Abstract
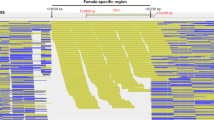
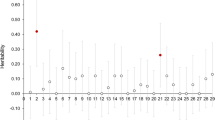
Female Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus grow more rapidly than the male. The goal of all-female commercial production requires an efficient method of genetic sex identification. We conducted genome-wide association analysis of female and male farmed Japanese flounder (n = 24 per phenotypic sex) and found all regions of chromosome 24 to be significantly associated with phenotypic sex, suggesting it as the sex chromosome. Genetic sex was identified based on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) on chromosome 24 (n = 3568) using multidimensional scaling analysis, and individuals were clearly separated according to sex by the first dimension. The 61 SNPs most highly associated with sex were selected, and an amplicon-based SNP panel was developed. This was used to determine genetic sex of 39 females and 40 males. Eleven phenotypic males were assigned as female with XX genotype, suggesting sex reversal. Genetic sex was also assessed based on the indel of the amh gene promoter, which is the major candidate sex gene of Japanese flounder. We found four SNPs perfectly associated with genotypic sex in the sex-associated SNP panel, one of which was located in exon 2 of the amh gene. Along with the indel of the amh gene promoter, the sex-associated SNP panel will be of value in identifying genetic sex of farmed Japanese flounder. Molecular sexing will facilitate all-female production by breeding sex-reversed males.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the read data were available at the DDBJ database (BioProject accession: PRJDB15261).
References
Alonge M, Lebeigle L, Kirsche M, Jenike K, Ou S, Aganezov S, Wang X, Lippman ZB, Schatz MC, Soyk S (2022) Automated assembly scaffolding using RagTag elevates a new tomato system for high-throughput genome editing. Genome Biol 23:1–19
Arai K (2001) Genetic improvement of aquaculture finfish species by chromosome manipulation techniques in Japan. Aquaculture 197:205–228
Asahida T, Kobayashi T, Saitoh K, Nakayama I (1996) Tissue preservation and total DNA extraction form fish stored at ambient temperature using buffers containing high concentration of urea. Fish Sci 62:727–730
Bai SC, Lee S (2010) Culture of olive flounder: Korean perspective, practical flatfish culture and stock enhancement. John Wiley & Sons, pp 156–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780813810997.ch9
Baroiller JF, d’Cotta H (2001) Environment and sex determination in farmed fish. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 130:399–409
Barria A, López ME, Yoshida G, Carvalheiro R, Lhorente JP, Yáñez JM (2018) Population genomic structure and genome-wide linkage disequilibrium in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) using dense SNP genotypes. Front Genet 9:649
Beardmore JA, Mair GC, Lewis R (2001) Monosex male production in finfish as exemplified by tilapia: applications, problems, and prospects. Reproductive Biotechnology in Finfish Aquaculture, pp 283–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00590-7
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Castaño-Sánchez C, Fuji K, Ozaki A, Hasegawa O, Sakamoto T, Morishima K, Nakayama I, Fujiwara A, Masaoka T, Okamoto H (2010) A second generation genetic linkage map of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). BMC Genom 11:1–11
Catanach A, Ruigrok M, Bowatte D, Davy M, Storey R, Valenza-Troubat N, López-Girona E, Hilario E, Wylie MJ, Chagné D (2021) The genome of New Zealand trevally (Carangidae: Pseudocaranx georgianus) uncovers a XY sex determination locus. BMC Genom 22:1–16
Cheng H, Concepcion GT, Feng X, Zhang H, Li H (2021) Haplotype-resolved de novo assembly using phased assembly graphs with hifiasm. Nat Methods 18:170–175
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA, Handsaker RE, Lunter G, Marth GT, Sherry ST, McVean G, Durbin R (2011) The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 27:2156–2158
Devlin RH, Nagahama Y (2002) Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: an overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 208:191–364
Earl DA, Von Holdt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Fiske P, Lund RA, Hansen LP (2006) Relationships between the frequency of farmed Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., in wild salmon populations and fish farming activity in Norway, 1989–2004. ICES J Mar Sci 63:1182–1189
Fuji K, Kobayashi K, Hasegawa O, Coimbra MRM, Sakamoto T, Okamoto N (2006) Identification of a single major genetic locus controlling the resistance to lymphocystis disease in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 254:203–210
Hattori RS, Kumazawa K, Nakamoto M, Nakano Y, Yamaguchi T, Kitano T, Yamamoto E, Fuji K, Sakamoto T (2022) Y-specific amh allele, amhy, is the master sex-determining gene in Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Front Genet 13:1007548
