Abstract
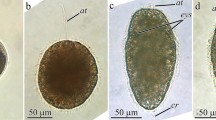
The toxic flatworm, Planocera multitentaculata, possesses highly concentrated tetrodotoxin (TTX), also known as pufferfish toxin, throughout its life cycle, including the egg and larval stages. Additionally, TTX analogues, 5,6,11-trideoxyTTX and 11-norTTX-6(S)-ol, have also been detected in the flatworm. The high concentration of TTX in the eggs and larvae appears to be for protection against predation, and 11-norTTX-6(S)-ol in the pharyngeal tissue in the adults is likely used to sedate or kill prey during predation. However, information on the role of 5,6,11-trideoxyTTX, a potential important biosynthetic intermediate of TTX, in the toxic flatworm is lacking. Here, we aimed to determine the region of localization of TTX and its analogues in the flatworm body, understand their pharmacokinetics during maturation, and speculate on their function. Flatworm specimens in four stages of maturity, namely juvenile, mating, spawning, and late spawning, were subjected to LC–MS/MS analysis, using the pharyngeal tissue, oocytes in seminal receptacle, sperm, and tissue from 12 other sites. Although TTX was consistently high in the pharyngeal tissue throughout maturation, it was extremely high in the oocytes during the spawning period. Meanwhile, 5,6,11-trideoxyTTX was almost undetectable in the pharyngeal part throughout the maturation but was very abundant in the oocytes during spawning. 11-norTTX-6(S)-ol consistently localized in the pharyngeal tissue. Although the localization of TTX and its analogues was approximately consistent with the MS imaging data, TTX and 11-norTTX-6(S)-ol were found to be highly localized in the parenchyma surrounding the pharynx, which suggests the parenchyma is involved in the accumulation and production of TTXs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and supplementary information.
References
Adachi M, Sakakibara R, Satake Y, Isobe M, Nishikawa T (2014) Synthesis of 5,6,11-trideoxytetrodotoxin. Chem Lett 43:1719–1721
Chen XW, Liu HX, Jin YB, Li SF, Bi X, Chung S, Zhang SS, Jiang YY (2011) Separation, identification and quantification of tetrodotoxin and its analogs by LC-MS without calibration of individual analogs. Toxicon 57:938–943
Colquhon D, Henderson R, Ritchie JM (1972) The binding of labeled tetrodotoxin to non-myelineated nerve fibres. J Physiol 227:95–126
Göransson U, Jacobsson E, Strand M, Andersson SH (2019) The toxins of nemertean worms. Toxins 11:120
Goto-Inoue N, Kashiwagi A, Kashiwagi K, Mori T (2016) Metabolomic approach for identifying and visualizing molecular tissue markers in tadpoles of Xenopus tropicalis by mass spectrometry imaging. Biol Open 5:1252–1259
Goto-Inoue N, Manabe Y, Miyatake S, Ogino S, Morishita A, Hayasaka T, Masaki N, Setou M, Fujii NL (2012) Visualization of dynamic change in contraction-induced lipid composition in mouse skeletal muscle by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:1863–1871
Honda S, Arakawa O, Takatani T, Tachibana K, Yagi M, Tanigawa A, Noguchi T (2005) Toxification of cultured puffer fish Takifugu rubripes by feeding on tetrodotoxin-containing diet. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 71:815–820
Hwang DF, Lu SC, Jeng SS (1991) Occurrence of tetrodotoxin in the gastropods Rapana rapiformis and R. venosa venosa. Mar Biol 111:65–69
Hwang DF, Tsai YH, Chai RJ, Jeng SS (1996) Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and paralytic shellfish poison in Taiwan Crab Zosimus aeneus. Fish Sci 62:500–501
Hwang PA, Noguchi T, Hwang DF (2004) Neurotoxin tetrodotoxin as attractant for toxic snails. Fish Sci 70:1106–1112
Ito M, Furukawa R, Yasukawa S, Sato M, Oyama H, Okabe T, Suo R, Sugita H, Takatani T, Arakawa O, Adachi M, Nishikawa T, Itoi S (2022) Local differences in the toxin amount and composition of tetrodotoxin and related compounds in pufferfish (Chelonodon patoca) and toxic goby (Yongeichthys criniger) juveniles. Toxins 14:150
