Abstract
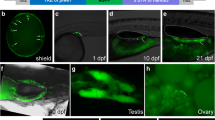
Primordial germ cells (PGCs) as the precursors of germ cells are responsible for transmitting genetic information to the next generation. Visualization of teleost PGCs in vivo is essential to research the origination and development of germ cells and facilitate further manipulation on PGCs isolation, cryopreservation, and surrogate breeding. In this study, artificially synthesized mRNAs constructed by fusing fluorescent protein coding region to the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of nanos3 or vasa (mCherry-Smnanos3 3′UTR or mCherry-Smvasa 3′UTR mRNA) were injected into turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) fertilized eggs for tracing PGCs. The results demonstrated that the fluorescent PGCs differentiated from somatic cells and aligned on both sides of the trunk at the early segmentation period, then migrated and located at the dorsal part of the gut where the gonad would form. In the same way, we also found that the zebrafish (Danio rerio) vasa 3′UTR could trace turbot PGCs, while the vasa 3′UTR s of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) and red seabream (Pagrus major) failed, although they could label the marine medaka PGCs. In addition, through comparative analysis, we discovered that some potential sequence elements in the3 ′UTRs of nanos3 and vasa, such as GCACs, 62-bp U-rich regions and nucleotide 187–218 regions might be involved in PGCs stabilization. The results of this study provided an efficient, rapid, and specific non-transgenic approach for visualizing PGCs of economical marine fish in vivo.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki Y, Nakamura S, Ishikawa Y, Tanaka M (2009) Expression and syntenic analyses of four nanos genes in medaka. Zool Sci 26:112–118
Bailey TL, Elkan C (1994) Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 2:28–36
Braat AK, Speksnijder JE, Zivkovic D (1999) Germ line development in fishes. Int J Dev Biol 43:745–760
Curtis D, Treiber DK, Tao F, Zamore PD, Williamson JR, Lehmann R (1997) A CCHC metal-binding domain in Nanos is essential for translational regulation. EMBO J 16:834–843
Draper BW, McCallum CM, Moens CB (2007) nanos1 is required to maintain oocyte production in adult zebrafish. Dev Biol 305:589–598
Fujiwara Y, Komiya T, Kawabata H, Sato M, Fujimoto H, Furusawa M, Noce T (1994) Isolation of a DEAD-family protein gene that encodes a murine homolog of Drosophila vasa and its specific expression in germ cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:12258–12262
Goto R, Saito T, Kawakami Y, Kitauchi T, Takagi M, Todo T, Arai K, Yamaha E (2016) Visualization of primordial germ cells in the fertilized pelagic eggs of the barfin flounder Verasper moseri. Int J Dev Biol 59:465–470
Hartung O, Forbes MM, Marlow FL (2014) Zebrafish vasa is required for germ-cell differentiation and maintenance. Mol Reprod Dev 81:946–961
Hay B, Jan LY, Jan YN (1988) A protein component of Drosophila polar granules is encoded by vasa and has extensive sequence similarity to ATP-dependent helicases. Cell 55:577–587
Houston DW, King ML (2000) Germ plasm and molecular determinants of germ cell fate. Curr Top Dev Biol 50:155–181
Kataoka K, Yamaguchi T, Orii H, Tazaki A, Watanabe K, Mochii M (2006) Visualization of the Xenopus primordial germ cells using a green fluorescent protein controlled by cis elements of the 3′ untranslated region of the DEADSouth gene. Mech Dev 123:746–760
Kawakami Y, Saito T, Fujimoto T, Goto-Kazeto R, Takahashi E, Adachi S, Yamaha E (2011) Visualization and motility of primordial germ cells using green fluorescent protein fused to 3′UTR of common carp nanos-related gene. Aquaculture 317:245–250
Kawakami Y, Ishihara M, Saito T, Fujimoto T, Yamaha E (2012) Cryopreservation of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-labeled primordial germ cells with GFP fused to the 3′UTR of the nanos gene by vitrification of Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica) somite-stage embryos. J Anim Sci 90:4256–4265
