Abstract
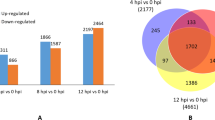
Low temperatures cause severe damage to none cold hardy grapevines. A preliminary survey with Solexa sequencing technology was used to analyze gene expression profiles of cold hardy Vitis amurensis ‘Zuoshan-1’ after cold acclimation at 4 °C for 48 h. A total of 16,750 and 18,068 putative genes were annotated for 4 °C-treated and control library, respectively. Among them, 393 genes were upregulated for at least 20-fold, while 69 genes were downregulated for at least 20-fold under the 4 °C treatment for 48 h. A subset of 101 genes from this survey was investigated further using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Genes associated with signaling events in pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-triggered immunity (PTI), including generation of calcium signals (CNGC, CMLs), jasmonic acid signal (JAZ1), oxidative burst (Rboh), and phosphorylation (FLS2, BAK, MEKK1, MKKs) cascades, were upregulated after cold acclimation. Disease resistance genes (RPM1, RPS5, RIN4, PBS1) in the process of effector-triggered immunity (ETI) were also upregulated in the current condition. Defense-related genes (WRKYs, PR1, MIN7) involved in both PTI and ETI processes were abundantly expressed after cold acclimation. Our results indicated that plant–pathogen interaction pathways were linked to the cold acclimation in V. amurensis grapevine. Other biotic- and abiotic-related genes, such as defense (protein phosphatase 2C, U-box domain proteins, NCED1, stilbene synthase), transcription (DREBs, MYBs, ERFs, ZFPs), signal transduction (kinase, calcium, and auxin signaling), transport (ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, auxin:hydrogen symporter), and various metabolism, were also abundantly expressed in the cold acclimation of V. Amurensis ‘Zuoshan-1’ grapevine. This study revealed a series of critical genes and pathways to delineate important biological processes affected by low temperature in ‘Zuoshan-1’.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AC’t Hoen P, Ariyurek Y, Thygesen HH et al (2008) Deep sequencing-based expression analysis shows major advances in robustness, resolution and inter-lab portability over five microarray platforms. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e141
Agarwal M, Hao Y, Kapoor A et al (2006) A R2R3 type MYB transcription factor is involved in the cold regulation of CBF genes and in acquired freezing tolerance. J Biol Chem 281:37636–37645
Ait Barka E, Audran J (1997) Response of champenoise grapevine to low temperatures: changes of shoot and bud proline concentrations in response to low temperatures and correlations with freezing tolerance. J Horticult Sci 72:577–582
Alexander D, Goodman RM, Gut-Rella M et al (1993) Increased tolerance to two oomycete pathogens in transgenic tobacco expressing pathogenesis-related protein 1a. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:7327–7331
Anchordoguy TJ, Rudolph AS, Carpenter JF et al (1987) Modes of interaction of cryoprotectants with membrane phospholipids during freezing. Cryobiology 24:324–331
Antikainen M, Griffith M (1997) Antifreeze protein accumulation in freezing‐tolerant cereals. Physiol Plant 99:423–432
Beck EH, Heim R, Hansen J (2004) Plant resistance to cold stress: mechanisms and environmental signals triggering frost hardening and dehardening. J Biosci 29:449–459
Benedict C, Skinner JS, Meng R et al (2006) The CBF1‐dependent low temperature signalling pathway, regulon and increase in freeze tolerance are conserved in Populus spp. Plant Cell Environ 29:1259–1272
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Methodological) 57:289–300
Berger D, Altmann T (2000) A subtilisin-like serine protease involved in the regulation of stomatal density and distribution in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev 14:1119–1131
Brüggemann W, Beyel V, Brodka M et al (1999) Antioxidants and antioxidative enzymes in wild-type and transgenic Lycopersicon genotypes of different chilling tolerance. Plant Sci 140:145–154
Carpaneto A, Ivashikina N, Levchenko V et al (2007) Cold transiently activates calcium-permeable channels in Arabidopsis mesophyll cells. Plant Physiol 143:487–494
Chen R, Jiang H, Li L et al (2012) The Arabidopsis mediator subunit MED25 differentially regulates jasmonate and abscisic acid signaling through interacting with the MYC2 and ABI5 transcription factors. Plant Cell Online 24:2898–2916
Christersson L (1978) The influence of photoperiod and temperature on the development of frost hardiness in seedlings of Pinus silvestris and Picea abies. Physiol Plant 44:288–294
Christie PJ, Alfenito MR, Walbot V (1994) Impact of low-temperature stress on general phenylpropanoid and anthocyanin pathways: enhancement of transcript abundance and anthocyanin pigmentation in maize seedlings. Planta 194:541–549
Cocozza C, Lasserre B, Giovannelli A et al (2009) Low temperature induces different cold sensitivity in two poplar clones (Populus × canadensis Mönch ‘I-214’ and P. deltoides Marsh. ‘Dvina’). J Exp Bot 60:3655–3664
Collinge M, Boller T (2001) Differential induction of two potato genes, Stprx2 and StNAC, in response to infection by Phytophthora infestans and to wounding. Plant Mol Biol 46:521–529
Cook D, Fowler S, Fiehn O et al (2004) A prominent role for the CBF cold response pathway in configuring the low-temperature metabolome of Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15243–15248
Dai R, Ge H, Howard S et al (2012) Transcriptional expression of stilbene synthase genes are regulated developmentally and differentially in response to powdery mildew in Norton and Cabernet Sauvignon grapevine. Plant Sci 197:70–76
Doherty CJ, Van Buskirk HA, Myers SJ et al (2009) Roles for Arabidopsis CAMTA transcription factors in cold-regulated gene expression and freezing tolerance. Plant Cell Online 21:972–984
Dong C-H, Agarwal M, Zhang Y et al (2006) The negative regulator of plant cold responses, HOS1, is a RING E3 ligase that mediates the ubiquitination and degradation of ICE1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:8281–8286
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S et al (2000) The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 5:199–206
Fan J, Hill L, Crooks C et al (2009) Abscisic acid has a key role in modulating diverse plant-pathogen interactions. Plant Physiol 150:1750–1761
Fowler S, Thomashow MF (2002) Arabidopsis transcriptome profiling indicates that multiple regulatory pathways are activated during cold acclimation in addition to the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Cell 14:1675–1690
Fuchigami L, Weiser C, Evert D (1971) Induction of cold acclimation in Cornus stolonifera Michx. Plant Physiol 47:98–103
Fuller M, Telli G (1999) An investigation of the frost hardiness of grapevine (Vitis vinifera) during bud break. Ann Appl Biol 135:589–595
Gao Y, Li H, Deng D et al (2012) Characterization and expression analysis of the maize RING-H2 finger protein gene ZmXERICO responsive to plant hormones and abiotic stresses. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1529–1535
Gatschet M, Taliaferro C, Porter D et al (1996) A cold-regulated protein from bermudagrass crowns is a chitinase. Crop Sci 36:712–718
Gilmour SJ, Zarka DG, Stockinger EJ et al (1998) Low temperature regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF family of AP2 transcriptional activators as an early step in cold-induced COR gene expression. Plant J 16:433–442
Haake V, Cook D, Riechmann J et al (2002) Transcription factor CBF4 is a regulator of drought adaptation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 130:639–648
Hamel L-P, Benchabane M, Major I et al (2011) The genomics of poplar-rust interactions to improve tree resistance against fungal disease. BMC Proc 5(Suppl 7):I12
Hegedus D, Yu M, Baldwin D et al (2003) Molecular characterization of Brassica napus NAC domain transcriptional activators induced in response to biotic and abiotic stress. Plant Mol Biol 53:383–397
Hill L, Reimholz R, Schröder R et al (1996) The onset of sucrose accumulation in cold‐stored potato tubers is caused by an increased rate of sucrose synthesis and coincides with low levels of hexose‐phosphates, an activation of sucrose phosphate synthase and the appearance of a new form of amylase. Plant Cell Environ 19:1223–1237
Hincha DK, Meins F Jr, Schmitt JM (1997) [beta]-1,3-Glucanase is cryoprotective in vitro and is accumulated in leaves during cold acclimation. Plant Physiol 114:1077–1083
Hon WC, Griffith M, Chong P et al (1994) Extraction and isolation of antifreeze proteins from winter rye (Secale cereale L.) leaves. Plant Physiol 104:971–980
Hon WC, Griffith M, Mlynarz A et al (1995) Antifreeze proteins in winter rye are similar to pathogenesis-related proteins. Plant Physiol 109:879–889
Hu X, Liu L, Xiao B et al (2010) Enhanced tolerance to low temperature in tobacco by over-expression of a new maize protein phosphatase 2C, ZmPP2C2. J Plant Physiol 167:1307–1315