Hosoya S, Kikuchi K, Nagashima H, Onodera J, Sugimoto K, Satoh K, Matsuzaki K, Yasugi M, Nagano AJ, Kumagayi A (2018) Assessment of genetic diversity in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) populations with no family records using ddRAD-seq. BMC Res Notes 11:1–5
í Kongsstovu S, Dahl HA, Gislason H, Homrun E, Jacobsen JA, Flicek P, Mikalsen SO (2020) Identification of male heterogametic sex-determining regions on the Atlantic herring Clupea harengus genome. J Fish Biol 97:190–201
Jiang H, Liu H, Wang G, Zhang X, Bao J, Jiang L (2017) Fast development of genetically uniform strains by gynogenesis in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquac Res 48:2032–2038
Kamiya T, Kai W, Tasumi S, Oka A, Matsunaga T, Mizuno N, Fujita M, Suetake H, Suzuki S, Hosoya S, Tohari S, Brenner S, Miyadai T, Venkatesh B, Suzuki Y, Kikuchi K (2012) A trans-species missense SNP in Amhr2 is associated with sex determination in the tiger pufferfish, Takifugu rubripes (fugu). PLoS Genet 8:e1002798
Kavakiotis I, Triantafyllidis A, Ntelidou D, Alexandri P, Megens HJ, Crooijmans RP, Groenen MA, Tsoumakas G, Vlahavas I (2015) TRES: identification of discriminatory and informative SNPs from population genomic data. J Hered 106:672–676
Kikuchi K, Hamaguchi S (2013) Novel sex-determining genes in fish and sex chromosome evolution. Dev Dyn 242:339–353
Kikuchi K, Takeda S (2001) Present status of research and production of Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, in Japan. J Appl Aquacult 11:165–175
Kitano T, Takamune K, Kobayashi T, Nagahama Y, Abe S (1999) Suppression of P450 aromatase gene expression in sex-reversed males produced by rearing genetically female larvae at a high water temperature during a period of sex differentiation in the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). J Mol Endocrinol 23:167–176
Koyama T, Nakamoto M, Morishima K, Yamashita R, Yamashita T, Sasaki K, Kuruma Y, Mizuno N, Suzuki M, Okada Y (2019) A SNP in a steroidogenic enzyme is associated with phenotypic sex in Seriola fishes. Curr Biol 29:e1908–1909
Langmead B, Wilks C, Antonescu V, Charles R (2019) Scaling read aligners to hundreds of threads on general-purpose processors. Bioinformatics 35:421–432
Li H (2011) A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 27:2987–2993
Li Y, Zhang B, Lu S, Tian Y, Yang Y, Chen S (2018) Genetic parameters estimates for growth performance traits at harvest in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 489:56–61
Liyanage D, Lee S, Yang H, Lim C, Omeka W, Sandamalika WG, Udayantha H, Kim G, Ganeshalingam S, Jeong T (2022) Genome-wide association study of VHSV-resistance trait in Paralichthys olivaceus Fish Shellfish Immunol 124:391–400
Manni M, Berkeley MR, Seppey M, Simão FA, Zdobnov EM (2021) BUSCO update: novel and streamlined workflows along with broader and deeper phylogenetic coverage for scoring of eukaryotic, prokaryotic, and viral genomes. Mol Biol Evol 38:4647–4654
Martínez P, Robledo D, Taboada X, Blanco A, Moser M, Maroso F, Hermida M, Gómez-Tato A, Álvarez-Blázquez B, Cabaleiro S (2021) A genome-wide association study, supported by a new chromosome-level genome assembly, suggests sox2 as a main driver of the undifferentiatiated ZZ/ZW sex determination of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Genomics 113:1705–1718
Mayjonade B, Gouzy J, Donnadieu C, Pouilly N, Marande W, Callot C, Langlade N, Muños S (2016) Extraction of high-molecular-weight genomic DNA for long-read sequencing of single molecules. Biotechniques 61:203–205
Meirmans PG, Van Tienderen PH (2004) GENOTYPE and GENODIVE: two programs for the analysis of genetic diversity of asexual organisms. Mol Ecol Notes 4:792–794
Mizuta A, Tabata K, Kanao H (1996) Acceleration of testicular maturation of sex reversed gynogenetic females (phenotypically males) hirame, Paralichthys olivaceus due to long photoperiod and low water temperature treatments. Aquacult Sci 44:91–98
Paetkau D, Calvert W, Stirling I, Strobeck C (1995) Microsatellite analysis of population structure in Canadian polar bears. Mol Ecol 4:347–354
Paetkau D, Slade R, Burden M, Estoup A (2004) Genetic assignment methods for the direct, real-time estimation of migration rate: a simulation-based exploration of accuracy and power. Mol Ecol 13:55–65
Pandian TJ, Sheela SG (1995) Hormonal induction of sex reversal in fish. Aquaculture 138:1–22
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, De Bakker PI, Daly MJ (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Rohland N, Reich D (2012) Cost-effective, high-throughput DNA sequencing libraries for multiplexed target capture. Genome Res 22:939–946
Rosenberg NA, Li LM, Ward R, Pritchard JK (2003) Informativeness of genetic markers for inference of ancestry. Am J Hum Genet 73:1402–1422
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386
Sakamoto T, Danzmann RG, Gharbi K, Howard P, Ozaki A, Khoo SK, Woram RA, Okamoto N, Ferguson MM, Holm LE (2000) A microsatellite linkage map of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) characterized by large sex-specific differences in recombination rates. Genetics 155:1331–1345
Salas-Lizana R, Oono R (2018) Double-digest RAD seq loci using standard Illumina indexes improve deep and shallow phylogenetic resolution of Lophodermium, a widespread fungal endophyte of pine needles. Ecol Evol 8:6638–6651
Sauna ZE, Kimchi-Sarfaty C (2011) Understanding the contribution of synonymous mutations to human disease. Nat Rev Genet 12:683–691
Saura M, Caballero A, Santiago E, Fernández A, Morales-González E, Fernández J, Cabaleiro S, Millán A, Martínez P, Palaiokostas C (2021) Estimates of recent and historical effective population size in turbot, seabream, seabass and carp selective breeding programmes. Genet Sel Evol 53:1–8
Sawayama E, Takagi M (2016) Genetic diversity and structure of domesticated strains of red sea bream, Pagrus major, inferred from microsatellite DNA markers. Aquac Res 47:379–389
Sawayama E, Sakamoto S, Takagi M (2012) Abnormal elongation of the lower jaw in juvenile Japanese flounder: combined effects of a rotifer diet enriched with Nannochloropsis preserved by various methods and parentage. Fish Sci 78:631–640
Sawayama E, Asahina K, Takagi M (2014) Parentage assessment of incomplete ossification in larval Japanese flounder by microsatellite DNA markers. Aquaculture 420–421:S98–S103
Sawayama E, Nakao H, Kobayashi W, Minami T, Takagi M (2019) Identification and quantification of farmed red sea bream escapees from a large aquaculture area in Japan using microsatellite DNA markers. Aquat Living Resour 32:26
Seikai T (2002) Flounder culture and its challenges in Asia. Rev Fish Sci 10:421–432
Shao C, Bao B, Xie Z, Chen X, Li B, Jia X, Yao Q, Orti G, Li W, Li X (2017) The genome and transcriptome of Japanese flounder provide insights into flatfish asymmetry. Nat Genet 49:119–124
Shen X, Song S, Li C, Zhang J (2022) Synonymous mutations in representative yeast genes are mostly strongly non-neutral. Nature 606:725–731
Shriver MD, Smith MW, Jin L, Marcini A, Akey JM, Deka R, Ferrell RE (1997) Ethnic-affiliation estimation by use of population-specific DNA markers. Am J Hum Genet 60:957
Shumate A, Salzberg SL (2021) Liftoff: accurate mapping of gene annotations. Bioinformatics 37:1639–1643
Stejskal V, Kouřil J, Musil J, Hamáčková J, Policar T (2009) Growth pattern of all-female perch (Perca fluviatilis L.) juveniles–is monosex perch culture beneficial? J Appl Ichthyol 25:432–437
Tabata K (1991) Induction of gynogenetic diploid males and presumption of sex determination mechanisms in the hirame Paralichthys olivaceus Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57:845–850
Takeno K, Hamanaka Y, Kinoshita I, Miyajima T (1999) Maturity of the Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in western Wakasa Bay, the Japan Sea. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 65:1023–1029
Wang S, Cheng Y, Liu S, Xu Y, Gao Y, Wang C, Wang Z, Feng T, Lu G, Song J (2021) A synonymous mutation in IGF-1 impacts the transcription and translation process of gene expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 26:1446–1465
Wessels S, Sharifi RA, Luehmann LM, Rueangsri S, Krause I, Pach S, Hoerstgen-Schwark G, Knorr C (2014) Allelic variant in the anti-müllerian hormone gene leads to autosomal and temperature-dependent sex reversal in a selected Nile tilapia line. PLoS One 9:e104795
Wilson CA, High SK, McCluskey BM, Amores A, Yan YL, Titus TA, Anderson JL, Batzel P, Carvan MJ III, Schartl M (2014) Wild sex in zebrafish: loss of the natural sex determinant in domesticated strains. Genetics 198:1291–1308
Wright S (1949) The genetical structure of populations. Ann Eugen 15:323–354
Yamamoto E (1999) Studies on sex-manipulation and production of cloned populations in hirame, Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck et Schlegel). Aquaculture 173:235–246
Yamazaki F (1983) Sex control and manipulation in fish. Aquaculture 33:329–354
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff of Marua Suisan Co., Ltd., for collecting the fish samples.
Funding
This work was partially supported by a research grant from the Toyo Suisan Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mari Maekawa and Eitaro Sawayama conceived and designed the study. Mari Maekawa, Emili Yoshii, and Eitaro Sawayama conducted genetic analysis and analyzed the data. Yuri Akase, Sota Yoshikawa, Masahiko Matsuda, and Yosuke Kuruma provided fish sample with phenotype data. He Huang provided PacBio sequencing data. Mari Maekawa and Eitaro Sawayama drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and validated the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All experiments described in this manuscript were carried out in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals from Nihon University.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maekawa, M., Yoshii, E., Akase, Y. et al. Sex-Associated SNP Confirmation of Sex-Reversed Male Farmed Japanese Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Mar Biotechnol 25, 718–728 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-023-10235-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-023-10235-2