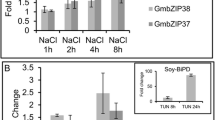
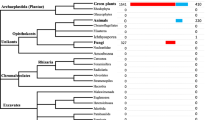
Abstract
Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-α (LITAF) is a membrane protein that is highly dependent on correct location to exert transcription factor activity and protein quality control. In humans, LITAF, PIG7 (p53-inducible gene 7), and SIMPLE (small integral membrane protein of the lysosome/late endosome) refer to the same gene, which acts as a tumor suppressor. Several studies have shown that the transcription factor activity and nuclear translocation of LITAF protein are critical for the induction of several immune cells via classical pathways. In plants, LITAF protein corresponds to the plasma membrane protein AtGILP (Arabidopsis thaliana GSH-induced LITAF domain protein). The conservation of LITAF proteins across species and their putative role is still unclear. In this study, we investigate the LITAF-containing proteins, which we call GILP proteins, in Viridiplantae. We identified a total of 59 genes in 46 species, whose gene copies range from one to three. Phylogenetic analysis showed that multiple copies were originated via block duplication posteriorly to monocot and eudicot separation. Analysis of the LITAF domain of GILP proteins allowed the identification of a putative domain signature in Viridiplantae, containing a CXXCX41HXCPXC motif. The subcellular location for the majority of GILP proteins was predicted to be in the plasma membrane, based on a transmembrane domain positioned within the LITAF domain. In silico analysis showed that the GILP genes are neither tissue-specific nor ubiquitously expressed, being responsive to stress conditions. Finally, investigation of the GILP protein network resulted in the identification of genes whose families are known to be involved with biotic and/or abiotic stress responses. Together, the expression modulation of GILP genes associated with their plasma membrane location suggests that they could act in the signaling of biotic/abiotic stress response in plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abba MC, Drake JA, Hawkins KA, Yuhui H, Hongxia S, Notcovich C, Gaddis S, Sahin A, Baggerly K, Aldaz CM (2004) Transcriptomic changes in human breast cancer progression as determined by serial analysis of gene expression. Breast cancer research: BCR 6(5):R499–R513
Andolfo, G.; Ercolano, M.R. (2015) Plant innate immunity multicomponent model. Frontiers in plant science, 6(November), p.987
Bozorgmehr JEHJ (2012) The effect of functional compensation among duplicate genes can constrain their evolutionary divergence. Genet, 91:1
Cabreira C, Cagliari A, Bücker-Neto L, Margis-Pinheiro M, de Freitas LB, Bodanese-Zanettini MH (2015) The phylogeny and evolutionary history of the Lesion Simulating Disease (LSD) gene family in Viridiplantae. Mol Genet Genomics 290(6):2107–2119
Chin LS, Lee SM, Li L (2013) Simple: a new regulator of endosomal trafficking and signaling in health and disease. Communicative and Integrative Biology 6(3)
Coll, N. S.; Vercammen, D.; Smidler, A.; Clover, C.; Van Breusegem, F.; Dangl, J. L.; Epple, P. (2010). Arabidopsis type I metacaspases control cell death. Science (New York, N.Y.), 330(6009), pp.1393–1397
Coll NS, Epple P, Dangl JL (2011) Programmed cell death in the plant immune system. Cell Death Differ 18(8):1247–1256
Cona A, Rea G, Angelini R, Federico R, Tavladoraki P (2006) Functions of amine oxidases in plant development and defence. Trends Plant Sci 11(2):80–88
Dietrich RA, Richberg MH, Schmidt R, Dean C, Dangl JL (1997) A novel zinc finger protein is encoded by the arabidopsis LSD1 gene and functions as a negative regulator of plant cell death. Cell 88(5):685–694
Ding B, Wang G-L (2015) Chromatin versus pathogens: the function of epigenetics in plant immunity. Front Plant Sci 6:675
Drummond, A. J.; Rambaut, A. (2007) BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC evolutionary biology, 7(1), p.214
Epple P, Mack AA, Morris VR, Dangl JL (2003) Antagonistic control of oxidative stress-induced cell death in Arabidopsis by two related, plant-specific zinc finger proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(11):6831–6836
Fagundes D, Bohn B, Cabreira C, Leipelt F, Dias N, Bodanese-Zanettini MH, Cagliari A (2015) Caspases in plants: metacaspase gene family in plant stress responses. Functional and Integrative Genomics 15(6):639–649
Fernandez-Cobo M, Holland JF, Pogo BG (2006) Transcription profiles of non-immortalized breast cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer 6:992006
He S, Tan G, Liu Q, Huang K, Ren J, Zhang X, Yu X, Huang P, An C (2011) The lsd1-interacting protein gilp is a litaf domain protein that negatively regulates hypersensitive cell death in arabidopsis. PLoS One 6(4)
Jain M, Nijhawan A, Arora R, Agarwal P, Ray S, Sharma P, Kapoor S, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP (2007) F-box proteins in rice: genome-wide analysis, classification, temporal and spatial gene expression during panicle and seed development, and regulation by light and abiotic stress. Plant Physiol 143(4):1467–1483
Kaminaka H, Nake C, Epple P, Dittgen J, Schutze K, Chaban C, Holt BFIII, Merkle T, Schafer E, Harter K, Dangl JL (2006) bZIP10-LSD1 antagonism modulates basal defense and cell death in Arabidopsis following infection. EMBO J 25(18):4400–4411
Lacerda, A. F.; Hartjes, E.; Brunetti, C. R. (2014) LITAF mutations associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 1C show mislocalization from the late endosome/lysosome to the mitochondria. PloS one, 9(7), p.e103454
Lawton-Rauh A (2003) Evolutionary dynamics of duplicated genes in plants. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29(3):396–409
Libault M., Farmer A., Joshi T., Takahashi K., Langley R. J., Franklin L. D., et al. (2010). An integrated transcriptome atlas of the crop model Glycine max, and its use in comparative analyses in plants. Plant J. 63, 86–99. 1
Ludes-Meyers JH, Kil H, Bednarek AK, Drake J, Bedford MT, Aldaz CM (2004) WWOX binds the specific proline-rich ligand PPXY: identification of candidate interacting proteins. Oncogene 23(29):5049–5055
Magadum S, Banerjee U, Murugan P, Gangapur D, Ravikesavan R (2013) Gene duplication as a major force in evolution. J Genet 92(1):155–161
Marcussen, T.; Sandve S. R.; Heier, L.; Spannagl, M.; Pfeifer, M.; International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium.; Jakobsen, K. S.; Wulff, B. B.; Steuernagel, B.; Mayer, K. F.; Olsen, O. A. (2014) Ancient hybridizations among the ancestral genomes of bread wheat. Science, 345(6194), p.1250092
Matsumura Y, Matsumura Y, Nishigori C, Horio T, Miyachi Y (2004) PIG7/LITAF gene mutation and overexpression of its gene product in extramammary Paget’s disease. Int J Cancer 111:218–223
Merrill JC, Jou J, Constable C, Leeman SE, Amar S (2011) Whole-body deletion of LPS-induced TNF- factor (LITAF) markedly improves experimental endotoxic shock and inflammatory arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(52):21247–21252
Mohanta TK, Park Y-H, Bae H (2016) Novel genomic and evolutionary insight of WRKY transcription factors in plant lineage. Sci Rep 6:37309
Monaghan J, Zipfel C (2012) Plant pattern recognition receptor complexes at the plasma membrane. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15(4):349–357
Moriwaki Y, Begum NA, Kobayashi M, Matsumoto M, Toyoshima K, Seya T (2001) Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin and its cell wall complex induce a novel lysosomal membrane protein, SIMPLE, that bridges the missing link between lipopolysaccharide and p53-inducible gene, LITAF(PIG7), and estrogen-inducible gene, EET-1. J Biol Chem 276(25):23065–23076
Myokai F, Takashiba S, Lebo R, Amar S (1999) A novel lipopolysaccharide-induced transcription factor regulating tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression: molecular cloning, sequencing, characterization, and chromosomal assignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(8):4518–4523
Pant SR, Krishnavajhala A, McNeece BT, Lawrence, GW, Klink VP (2015) The syntaxin 31-induced gene, LESION SIMULATING DISEASE1 (LSD1), functions in Glycine max defense to the root parasite Heterodera glycines. Plant Signal Behav, 10(1):e977737
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1997) A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature 389(6648):300–305
Ponting CP, Mott R, Bork P, Copley RR (2001) Novel protein domains and repeats in Drosophila melanogaster: insights into structure, function, and evolution. Genome Res 11(12):1996–2008
Schmid M, Davison TS, Henz SR, Pape UJ, Demar M, Vingron M, Schölkopf B, Weigel D, Lohmann JU (2005) A gene expression map of Arabidopsis thaliana development. Nat Genet 37(5):501–506
Shirk AJ, Anderson SK, Hashemi SH, Chance PF, Bennett CL (2005) SIMPLE interacts with NEDD4 and TSG101: evidence for a role in lysosomal sorting and implications for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Neurosci Res 82(1):43–50
Sinkiewicz-Darol E, Lacerda AF, Kostera-Pruszczyk A, Potulska-Chromik A, Sokołowska B, Kabzińska D, Brunetti CR, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I, Kochański A (2015) The LITAF/SIMPLE I92V sequence variant results in an earlier age of onset of CMT1A/HNPP diseases. Neurogenetics 16:27–32
Smith RC, Eappen AG, Radtke AJ, Jacobs-Lorena M (2012) Regulation of Anti-Plasmodium Immunity by a LITAF-like Transcription Factor in the Malaria Vector Anopheles gambiae. PLoS Pathog, 8(10):e1002965
Stucchi A, Reed K, O'Brien M, Cerda S, Andrews C, Gower A, Bushell K, Amar S, Leeman S, Becker J (2006) A new transcription factor that regulates TNF-alpha gene expression, LITAF, is increased in intestinal tissues from patients with CD and UC. Inflamm Bowel Dis, Jul 12(7):581–7
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Tang X, Fenton MJ, Amar S (2003) Identification and functional characterization of a novel binding site on TNF-alpha promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100(7):4096–101
Tang X, Metzger D, Leeman S, Amar S (2006) ImmunologyLPS-induced TNF-α factor (LITAF)-deficient mice express reduced LPS-induced cytokine: Evidence for LITAF-dependent LPS signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103(37):13777–13782
Toufighi K, Brady SM, Austin R, Ly E, Provart NJ (2005) The botany array resource: e-northerns, expression angling, and promoter analyses. Plant J 43:153–163
Wang D, Liu J, Tang K, Xu Z, Xiong X, Rao Q, Wang M, Wang J (2009) Expression of pig7 gene in acute leukemia and its potential to modulate the chemosensitivity of leukemic cells. Leuk Res 33(1):28–38
Wang F, Vandepoele K, Van Lijsebettens M (2012) Tetraspanin genes in plants. Plant Sci 190:9–15
Zhu, H.; Guariglia, S.; Yu, R. Y.; Li, W.; Brancho, D.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D.; Salzer, J.; Bennett, C.; Chow, C. W. (2013) Mutation of SIMPLE in Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1C alters production of exosomes. Mol Biol Cell, 24(11), pp. 1619–1637, S1-3
Zhou J, Yang Z, Tsuji T, Gong J, Xie J, Chen C, Li W, Amar S, Luo Z (2011) LITAF and TNFSF15, two downstream targets of AMPK, exert inhibitory effects on tumor growth. Oncogene 30:1892–1900
Zou J, Guo P, Lv N, Huang D (2015) Lipopolysaccharide-induce tumor necrosis factor-α enhances inflammation and is associated with cancer. Mol Med Rep 12(5)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
Detailed data on gene acronym and locus of GILP genes. (PDF 78 kb)
ESM 2
Prediction of subcellular localization of the proteins encoded by GILP genes. The analysis of the existence of signal peptide was performed using the tools SignalP and TargetP. Considering the reliability score of Target, 1 indicates the strongest prediction. Phobius and TMHMM tools were employed to predict the existence of transmembrane domain. (PDF 53 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cabreira-Cagliari, C., Fagundes, D.G.S., Dias, N.C.F. et al. GILP family: a stress-responsive group of plant proteins containing a LITAF motif. Funct Integr Genomics 18, 55–66 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-017-0574-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-017-0574-8