Abstract
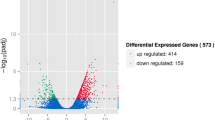
Guppy (Poecilia reticulata) can adapt to a wide range of salinity changes. To investigate the gene expression changes in the guppy exposed to seawater, we characterized its gill transcriptome using RNA sequencing. Experimental fish were exposed to salinity increase from 0 to 30‰ within 4 days, while control fish were cultured in freshwater (0‰ salinity). Seven days after salinity exposure, the gills were sampled and the mortality within 2 weeks was recorded. No significant difference in the cumulative mortality at the second week was found between the two groups. Transcriptomic analysis identified 3477 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), including 1067 upregulated and 2410 downregulated genes. These DEGs were enriched in several biological processes, including ion transport, ion homeostasis, ATP biosynthetic process, metabolic process, and immune system process. Oxidative phosphorylation was the most activated pathway. DEGs involved in the pathway “endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-mediated phagocytosis,” “starch and sucrose metabolism,” and “steroid biosynthesis” were mainly downregulated; chemokines and interleukins involved in “cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction” were differentially expressed. The present results suggested that oxidative phosphorylation had essential roles in osmoregulation in the gills of seawater acclimated guppy, during which the decline in the expression of genes encoding V-ATPases and calreticulin had a negative effect on the phagocytosis and immune response. Besides, several metabolic processes including “starch and sucrose metabolism” and “steroid biosynthesis” were affected. This study elucidates transcriptomic changes in osmotic regulation, metabolism, and immunity in seawater acclimated guppy.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data supporting our findings are contained within the manuscript. The raw sequence data generated from this study have been deposited in the Genome Sequence Archive (GSA) database in the BIG Data Center (http://gsa.big.ac.cn/index.jsp) under the accession number CRA002620 and will be made publicly available upon acceptance of this manuscript for publishing. Shared URL: https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa/s/BBfv9BLi
Abbreviations
- act-1a :
-
Actinidain
- actbb :
-
Actin, cytoplasmic 2
- acvr1 :
-
Activin receptor type-1
- amh :
-
Anti-Müllerian hormone
- amy1 :
-
Alpha-amylase 1
- amy2 :
-
Pancreatic alpha-amylase
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphophate
- atp1a1 :
-
ATPase Na + /K + transporting subunit alpha 1
- atp5f1a :
-
ATP synthase F1 subunit alpha
- atp5o :
-
ATP synthase subunit O
- atp6v1a :
-
V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A
- atp6v1b2 :
-
V-type proton ATPase subunit B, brain isoform
- atp6v1e1 :
-
V-type proton ATPase subunit E 1
- BP:
-
Biological process
- ca1 :
-
Carbonic anhydrase 1
- calr :
-
Calreticulin
- CC:
-
Cellular component
- ccl19 :
-
C-C chemokine ligand 19
- ccl20 :
-
C-C chemokine ligand 20
- ccl21 :
-
C-C chemokine ligand 21
- ccl4 :
-
C-C motif chemokine ligand 4
- ccr4 :
-
C-C chemokine receptor type 4
- ccr6 :
-
C-C chemokine receptor type 6
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- cftr :
-
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
- cox4i1 :
-
Cytochrome C oxidase subunit IV isoform 1
- cox5a :
-
Cytochrome c oxidase subunits Va
- Ct:
-
Cycle threshold
- ctsl :
-
Procathepsin L
- cyia :
-
Actin, cytoskeletal 1A
- cyp24a1 :
-
Cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A member 1
- cyp2r1 :
-
Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily R member 1
- cyp51a1 :
-
Cytochrome P450 family 51 subfamily A member 1
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- ebp :
-
Emopamil-binding protein
- edar :
-
Ectodysplasin A receptor
- enpp3 :
-
Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/ phosphodiesterase 3
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- faxdc2 :
-
Fatty acid hydroxylase domain containing 2
- FC:
-
Fold change
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- g6pc :
-
Glucose-6-phosphatase
- gapdh :
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- gck :
-
Glucokinase
- Gh/Igf1:
-
Growth hormone/insulin growth factor-1
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- gpi :
-
Glucose phosphate isomerase
- GSA:
-
Genome Sequence Archive
- gys2 :
-
Glycogen synthase 2
- h2-aa :
-
H-2 class II histocompatibility antigen, A-U alpha chain
- h2-eb1 :
-
Ig-like domain-containing protein
- h2-t23 :
-
H-2 class I histocompatibility antigen, D-37 alpha chain
- hla-c :
-
Human leukocyte antigen class I C
- hla-dpa1 :
-
HLA Class II histocompatibility antigen, DP alpha 1 chain
- hla-dra :
-
HLA Class II histocompatibility antigen, DR alpha chain
- hsd17b7 :
-
17-Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 7
- ifnar2 :
-
Interferon alpha/beta receptor 2
- il-1 :
-
Interleukin-1
- il10 :
-
Interleukin-10
- il10ra :
-
Interleukin 10 receptor subunit alpha
- il11 :
-
Interleukin-11
- il12 :
-
Interleukin-12
- il12rb2 :
-
Interleukin 12 receptor beta 2
- il-17 :
-
Interleukin-17
- il17rb :
-
Interleukin 17 receptor beta
- il1b :
-
Interleukin 1, beta
- il1r2 :
-
Interleukin 1 receptor type 2
- il1rap :
-
Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein
- il20rb :
-
Interleukin 20 receptor beta
- il26 :
-
Interleukin-26
- il8 :
-
Interleukin-8
- iTRAQ:
-
Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- kita:
-
Tyrosine-protein kinase kit
- lss :
-
Lanosterol synthase
- lta :
-
Lymphotoxins A
- ltbr :
-
Lymphotoxin-beta receptor
- MF:
-
Molecular function
- mgam :
-
Maltase-glucoamylase
- MHC-I:
-
Major histocompatibility complex class I
- MHC-II:
-
Major histocompatibility complex class II
- mpo :
-
Myeloperoxidase
- mr1 :
-
MHC-related protein 1
- mx:
-
Myxovirus resistance
- NADH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- ndufa1 :
-
NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex 1
- ndufa4 :
-
NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 4
- ndufs1 :
-
NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 1
- ndufv1 :
-
NADH dehydrogenase ubiquinone flavoprotein
- nos1 :
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- nsdhl :
-
Sterol-4-alpha-carboxylate 3-dehydrogenase, decarboxylating
- odc1 :
-
Ornithine decarboxylase 1
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- pgm1 :
-
Phosphoglucomutase-1
- pygl :
-
Glycogen phosphorylase, liver form
- pH:
-
Potential of hydrogen
- prl :
-
Prolactin
- pygm :
-
Glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- RIN:
-
RNA integrity number
- RNA-seq:
-
High-throughput RNA sequencing
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- rt1-b :
-
RT1 class II histocompatibility antigen
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- scn1b :
-
Sodium voltage-gated channel beta subunit 1
- sec61a :
-
Protein transport protein sec61 subunit alpha
- slc4a4 :
-
Sus scrofa domestica sodium bicarbonate cotransporter member 4
- slc9a2 :
-
Solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 2
- slc12a2 :
-
Solute carrier family 12 member 2
- slc12a3 :
-
Solute carrier family 12 member 3
- slc13a1 :
-
Solute carrier family 13 member 1
- soat1 :
-
Sterol O-acyltransferase 1
- SPSS:
-
Statistical product and service solutions
- tcirg1 :
-
T-cell immune regulator 1
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- tm7sf2 :
-
Transmembrane 7 superfamily member 2
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- treh :
-
Trehalase
- trpv4 :
-
Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4
- ugp2 :
-
UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase
- ugt1a1 :
-
UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A1
- ugt1a5 :
-
UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A5
- ugt2a1 :
-
UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 2 member A1
- ugt2a2 :
-
UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 2 member A2
- ugt2a3 :
-
UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 2 member A3
- uqcrfs1 :
-
Ubiquinol-cytochrome C reductase iron-sulfur subunit 1
- uqcrh :
-
Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase hinge protein
References
Aptsiauri N, Osuna FRC (2008) HLA Class I. In: Schwab M. (eds) Encyclopedia of Cancer. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-47648-1-2766
Aruna A, Nagarajan G, Chang CF (2015) The acute salinity changes activate the dual pathways of endocrine responses in the brain and pituitary of tilapia. Gen Comp Endocr 211:154–164.