Kedde M, Strasser MJ, Boldajipour B, Oude Vrielink JA, Slanchev K, le Sage C, Nagel R, Voorhoeve PM, van Duijse J, Ørom UA, Lund AH, Perrakis A, Raz E, Agami R (2007) RNA-binding protein Dnd1 inhibits microRNA access to target mRNA. Cell 131:1273–1286
Knaut H, Pelegri F, Bohmann K, Schwarz H, Nüsslein-Volhard C (2000) Zebrafish vasa RNA but not its protein is a component of the germ plasm and segregates asymmetrically before germline specification. J Cell Biol 149:875–888
Knaut H, Steinbeisser H, Schwarz H, Nüsslein-Volhard C (2002) An evolutionary conserved region in the vasa 3′ UTR targets RNA translation to the germ cells in the zebrafish. Curr Biol 12:454–466
Kobayashi T, Kajiura-Kobayashi H, Nagahama Y (2000) Differential expression of vasa homologue gene in the germ cells during oogenesis and spermatogenesis in a teleost fish, tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Mech Dev 99:139–142
Koprunner M, Thisse C, Thisse B, Raz E (2001) A zebrafish nanos-related gene is essential for the development of primordial germ cells. Genes Dev 15:2877–2885
Kuersten S, Goodwin EB (2003) The power of the 3′ UTR: translational control and development. Nat Rev Genet 4:626–637
Kurokawa H, Aoki Y, Nakamura S, Ebe Y, Kobayashi D, Tanaka M (2010) Time-lapse analysis reveals different modes of primordial germ cell migration in the medaka Oryzias latipes. Develop Growth Differ 48:209–221
Lei JL (2003) The development direction of turbot farming industry in China (in Chinese). Sci Fish Farm 7:26–28
Li M, Hong N, Xu H, Yi M, Li C, Gui J, Hong Y (2009) Medaka vasa is required for migration but not survival of primordial germ cells. Mech Dev 126:366–381
Li M, Tan X, Jiao S, Wang Q, Wu Z, You F, Zou Y (2015) A new pattern of primordial germ cell migration in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) identified using nanos3. Dev Genes Evol 225:195–206
Li M, Tan X, Sui Y, Jiao S, Wu Z, You F (2016) Conserved elements in the nanos3 3′ UTR of olive flounder are responsible for the selective retention of RNA in germ cells. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 198:66–72
Lin F, Xu S, Ma D, Xiao Z, Zhao C, Xiao Y, Chi L, Liu Q, Li J (2012a) Germ line specific expression of a vasa homologue gene in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus): evidence for vasa localization at cleavage furrows in Euteleostei. Mol Reprod Dev 79:803–813
Lin F, Liu Q, Li M, Li Z, Hong N, Li J, Hong Y (2012b) Transient and stable GFP expression in germ cells by the vasa regulatory sequences from the red seabream (Pagrus major). Int J Biol Sci 8:882–890
Lin F, Zhao CY, Xu SH, Ma DY, Xiao ZZ, Xiao YS, Xu CA, Liu QH, Li J (2013) Germline-specific and sexually dimorphic expression of a dead end gene homologue in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Theriogenology 80:665–672
Lindeman RE, Pelegri F (2010) Vertebrate maternal-effect genes: insights into fertilization, early cleavage divisions, and germ cell determinant localization from studies in the zebrafish. Mol Reprod Dev 77:299–313
Mishima Y, Giraldez AJ, Takeda Y, Fujiwara T, Sakamoto H, Schier AF, Inoue K (2006) Differential regulation of germline mRNAs in soma and germ cells by zebrafish miR-430. Curr Biol 16:2135–2142
Presslauer C, Nagasawa K, Fernandes JM, Babiak I (2012) Expression of vasa and nanos3 during primordial germ cell formation and migration in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Theriogenology 78:1262–1277
Raz E (2003) Primordial germ-cell development: the zebrafish perspective. Nat Rev Genet 4:690–700
Saito T, Fujimoto T, Maegawa S, Inoue K, Yamaha E (2006) Visualization of primordial germ cells in vivo using GFP-nos1 3′UTR mRNA. Int J Dev Biol 50:691–699
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Saitou M, Yamaji M (2012) Primordial germ cells in mice. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4:59–66
Shinomiya A, Tanaka M, Kobayashi T, Nagahama Y, