1972–1973
Carretero-Paulet L, Galstyan A, Roig-Villanova I, Martínez-García JF, Bilbao-Castro JR, Robertson DL (2010) Genome-wide classification and evolutionary analysis of the bHLH family of transcription factors in Arabidopsis, poplar, rice, moss, and algae. Plant Physiol 153(3):1398–1412
Castillon A, Shen H, Huq E (2007) Phytochrome interacting factors: central players in phytochrome-mediated light signaling networks. Trends Plant Sci 12(11):514–521
Chen Y, Yu M, Xu J, Chen X, Shi J (2009) Differentiation of eight tea (Camellia sinensis) cultivars in China by elemental fingerprint of their leaves. J Sci Food Agric 89(14):2350–2355
Chinnusamy V, Ohta M, Kanrar S, Lee B-H, Hong X, Agarwal M, Zhu J-K (2003) ICE1: a regulator of cold-induced transcriptome and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 17(8):1043–1054
Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21(18):3674–3676
Deng W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Cheng H, Xue Y (2014) HemI: a toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PLoS One 9(11):e111988
Duek PD, Fankhauser C (2003) HFR1, a putative bHLH transcription factor, mediates both phytochrome a and cryptochrome signalling. Plant J 34(6):827–836
Eddy SR (2008) A probabilistic model of local sequence alignment that simplifies statistical significance estimation. PLoS Comput Biol 4(5):e1000069
Feller A, Machemer K, Braun EL, Grotewold E (2011) Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J 66(1):94–116
Fischer S, Brunk BP, Chen F, Gao X, Harb OS, Iodice JB, Shanmugam D, Roos DS, Stoeckert CJ (2011) Using OrthoMCL to assign proteins to OrthoMCL-DB groups or to cluster proteomes into new Ortholog groups. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 6(12):11–16 12. 19
Friedrichsen DM, Nemhauser J, Muramitsu T, Maloof JN, Alonso J, Ecker JR, Furuya M, Chory J (2002) Three redundant brassinosteroid early response genes encode putative bHLH transcription factors required for normal growth. Genetics 162(3):1445–1456
Fursova OV, Pogorelko GV, Tarasov VA (2009) Identification of ICE2, a gene involved in cold acclimation which determines freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 429(1–2):98–103
Gilmour SJ, Sebolt AM, Salazar MP, Everard JD, Thomashow MF (2000) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis CBF3transcriptional activator mimics multiple biochemical changes associated with cold acclimation. Plant Physiol 124(4):1854–1865
Goodrich J, Carpenter R, Coen ES (1992) A common gene regulates pigmentation pattern in diverse plant species. Cell 68(5):955–964
Gremski K, Ditta G, Yanofsky MF (2007) The HECATE genes regulate female reproductive tract development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 134(20):3593–3601
Haak DC, Fukao T, Grene R, Hua Z, Ivanov R, Perrella G, Li S (2017) Multilevel regulation of abiotic stress responses in plants. Front Plant Sci 8:1564
Hall T (2011) BioEdit: an important software for molecular biology. GERF bull. Biosci 2(1):60–61
Heim MA, Jakoby M, Werber M, Martin C, Weisshaar B, Bailey PC (2003) The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in plants: a genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity. Mol Biol Evol 20(5):735–747. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msg088
Jiang Y, Yang B, Deyholos MK (2009) Functional characterization of the Arabidopsis bHLH92 transcription factor in abiotic stress. Mol Gen Genomics 282(5):503–516
Jin J, Tian F, Yang D-C, Meng Y-Q, Kong L, Luo J, Gao G (2017) PlantTFDB 4.0: toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 45(D1):D1040–D1045
Kavas M, Baloğlu MC, Atabay ES, Ziplar UT, Daşgan HY, Ünver T (2016) Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of common bean bHLH transcription factors in response to excess salt concentration. Mol Gen Genomics 291(1):129–143
Kiribuchi K, Jikumaru Y, Kaku H, MINAMI E, HASEGAWA M, KODAMA O, SETO H, OKADA K, NOJIRI H, YAMANE H (2005) Involvement of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor RERJ1 in wounding and drought stress responses in rice plants. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69(5):1042–1044
Komatsu M, Maekawa M, Shimamoto K, Kyozuka J (2001) The LAX1 and FRIZZY PANICLE 2 genes determine the inflorescence architecture of rice by controlling rachis-branch and spikelet development. Dev Biol 231(2):364–373
Kondou Y, Nakazawa M, Kawashima M, Ichikawa T, Yoshizumi T, Suzuki K, Ishikawa A, Koshi T, Matsui R, Muto S (2008) RETARDED GROWTH OF EMBRYO1, a new basic helix-loop-helix protein, expresses in endosperm to control EMBRYO growth. Plant Physiol 147(4):1924–1935
Kurbidaeva A, Novokreshchenova M, Ezhova T (2015) ICE genes in Arabidopsis thaliana: clinal variation in DNA polymorphism and sequence diversification. Biol Plant 59:245–252
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown N, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948
Ledent V, Vervoort M (2001) The basic helix-loop-helix protein family: comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis. Genome Res 11(5):754–770
Lee C-M, Thomashow MF (2012) Photoperiodic regulation of the C-repeat binding factor (CBF) cold acclimation pathway and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(37):15054–15059
Lee B-H, Henderson DA, Zhu J-K (2005) The Arabidopsis cold-responsive transcriptome and its regulation by ICE1. Plant Cell 17(11):3155–3175
Li X, Duan X, Jiang H, Sun Y, Tang Y, Yuan Z, Guo J, Liang W, Chen L, Yin J (2006) Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141(4):1167–1184
Li H, Sun J, Xu Y, Jiang H, Wu X, Li C (2007) The bHLH-type transcription factor AtAIB positively regulates ABA response in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 65(5):655–665
Li MY, Wang F, Jiang Q, Ma J, Xiong AS (2014) Identification of SSRs and differentially expressed genes in two cultivars of celery (Apium graveolens L.) by deep transcriptome sequencing. Hortic Res 1:10
Liljegren SJ, Roeder AH, Kempin SA, Gremski K, Østergaard L, Guimil S, Reyes DK, Yanofsky MF (2004) Control of fruit patterning in Arabidopsis by INDEHISCENT. Cell 116(6):843–853
Lindemose S, O'Shea C, Jensen MK, Skriver K (2013) Structure, function and networks of transcription factors involved in abiotic stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 14(3):5842–5878
Liu W, Tai H, Li S, Gao W, Zhao M, Xie C, Li WX (2014) bHLH122 is important for drought and osmotic stress resistance in Arabidopsis and in the repression of ABA catabolism. New Phytol 201(4):1192–1204
Liu Z-W, Wu Z-J, Li X-H, Huang Y, Li H, Wang Y-X, Zhuang J (2016) Identification, classification, and expression profiles of heat shock transcription factors in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) under temperature stress. Gene 576:52–59
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lou W, Sun S, Wu L, Sun K (2015) Effects of climate change on the economic output of the Longjing-43 tea tree. 1972–2013. Int J Biometeorol 59(5):593–603
Ludwig SR, Habera LF, Dellaporta SL, Wessler SR (1989) Lc, a member of the maize R gene family responsible for tissue-specific anthocyanin production, encodes a protein similar to transcriptional activators and contains the myc-homology region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86(18):7092–7096
Murre C, McCaw PS, Baltimore D (1989) A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell 56(5):777–783
Nesi N, Debeaujon I, Jond C, Pelletier G, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2000) The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis siliques. Plant Cell 12(10):1863–1878
Pires N, Dolan L (2010) Origin and diversification of basic-helix-loop-helix proteins in plants. Mol Biol Evol 27(4):862–874
Quattrocchio F, Wing JF, Leppen HT, Mol JN, Koes RE (1993) Regulatory genes controlling anthocyanin pigmentation are functionally conserved among plant species and have distinct sets of target genes. Plant Cell 5(11):1497–1512
Rajani S, Sundaresan V (2001) The Arabidopsis myc/bHLH gene ALCATRAZ enables cell separation in fruit dehiscence. Curr Biol 11(24):1914–1922
Riechmann JL, Ratcliffe OJ (2000) A genomic perspective on plant transcription factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3(5):423–434
Sailsbery JK, Dean RA (2012) Accurate discrimination of bHLH domains in plants, animals, and fungi using biologically meaningful sites. BMC Evol Biol 12:154
Sakamoto W, Ohmori T, Kageyama K, Miyazaki C, Saito A, Murata M, Noda K, Maekawa M (2001) The purple leaf (Pl) locus of rice: the Plw allele has a complex organization and includes two genes encoding basic helix-loop-helix proteins involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 42(9):982–991
Song XM, Huang ZN, Duan WK, Ren J, Liu TK, Li Y, Hou XL (2014) Genome-wide analysis of the bHLH transcription factor family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Mol Gen Genomics 289(1):77–91
Sun H, Fan HJ, Ling HQ (2015) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the bHLH gene family in tomato. BMC Genomics 16:9
Szécsi J, Joly C, Bordji K, Varaud E, Cock JM, Dumas C, Bendahmane M (2006) BIGPETALp, a bHLH transcription factor is involved in the control of Arabidopsis petal size. T. EMBO J 25(16):3912–3920
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729
Toledo-Ortiz G, Huq E, Quail PH (2003) The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 15(8):1749–1770
Wang Y, Jiang C-J, Li Y-Y, Wei C-L, Deng W-W (2012) CsICE1 and CsCBF1: two transcription factors involved in cold responses in Camellia sinensis. Plant Cell Rep 31(1):27–34
Wang Y-X, Liu Z-W, Wu Z-J, Li H, Zhuang J (2016a) Transcriptome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NAC gene family in tea plant [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze]. PLoS One 11(11):e0166727
Wang W, Xin H, Mingle Wang QM, Wang L, Kaleri NA, Wang Y, Li X (2016b) Transcriptomic analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms of drought-stress-induced decreases in Camellia sinensis leaf quality. Front Plant Sci 7:385
Wu Z-J, Li XH, Liu ZW, Xu Z-S, Zhuang J (2014) De novo assembly and transcriptome characterization: novel insights into catechins biosynthesis in Camellia sinensis. BMC Plant Biol 14:277
Yin J, Chang X, Kasuga T, Bui M, Reid MS, Jiang CZ (2015) A basic helix-loop-helixtranscription factor, PhFBH4, regulates flower senescence by modulating ethylene biosynthesis pathway in petunia. Hortic Res 2:15059
Yue H, Wang M, Liu S, Du X, Song W, Nie X (2016) Transcriptome-wide identification and expression profiles of the WRKY transcription factor family in broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) BMC Genomics 17:343
Zhang W, Sun Y, Timofejeva L, Chen C, Grossniklaus U, Ma H (2006) Regulation of Arabidopsis tapetum development and function by DYSFUNCTIONAL TAPETUM1 (DYT1) encoding a putative bHLH transcription factor. Development 133(16):3085–3095
Zhao L, Gao L, Wang H, Chen X, Wang Y, Yang H, Wei C, Wan X, Xia T (2013) The R2R3-MYB, bHLH, WD40, and related transcription factors in flavonoid biosynthesis. Funct Integr Genomics 13(1):75–98
Zhou L, Xu H, Mischke S, Meinhardt LW, Zhang D, Zhu X, Li X, Fang W (2014) Exogenous abscisic acid significantly affects proteome in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) exposed to drought stress. Hortic Res 1:14029
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570691).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: JZ, XC. Performed the experiments: XC, YXW, ZWL, WLW, HL. Analyzed the data: XC, YXW, JZ. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: JZ. Wrote the paper: XC. Revised the paper: JZ, XC, YXW. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, X., Wang, YX., Liu, ZW. et al. Transcriptome-wide identification and expression profile analysis of the bHLH family genes in Camellia sinensis. Funct Integr Genomics 18, 489–503 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0608-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0608-x