Beckman B, Mustafa T (1992) Arachidonic acid metabolism in gill homogenate and isolated gill cells from rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss: the effect of osmolality, electrolytes and prolactin. Fish Physiol Biochem 10:213–222.
Bibi A, Agarwal NK, Dihazi GH et al (2011) Calreticulin is crucial for calcium homeostasis mediated adaptation and survival of thick ascending limb of Henle's loop cells under osmotic stress. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43: 1187–1197.
Cardol P, Figueroa F, Remacle C, Franzén L, González-Halphen D (2009) Chapter 13 - oxidative phosphorylation: building blocks and related components. The Chlamydomonas Sourcebook. 2nd pp. 469–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-370873-1.00021-6
Castilho PC, Martins IA, Bianchini A (2001) Gill Na(+), K(+)-ATPase and osmoregulation in the estuarine crab, Chasmagnathus granulata Dana, 1851 (Decapoda, Grapsidae). J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 256:215–227.
Castro R, Bromage E, Abós B, Pignatelli J, González Granja A, Luque A et al (2014) CCR7 is mainly expressed in teleost gills, where it defines an IgD+IgM- B lymphocyte subset. J Immunol 192:1257–1266.
Chang JC, Wu SM, Tseng YC, Lee YC, Baba O, Hwang PP (2007) Regulation of glycogen metabolism in gills and liver of the euryhaline tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) during acclimation to seawater. J Exp Biol 210:3494–3504.
Chervinski J (1984) Salinity tolerance of the guppy, Poecilia reticulata Peters. J Fish Biol 24:449–452.
Chou JY, Mansfield BC (2008) Mutations in the glucose-6-phosphatase-a (G6PC) gene that cause type I a glycogen storage disease. Hum Mutat 29:921–930.
El-Leithy AAA, Hemeda SA, El Naby W, El Nahas AF, Hassan SAH, Awad ST et al (2019) Optimum salinity for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth and mRNA transcripts of ion-regulation, inflammatory, stress- and immune-related genes. Fish Physiol Biochem 45:1217–1232.
Endler JA, Houde AE (1995) Geographic variation in female preferences for male traits in Poecilia reticulata. Evolution Int J Org Evolution 49:456–468.
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85:97–177.
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Potts W (2015) Ionic transport in the fish gill epithelium. J Exp Zool 283:641–652.
Fucikova J, Spisek R, Kroemer G et al (2021) Calreticulin and cancer. Cell Res 31:5–16.
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I et al (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652.
Gu J, Dai S, Liu H, Cao Q, Yin S, Lai KP et al (2018) Identification of immune-related genes in gill cells of Japanese eels (Anguilla japonica) in adaptation to water salinity changes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 73:288–296.
Guo T, Yang Y, Meng F, Wang S, Xia S, Qian Y et al (2020) Effects of low salinity on gill and liver glycogen metabolism of great blue-spotted mudskippers ( Boleophthalmus pectinirostris). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 230:108709.
Hossain MA, Aktar S, Qin JG (2016) Salinity stress response in estuarine fishes from the Murray Estuary and Coorong. South Australia Fish Physiol Biochem 42:1571–1580.
Huth TJ, Place SP (2016) Transcriptome wide analyses reveal a sustained cellular stress response in the gill tissue of Trematomus bernacchii after acclimation to multiple stressors. BMC Genomics 17:127.
Ivanis G, Esbaugh AJ, Perry SF (2008) Branchial expression and localization SLC9A2 and SLC9A3 sodium/hydrogen exchangers and their possible role in acid-base regulation in freshwater rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 211:2467–2477.
Jia Y, Yin S, Li L, Li P, Liang F, Wang X et al (2016) iTRAQ proteomic analysis of salinity acclimation proteins in the gill of tropical marbled eel ( Anguilla marmorata). Fish Physiol Biochem 42:935–946.
Kolbadinezhad SM, Coimbra J, Wilson J M (2018) Effect of dendritic organ ligation on striped eel catfish plotosus lineatus osmoregulation. PLoS One 13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206206
Koppang EO, Fischer U, Moore L, Tranulis MA, Dijkstra JM, Köllner B et al (2010) Salmonid T cells assemble in the thymus, spleen and in novel interbranchial lymphoid tissue. J Anat 217:728–739.
Koppang E O, Kvellestad A, Fischer U (2015) Fish mucosal immunity: gill. Mucosal Health in Aquaculture. pp. 93–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-417186-2.00005-4
Künstner A, Hoffmann M, Fraser BA, Kottler VA, Sharma E, Weigel D et al (2016) The genome of the trinidadian guppy, Poecilia reticulata, and variation in the guanapo population. PLoS One 11(12):e0169087.
Lam SH, Lui EY, Li Z, Cai S, Sung WK, Mathavan S et al (2014) Differential transcriptomic analyses revealed genes and signaling pathways involved in iono-osmoregulation and cellular remodeling in the gills of euryhaline Mozambique tilapia. Oreochromis Mossambicus BMC Genomics 15:921.
Leitemperger J, Müller TE, Cerezer C, Marins AT, de Moura LK, Loro VL (2019) Behavioural and biochemical parameters in guppy (Poecilia vivipara) following exposure to waterborne zinc in salt or hard water. Mol Biol Rep 46:3399–3409.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods (san Diego, Calif) 25:402–408.
Mohammed-Geba K, González AA, Suárez RA, Galal-Khallaf A, Martos-Sitcha JA, Ibrahim HM et al (2017) Molecular performance of Prl and Gh/Igf1 axis in the Mediterranean meager, Argyrosomus regius, acclimated to different rearing salinities. Fish Physiol Biochem 43:203–216.
Moniruzzaman M, Mukherjee J, Jacquin L, Mukherjee D, Mitra P, Ray S et al (2018) Physiological and behavioural responses to acid and osmotic stress and effects of mucuna extract in guppies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:37–46.
Nakajima M, Taniguchi N (2001) Genetics of the guppy as a model for experiment in aquaculture. Genetica 111:279–289.
Oppenheim JJ (2001) Cytokines: past, present, and future. Int J Hematol 74:3–8.
Posey AL (2010) Effects of salinity on the reproductive biology of the guppy. Lamar University - Beaumont, Poecilia reticulata
Riazanski V, Gabdoulkhakova AG, Boynton LS et al (2015) TRPC6 channel translocation into phagosomal membrane augments phagosomal function. PNAS 112:E6486–E6495.
Ribeiro N, Streiff S, Heissler D, Elhabiri M, Ourisson G (2007) Reinforcing effect of bi- and tri-cyclopolyprenols on ‘primitive’ membranes made of polyprenyl phosphates. Tetrahedron 63:3395–3407.
Schmitz M, Baekelandt S, Bequet S, Kestemont P (2017) Chronic hyperosmotic stress inhibits renal Toll-Like Receptors expression in striped catfish ( Pangasianodon hypophthalmus Sauvage) exposed or not to bacterial infection. Dev Comp Immunol 73139–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2017.03.020
Shikano T, Fujio Y (2015) Immunolocalization of Na+, K+-ATPase and morphological changes in two types of chloride cells in the gill epithelium during seawater and freshwater adaptation in a euryhaline teleost, Poecilia reticulata. J Exp Zool Part B 281:80–89.
Si Y, Wen H, Li Y, He F, Li J, Li S et al (2018) Liver transcriptome analysis reveals extensive transcriptional plasticity during acclimation to low salinity in Cynoglossus semilaevis. BMC Genomics 19:464.
Sokolovska A, Becker C, Ip W et al (2013) Activation of caspase-1 by the NLRP3 inflammasome regulates the NADPH oxidase NOX2 to control phagosome function. Nat Immunol 14:543–553.
Su H, Ma D, Zhu H, Liu Z, Gao F (2020) Transcriptomic response to three osmotic stresses in gills of hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus female ×O. urolepis hornorum male). BMC Genomics 21:110.
Su M, Zhou J, Duan Z, Zhang J (2019) Transcriptional analysis of renal dopamine-mediated Na(+) homeostasis response to environmental salinity stress in Scatophagus argus. BMC Genomics 20:418.
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J et al (2015) STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43:447–452.
Uribe-Querol E, Rosales C (2021) Phagocytosis. Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818731-9.00049-5
Valenzuela-Muñoz V, Váldes JA, Gallardo-Escárate C (2021) Transcriptome profiling of long non-coding RNAs during the Atlantic salmon smoltification process. Mar Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-021-10024-9
Wang D, Cao Q, Zhu W, Hu Y, Zhang X, Yin S et al (2019) Individual and combined effects of salinity and lipopolysaccharides on the immune response of juvenile Takifugu fasciatus. Fish Physiol Biochem 45:965–976.
Wong MK, Ozaki H, Suzuki Y, Iwasaki W, Takei Y (2014) Discovery of osmotic sensitive transcription factors in fish intestine via a transcriptomic approach. BMC genomics 15:1134. Epub 2014/12/19.
Xu Z, Gan L, Li T, Xu C, Chen K, Wang X et al (2015) Transcriptome profiling and molecular pathway analysis of genes in association with salinity adaptation in nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. PLoS One 10:e0136506.
Yuan X, He S, Liang X, Luo X, Li A, Zhou Y (2017) Food conditions and water salinity affect survival and growth of golden mandarin fish, Siniperca sherzeri, larvae through transcriptional regulation of growth and lipometabolic genes. J World Aquacult Soc. https://doi.org/10.1111/jwas.12450
Zhang H, Hou J, Liu H, Zhu H, Xu J (2020) Adaptive evolution of low-salinity tolerance and hypoosmotic regulation in a euryhaline teleost, Takifugu obscurus. Mar Biol 167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-020-03705-x
Zhang X, Wen H, Wang H, Ren Y, Zhao J, Li Y (2017) Rna-seq analysis of salinity stress-responsive transcriptome in the liver of spotted sea bass ( Lateolabrax maculatus). PLoS One 12:e0173238.
Zhao J, Benlekbir S, Rubinstein J (2015) Electron cryomicroscopy observation of rotational states in a eukaryotic V-ATPase. Nature 521:241–245.
Funding
This study was supported by Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Grant No. 2015R1019-13, 2018R1019-6), and General Projects of Fujian Academy of Agricultural Science (AC2017-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HG conceived and supervised the study. XC wrote the manuscript. XC and HC conducted the salinity challenge experiment. XC and HG performed the analysis and designed the charts and tables. XC and BX extracted total RNA from the gill tissues. XC, HC, BX, and ZZ collected the samples. HG and XC revised the manuscript. YB participated in PPI analysis. All the authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The Research Ethics Committee of Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences approved the study. All experimental fish procedures were performed in accordance with the regulations for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals, approved by the State Council of China.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Gong, H., Chi, H. et al. Gill Transcriptome Analysis Revealed the Difference in Gene Expression Between Freshwater and Seawater Acclimated Guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Mar Biotechnol 23, 615–627 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-021-10053-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-021-10053-4