Jaglo KR, Kleff S, Amundsen KL et al (2001) Components of the Arabidopsis C-repeat/dehydration-responsive element binding factor cold-response pathway are conserved in Brassica napus and other plant species. Plant Physiol 127:910–917
John P (1997) Ethylene biosynthesis: the role of 1‐aminocyclopropane‐1‐carboxylate (ACC) oxidase, and its possible evolutionary origin. Physiol Plant 100:583–592
Jonak C, Kiegerl S, Ligterink W et al (1996) Stress signaling in plants: a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is activated by cold and drought. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:11274–11279
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329
Kang HM, Saltveit ME (2001) Activity of enzymatic antioxidant defense systems in chilled and heat shocked cucumber seedling radicles. Physiol Plant 113:548–556
Kaplan F, Kopka J, Haskell DW et al (2004) Exploring the temperature-stress metabolome of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136:4159–4168
Kim JC, Lee SH, Cheong YH et al (2001) A novel cold‐inducible zinc finger protein from soybean, SCOF‐1, enhances cold tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant J 25:247–259
Kim JY, Kim WY, Kwak KJ et al (2010) Zinc finger‐containing glycine‐rich RNA‐binding protein in Oryza sativa has an RNA chaperone activity under cold stress conditions. Plant Cell Environ 33:759–768
Knight MR, Campbell AK, Smith SM et al (1991) Transgenic plant aequorin reports the effects of touch and cold-shock and elicitors on cytoplasmic calcium. Nature 352:524–526
Knight H, Trewavas AJ, Knight MR (1996) Cold calcium signaling in Arabidopsis involves two cellular pools and a change in calcium signature after acclimation. Plant Cell Online 8:489–503
Korn M, Gartner T, Erban A et al (2010) Predicting Arabidopsis freezing tolerance and heterosis in freezing tolerance from metabolite composition. Mol Plant 3:224–235
Krol M, Huner NP (1985) Growth and development at cold-hardening temperatures. Pigment and benzoquinone accumulation in winter rye. Can J Bot 63:716–721
Kumar S, Kaur G, Nayyar H (2008) Exogenous application of abscisic acid improves cold tolerance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J Agron Crop Sci 194:449–456
Lafuente M, Zacarias L, Martínez-Téllez M et al (2001) Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase as related to ethylene in the development of chilling symptoms during cold storage of citrus fruits. J Agric Food Chem 49:6020–6025
Leyva A, Jarillo JA, Salinas J et al (1995) Low temperature induces the accumulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and chalcone synthase mRNAs of Arabidopsis thaliana in a light-dependent manner. Plant Physiol 108:39–46
Li C, Junttila O, Ernstsen A et al (2003) Photoperiodic control of growth, cold acclimation and dormancy development in silver birch (Betula pendula) ecotypes. Physiol Plant 117:206–212
Li ZT, Dhekney SA, Gray DJ (2011) PR-1 gene family of grapevine: a uniquely duplicated PR-1 gene from a Vitis interspecific hybrid confers high level resistance to bacterial disease in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 30:1–11
Lissarre M, Ohta M, Sato A, Miura K (2010) Cold-responsive gene regulation during cold acclimation in plants. Plant Signal Behav 5:948–952
Liu K, Wang L, Xu Y et al (2007) Overexpression of OsCOIN, a putative cold inducible zinc finger protein, increased tolerance to chilling, salt and drought, and enhanced proline level in rice. Planta 226:1007–1016
Liu H, Zhang H, Yang Y et al (2008) Functional analysis reveals pleiotropic effects of rice RING-H2 finger protein gene OsBIRF1 on regulation of growth and defense responses against abiotic and biotic stresses. Plant Mol Biol 68:17–30
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Llorente F, Oliveros JC, Martinez-Zapater JM et al (2000) A freezing-sensitive mutant of Arabidopsis, frs1, is a new aba3 allele. Planta 211:648–655
Mare C, Mazzucotelli E, Crosatti C et al (2004) Hv-WRKY38: a new transcription factor involved in cold- and drought-response in barley. Plant Mol Biol 55:399–416
Marin E, Divol F, Bechtold N et al (2006) Molecular characterization of three Arabidopsis soluble ABC proteins which expression is induced by sugars. Plant Sci 171:84–90
Maruyama K, Takeda M, Kidokoro S et al (2009) Metabolic pathways involved in cold acclimation identified by integrated analysis of metabolites and transcripts regulated by DREB1A and DREB2A. Plant Physiol 150:1972–1980