Itoi S, Kozaki A, Komori K, Tsunashima T, Noguchi S, Kawane M, Sugita H (2015) Toxic Takifugu pardalis eggs found in Takifugu niphobles gut: implications for TTX accumulation in the pufferfish. Toxicon 108:141–146
Itoi S, Sato T, Takei M, Yamada R, Ogata R, Oyama H, Teranishi S, Kishiki A, Wada T, Noguchi K, Abe M, Okabe T, Akagi H, Kashitani M, Suo R, Koito T, Takatani T, Arakawa O, Sugita H (2020a) The planocerid flatworm is a main supplier of toxin to tetrodotoxin-bearing fish juveniles. Chemosphere 249:126217
Itoi S, Suzuki M, Asahina K, Sawayama E, Nishikubo J, Oyama H, Takei M, Shiibashi N, Takatani T, Arakawa O, Sugita H (2018a) Role of maternal tetrodotoxin in survival of larval pufferfish. Toxicon 148:95–100
Itoi S, Tabuchi S, Abe M, Ueda H, Oyama H, Ogata R, Okabe T, Kishiki A, Sugita H (2020b) Difference in tetrodotoxin content between two sympatric planocerid flatworms, Planocera multitentaculata and Planocera reticulata. Toxicon 173:57–61
Itoi S, Ueda H, Yamada R, Takei M, Sato T, Oshikiri S, Wajima Y, Ogata R, Oyama H, Shitto T, Okuhara K, Tsunashima T, Sawayama E, Sugita H (2018b) Including planocerid flatworms in the diet effectively toxifies the pufferfish, Takifugu niphobles. Sci Rep 8:12302
Itoi S, Yoshikawa S, Asahina K, Suzuki M, Ishizuka K, Takimoto N, Mitsuoka R, Yokoyama N, Detake A, Takayanagi C, Eguchi M, Tatsuno R, Kawane M, Kokubo S, Takanashi S, Miura A, Suitoh K, Takatani T, Sugita H (2014) Larval pufferfish protected by maternal tetrodotoxin. Toxicon 78:35–40
Katikou P, Gokbulut C, Kosker AR, Campàs M, Ozogul F (2022) An updated review of tetrodotoxin and its peculiarities. Mar Drugs 20:47
Kodama M, Ogata T, Sato S (1985) External secretion of tetrodotoxin from puffer fishes stimulated by electric shock. Mar Biol 87:199–202
Kodama M, Sato S, Ogata T, Suzuki Y, Kaneko T, Aida K (1986) Tetrodotoxin secreting glands in the skin of puffer fishes. Toxicon 24:819–829
Mahmud Y, Okada K, Takatani T, Kawatsu K, Hamano Y, Arakawa O, Noguchi T (2003) Intra-tissue distribution of tetrodotoxin in two marine puffers Takifugu vermicularis and Chelonodon patoca. Toxicon 41:13–18
Malykin GV, Chernyshev AV, Magarlamov TY (2021) Intrabody tetrodotoxin distribution and possible hypothesis for its migration in ribbon worms Cephalothrix cf. simula (Palaeonemertea, Nemertea). Mar Drugs 19:494
Matsui T, Hamada S, Konosu S (1981) Difference in accumulation of puffer fish toxin and crystalline tetrodotoxin in the puffer fish, Fugu rubripes rubripes. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 47:535–537
Matsumoto T, Nagashima Y, Kusuhara H, Ishizaki S, Shimakura K, Shiomi K (2008) Pharmacokinetics of tetrodotoxin in puffer fish Takifugu rubripes by a single administration technique. Toxicon 51:1051–1059
Matsumura K (1995) Tetrodotoxin as a pheromone. Nature 378:563–564
Miyazawa K, Jeon JK, Noguchi T, Ito K, Hashimoto K (1987) Distribution of tetrodotoxin in the tissues of the flatworm Planocera multitentaculata (Platyhelminthes). Toxicon 25:975–980
Miyazawa K, Noguchi T (2001) Distribution and origin of tetrodotoxin. J Toxicol Toxin Rev 20:11–33
Mosher HS, Fuhrman FA, Buchwald HD, Fischer HG (1964) Tarichatoxin—Tetrodotoxin: A potent neurotoxin. Science 144:1100–1110
Nagashima Y, Toyoda M, Hasobe M, Shimakura K, Shiomi K (2003) In vitro accumulation of tetrodotoxin in puffer liver tissue slices. Toxicon 41:569–574
Narahashi T (2001) Pharmacology of tetrodotoxin. J Toxicol Toxin Rev 20:67–84
Newman CF, Havelund R, Passarelli MK, Marshall PS, Francis I, West A, Alexander MR, Gilmore IS, Dollery CT (2017) Intracellular drug uptake—a comparison of single cell measurements using ToF-SIMS imaging and quantification from cell populations with LC/MS/MS. Anal Chem 89:11944–11953
Noguchi T, Arakawa O (2008) Tetrodotoxin—distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar Drugs 6:220–242
Noguchi T, Arakawa O, Takatani T (2006a) TTX accumulation in pufferfish. Comp Biochem Physiol D 1:145–152
Noguchi T, Arakawa O, Takatani T (2006b) Toxicity of pufferfish Takifugu rubripes cultured in netcages at sea or aquaria on land. Comp Biochem Physiol D 1:153–157
Noguchi T, Hashimoto Y (1973) Isolation of tetrodotoxin from a goby Gobius criniger. Toxicon 11:305–307
Noguchi T, Jeon JK, Arakawa O, Sugita H, Deguchi Y, Shida Y, Hashimoto K (1986) Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and anhydrotetrodotoxin in Vibrio sp. isolated from the intestines of a xanthid crab, Atergatis floridus. J Biochem 99:311–314
Noguchi Y, Suzuki T, Matsutani K, Sakakibara R, Nakahigashi R, Adachi M, Nishikawa T, Abe H (2022) An almost nontoxic tetrodotoxin analog, 5,6,11-trideoxytetrodotoxin, as an odorant for the grass puffer. Sci Rep 12:15087
Okabe T, Oyama H, Kashitani M, Ishimaru Y, Suo R, Sugita H, Itoi S (2019) Toxic flatworm egg plates serve as a possible source of tetrodotoxin for pufferfish. Toxins 11:402
Okabe T, Saito R, Yamamoto K, Watanabe R, Kaneko Y, Yanaoka M, Furukoshi S, Yasukawa S, Ito M, Oyama H, Suo R, Suzuki M, Takatani T, Arakawa O, Sugita H, Itoi S (2021) The role of toxic planocerid flatworm larvae on tetrodotoxin accumulation in marine bivalves. Aquat Toxicol 237:105908
Okita K, Yamazaki H, Sakiyama K, Yamane H, Niina S, Takatani T, Arakawa O, Sakakura Y (2013) Puffer smells tetrodotoxin. Ichthyol Res 60:386–389
Ritson-Williams R, Yotsu-Yamashita M, Paul VJ (2006) Ecological functions of tetrodotoxin in a deadly polyclad flatworm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3176–3179
Saito T, Kageyu K, Goto H, Murakami K, Noguchi T (2000) Tetrodotoxin attracts pufferfish (“torafugu”Takifugu rubripes). Bull Inst Oceanic Res Develop Tokai Univ 21:93–96
Salvitti LR, Wood SA, Winsor L, Cary SC (2015) Intracellular immunohistochemical detection of tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata (Gastropoda) and Stylochoplana sp. (Turbellaria). Mar Drugs 13:756–769
Sheumack DD, Howden MEH, Spence I (1978) Maculotoxin: A neurotoxin from the glands of the octopus, Hapalochlaena maculosa identified as tetrodotoxin. Science 199:188–189
Suo R, Tanaka M, Oyama H, Kojima Y, Adachi M, Nishikawa T, Sugita H, Itoi S (2022) Tetrodotoxins in the flatworm Planocera multitentaculata. Toxicon 216:169–173
Suzuki T, Nakahigashi R, Adachi M, Nishikawa T, Abe H (2022) Green spotted puffers detect a nontoxic TTX analog odor using crypt olfactory sensory neurons. Chem Senses 47:bjac011
Tanu MB, Mahmud Y, Arakawa O, Takatani T, Kajihara H, Kawatsu K, Hamano Y, Asakawa M, Miyazawa K, Noguchi T (2004) Immunoenzymatic visualization of tetrodotoxin (TTX) in Cephalothrix species (Nemertea: Anopla: Palaeonemertea: Cephalotrichidae) and Planocera reticulata (Platyhelminthes: Turbellaria: Polycladida: Planoceridae). Toxicon 44:515–520
Vlasenko AE, Magarlamov TY (2020) Tetrodotoxin and its analogues in Cephalothrix cf. simula (Nemertea: Palaeonemertea) from the Sea of Japan (Peter the Great Gulf): intrabody distribution and secretions. Toxins 12:745
Wang XJ, Yu RC, Luo X, Zhou MJ, Lin XT (2008) Toxin-screening and identification of bacteria isolated from highly toxic marine gastropod Nassarius semiplicatus. Toxicon 52:55–61
Williams BL, Caldwell RL (2009) Intra-organismal distribution of tetrodotoxin in two species of blue-ringed octopuses (Hapalochlaena fasciata and H. lunulata). Toxicon 54:345–353
Wu YJ, Lin CL, Chen CH, Hsieh CH, Jen HC, Jian SJ, Hwang DF (2014) Toxin and species identification of toxic octopus implicated into food poisoning in Taiwan. Toxicon 91:96–102
Wu ZL, Xie LP, Xia GL, Zhang JF, Nie YC, Hu JC, Wang SJ, Zhang RQ (2005) A new tetrodotoxin-producing actinomycete, Nocardiopsis dassonvillei, isolated from the ovaries of puffer fish Fugu rubripes. Toxicon 45:851–859
Yamada R, Tsunashima T, Takei M, Sato T, Wajima Y, Kawase M, Oshikiri S, Kajitani Y, Kosoba K, Ueda H, Abe K, Itoi S, Sugita H (2017) Seasonal changes in the tetrodotoxin content of the flatworm Planocera multitentaculata. Mar Drugs 15:56
Yamamori K, Kono M, Furukawa K, Matsui T (2004) The toxification of juvenile cultured kusafugu Takifugu niphobles by oral administration of crystalline tetrodotoxin. J Food Hyg Soc Jpn 45:73–75
Yamashita MY, Mebs D, Flachsenberger W (2007) Distribution of tetrodotoxin in the body of the blue-ringed octopus (Hapalochlaena maculosa). Toxicon 49:410–412
Yang G, Xu J, Liang S, Ren D, Yan X, Bao B (2010) A novel TTX-producing Aeromonas isolated from the ovary of Takifugu obscurus. Toxicon 56:324–329
Yin X, Kiriake A, Ohta A, Kitani Y, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y (2017) A novel function of vitellogenin subdomain, vWF type D, as a toxin-binding protein in the pufferfish Takifugu pardalis ovary. Toxicon 136:56–66
Yotsu M, Yamazaki T, Meguro Y, Endo A, Murata M, Naoki H, Yasumotoi T (1987) Production of tetrodotoxin and its derivatives by Pseudomonas sp. isolated from the skin of a pufferfish. Toxicon 25:225–228
Yotsu-Yamashita M, Abe Y, Kudo Y, Ritson-Williams R, Paul VJ, Konoki K, Cho Y, Adachi M, Imazu T, Nishikawa T, Isobe M (2013) First identification of 5,11-dideoxytetrodotoxin in marine animals, and characterization of major fragment ions of tetrodotoxin and its analogs by high resolution ESI-MS/MS. Mar Drugs 11:2799–2813
Yotsu-Yamashita M, Sugimoto A, Takai A, Yasumoto T (1999) Effects of specific modifications of several hydroxyls of tetrodotoxin on its affinity to rat brain membrane. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:1688–1696
Yotsu-Yamashita M, Sugimoto A, Terakawa T, Shoji Y, Miyazawa T, Yasumoto T (2001) Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of a novel soluble saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin binding protein from plasma of the pufferfish, Fugu pardalis. Eur J Biochem 268:5937–5946
Yotsu-Yamashita M, Yamaki H, Okoshi N, Araki N (2010) Distribution of homologous proteins to pufferfish saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin binding protein in the plasma of pufferfish and among the tissues of Fugu pardalis examined by Western blot analysis. Toxicon 55:1119–1124
Funding
This study was supported in part by the Grant-in-Aid for the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Fellows from JSPS (20J20428, H.O.), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) from JSPS (19H00954, S.I.), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from JSPS (19H02896, T.N.), Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientific Research from JSPS (20K15606, R.S.), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (Research in a proposed research area) from JSPS (17H06406, T.N.), and Research Grant for 2019 and 2020 from the Nihon University College of Bioresource Sciences (S.I.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: Hikaru Oyama, Rei Suo, Haruo Sugita, Tetsushi Mori, and Shiro Itoi; sample collection: Hikaru Oyama, Masaaki Ito, Rei Suo, Tetsushi Mori, and Shiro Itoi; chemical synthesis: Ryota Nakahigashi, Masaatsu Adachi, and Toshio Nishikawa; LC–MS/MS analysis: Hikaru Oyama, Masaaki Ito, and Rei Suo; MS imaging: Hikaru Oyama, Rei Suo, Naoko Goto-Inoue, Mizuki Morisasa, and Tsukasa Mori; manuscript drafting: Hikaru Oyama; critical revision: Shiro Itoi. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The authors declare that this manuscript complies with the springer ethical guidelines for journal publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Oyama, H., Ito, M., Suo, R. et al. Changes in Tissue Distribution of Tetrodotoxin and Its Analogues in Association with Maturation in the Toxic Flatworm, Planocera multitentaculata. Mar Biotechnol 24, 1158–1167 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-022-10179-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-022-10179-z