Mathiason K, He D, Grimplet J et al (2009) Transcript profiling in Vitis riparia during chilling requirement fulfillment reveals coordination of gene expression patterns with optimized bud break. Funct Integr Genomics 9:81–96
Medina J, Bargues M, Terol J et al (1999) The Arabidopsis CBF gene family is composed of three genes encoding AP2 domain-containing proteins whose expression is regulated by low temperature but not by abscisic acid or dehydration. Plant Physiol 119:463–470
Miguel G, Fontes C, Antunes D et al (2004) Anthocyanin concentration of “Assaria” pomegranate fruits during different cold storage conditions. BioMed Res Int 2004:338–342
Monroy AF, Dhindsa RS (1995) Low-temperature signal transduction: induction of cold acclimation-specific genes of alfalfa by calcium at 25 °C. Plant Cell Online 7:321–331
Monroy AF, Sarhan F, Dhindsa RS (1993) Cold-induced changes in freezing tolerance, protein phosphorylation, and gene expression (evidence for a role of calcium). Plant Physiol 102:1227–1235
Morrissy AS, Morin RD, Delaney A et al (2009) Next-generation tag sequencing for cancer gene expression profiling. Genome Res 19:1825–1835
Morsy MR, Jouve L, Hausman JF et al (2007) Alteration of oxidative and carbohydrate metabolism under abiotic stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes contrasting in chilling tolerance. J Plant Physiol 164:157–167
Mukhopadhyay A, Vij S, Tyagi AK (2004) Overexpression of a zinc-finger protein gene from rice confers tolerance to cold, dehydration, and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:6309–6314
Murray M, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Navarro M, Marque G, Ayax C et al (2009) Complementary regulation of four Eucalyptus CBF genes under various cold conditions. J Exp Bot 60:2713–2724
Nogueira FT, Schlögl PS, Camargo SR et al (2005) SsNAC23, a member of the NAC domain protein family, is associated with cold, herbivory and water stress in sugarcane. Plant Sci 169:93–106
Noji M, Inoue K, Kimura N et al (1998) Isoform-dependent differences in feedback regulation and subcellular localization of serine acetyltransferase involved in cysteine biosynthesis from Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 273:32739–32745
Nomura K, DebRoy S, Lee YH et al (2006) A bacterial virulence protein suppresses host innate immunity to cause plant disease. Science 313:220–223
Nordin Henriksson K, Trewavas A (2003) The effect of short‐term low‐temperature treatments on gene expression in Arabidopsis correlates with changes in intracellular Ca2+ levels. Plant Cell Environ 26:485–496
Novillo F, Alonso JM, Ecker JR et al (2004) CBF2/DREB1C is a negative regulator of CBF1/DREB1B and CBF3/DREB1A expression and plays a central role in stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:3985–3990
Novillo F, Medina J, Salinas J (2007) Arabidopsis CBF1 and CBF3 have a different function than CBF2 in cold acclimation and define different gene classes in the CBF regulon. PNAS 104:21002–21007
Peng X, Hu Y, Tang X et al (2012) Constitutive expression of rice WRKY30 gene increases the endogenous jasmonic acid accumulation, PR gene expression and resistance to fungal pathogens in rice. Planta 236:1485–1498
Pennycooke JC, Cox S, Stushnoff C (2005) Relationship of cold acclimation, total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity with chilling tolerance in petunia (Petunia × hybrida). Environ Exp Bot 53:225–232
Petrášek J, Friml J (2009) Auxin transport routes in plant development. Development 136:2675–2688
Pihakaski-Maunsbach K, Griffith M, Antikainen M et al (1996) Immunogold localization of glucanase-like antifreeze protein in cold acclimated winter rye. Protoplasma 191:115–125
Pihakaski‐Maunsbach K, Moffatt B, Testillano P et al (2001) Genes encoding chitinase‐antifreeze proteins are regulated by cold and expressed by all cell types in winter rye shoots. Physiol Plant 112:359–371
Pitzschke A, Hirt H (2006) Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species signaling in plants. Plant Physiol 141:351–356
Polisensky DH, Braam J (1996) Cold-shock regulation of the Arabidopsis TCH genes and the effects of modulating intracellular calcium levels. Plant Physiol 111:1271–1279
Rea PA (2007) Plant ATP-binding cassette transporters. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:347–375
Roxas VP, Lodhi SA, Garrett DK et al (2000) Stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco seedlings that overexpress glutathione S-transferase/glutathione peroxidase. Plant Cell Physiol 41:1229–1234
Ṣahin-Çevik M, Moore GA (2006) Identification and expression analysis of cold-regulated genes from the cold-hardy Citrus relative Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf. Plant Mol Biol 62:83–97
Saltveit ME (2000) Discovery of chilling injury. Discov Plant Biol 3:423–448
Sanders D, Pelloux J, Brownlee C et al (2002) Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell Online 14:S401–S417
Sangwan V, Foulds I, Singh J et al (2001) Cold-activation of Brassica napus BN115 promoter is mediated by structural changes in membranes and cytoskeleton, and requires Ca2+ influx. Plant J 27:1–12
Sarowar S, Kim YJ, Kim EN et al (2005) Overexpression of a pepper basic pathogenesis-related protein 1 gene in tobacco plants enhances resistance to heavy metal and pathogen stresses. Plant Cell Rep 24:216–224
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:217–223
Sigurðardóttir AG, Arnórsdóttir J, Thorbjarnardóttir SH et al (2009) Characteristics of mutants designed to incorporate a new ion pair into the structure of a cold adapted subtilisin-like serine proteinase. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Protein Proteomics 1794:512–518
Sowiński P, Dalbiak A, Tadeusiak J et al (1999) Relations between carbohydrate accumulation in leaves, sucrose phosphate synthase activity and photoassimilate transport in chilling treated maize seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 21:375–381
Talanova V, Titov A, Topchieva L et al (2009) Expression of WRKY transcription factor and stress protein genes in wheat plants during cold hardening and ABA treatment. Russ J Plant Physiol 56:702–708
Tattersall EA, Grimplet J, DeLuc L et al (2007) Transcript abundance profiles reveal larger and more complex responses of grapevine to chilling compared to osmotic and salinity stress. Funct Integr Genomics 7:317–333
Thomas SG, Phillips AL, Hedden P (1999) Molecular cloning and functional expression of gibberellin 2-oxidases, multifunctional enzymes involved in gibberellin deactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:4698–4703
Thomashow MF (2001) So what's new in the field of plant cold acclimation? Lots! Plant Physiol 125:89–93
Tillett RL, Wheatley MD, Tattersall EA et al (2012) The Vitis vinifera C-repeat binding protein 4 (VvCBF4) transcriptional factor enhances freezing tolerance in wine grape. Plant Biotechnol J 10:105–124
Tittarelli A, Santiago M, Morales A et al (2009) Isolation and functional characterization of cold-regulated promoters, by digitally identifying peach fruit cold-induced genes from a large EST dataset. BMC Plant Biol 9:121
Tornero P, Conejero V, Vera P (1997) Identification of a new pathogen-induced member of the subtilisin-like processing protease family from plants. J Biol Chem 272:14412–14419
Van Dam N (2009) How plants cope with biotic interactions. Plant Biol 11:1–5
Venter M, Groenewald J-H, Botha FC (2006) Sequence analysis and transcriptional profiling of two vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase isoforms in Vitis vinifera. J Plant Res 119:469–478
Vlachonasios KE, Thomashow MF, Triezenberg SJ (2003) Disruption mutations of ADA2b and GCN5 transcriptional adaptor genes dramatically affect Arabidopsis growth, development, and gene expression. Plant Cell Online 15:626–638
von Groll U, Berger D, Altmann T (2002) The subtilisin-like serine protease SDD1 mediates cell-to-cell signaling during Arabidopsis stomatal development. Plant Cell Online 14:1527–1539
Wanner LA, Junttila O (1999) Cold-induced freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 120:391–400
Watanabe N, Lam E (2011) Arabidopsis metacaspase 2d is a positive mediator of cell death induced during biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant J 66:969–982
Wegrzyn T, Reilly K, Cipriani G et al (2000) A novel α-amylase gene is transiently upregulated during low temperature exposure in apple fruit. Eur J Biochem 267:1313–1322
Weiser C (1970) Cold resistance and injury in woody plants knowledge of hardy plant adaptations to freezing stress may help us to reduce winter damage. Science 169:1269–1278
Welling A, Moritz T, Palva ET et al (2002) Independent activation of cold acclimation by low temperature and short photoperiod in hybrid aspen. Plant Physiol 129:1633–1641
Widjaja I, Lassowskat I, Bethke G et al (2010) A protein phosphatase 2C, responsive to the bacterial effector AvrRpm1 but not to the AvrB effector, regulates defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 61:249–258
Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhang H et al (2010) Whole genome wide expression profiles of Vitis amurensis grape responding to downy mildew by using Solexa sequencing technology. BMC Plant Biol 10:234
Xian L, Sun P, Hu S et al (2014) Molecular cloning and characterization of CrNCED1, a gene encoding 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase in Citrus reshni, with functions in tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses. Planta 239:61–77
Xiao H, Nassuth A (2006) Stress- and development-induced expression of spliced and unspliced transcripts from two highly similar dehydrin 1 genes in V. riparia and V. vinifera. Plant Cell Rep 25:968–977
Xiao H, Siddiqua M, Braybrook S et al (2006) Three grape CBF/DREB1 genes respond to low temperature, drought and abscisic acid. Plant Cell Environ 29:1410–1421
Xiao H, Tattersall EA, Siddiqua MK et al (2008) CBF4 is a unique member of the CBF transcription factor family of Vitis vinifera and Vitis riparia. Plant Cell Environ 31:1–10
Xin ZG, Browse J (1998) eskimo1 mutants of Arabidopsis are constitutively freezing-tolerant. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:7799–7804
Xin H, Zhu W, Wang L et al (2013) Genome wide transcriptional profile analysis of Vitis amurensis and Vitis vinifera in response to cold stress. PLoS ONE 8:e58740
Xiong L, Ishitani M, Lee H et al (2001) The Arabidopsis LOS5/ABA3 locus encodes a molybdenum cofactor sulfurase and modulates cold stress- and osmotic stress-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell 13:2063–2083
Xu W, Yu Y, Ding J et al (2010) Characterization of a novel stilbene synthase promoter involved in pathogen- and stress-inducible expression from Chinese wild Vitis pseudoreticulata. Planta 231:475–487
Yazaki K (2006) ABC transporters involved in the transport of plant secondary metabolites. FEBS Lett 580:1183–1191
Yeh S, Moffatt BA, Griffith M et al (2000) Chitinase genes responsive to cold encode antifreeze proteins in winter cereals. Plant Physiol 124:1251–1264
Yoshimune K, Galkin A, Kulakova L et al (2005) Cold-active DnaK of an Antarctic psychrotroph Shewanella sp. Ac10 supporting the growth of dnaK-null mutant of Escherichia coli at cold temperatures. Extremophiles 9:145–150
Yun KY, Park MR, Mohanty B et al (2010) Transcriptional regulatory network triggered by oxidative signals configures the early response mechanisms of japonica rice to chilling stress. BMC Plant Biol 10:16
Zhang X, Fowler SG, Cheng H et al (2004) Freezing-sensitive tomato has a functional CBF cold response pathway, but a CBF regulon that differs from that of freezing-tolerant Arabidopsis. Plant J 39:905–919
Zhao M-G, Chen L, Zhang L-L et al (2009) Nitric reductase-dependent nitric oxide production is involved in cold acclimation and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 151:755–767
Zhu BL, Chen TH, Li PH (1993) Expression of an ABA-responsive osmotin-like gene during the induction of freezing tolerance in Solanum commersonii. Plant Mol Biol 21:729–735
Zhu J, Shi H, Lee B et al (2004) An Arabidopsis homeodomain transcription factor gene, HOS9, mediates cold tolerance through a CBF-independent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9873–9878
Zhu J, Verslues PE, Zheng X et al (2005) HOS10 encodes an R2R3-type MYB transcription factor essential for cold acclimation in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:9966–9971
Zhu J, Dong CH, Zhu JK (2007) Interplay between cold-responsive gene regulation, metabolism and RNA processing during plant cold acclimation. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:290–295
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund (Grant No. 2012RC019) and earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (CARS-30-yz-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Additional File 1
List of DEGs selected for real-time RT-PCR. (DOCX 35 kb)
Additional File 2
Complete list of transcripts attributed to 4 °C in ‘Zuoshan-1’ grapevine. (XLSX 847 kb)
Additional File 3
List of ‘Zuoshan-1’ transcripts upregulated for at least 20-fold in 4 °C library. (XLSX 85 kb)
Additional File 4
Complete list of involved pathways for DEGs. Pathways with Q value < 0.05 are significantly enriched for DEGs. (DOC 576 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Zhang, Y., Yin, L. et al. Linkage of cold acclimation and disease resistance through plant–pathogen interaction pathway in Vitis amurensis grapevine. Funct Integr Genomics 14, 741–755 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-014-0392-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-014-0392-1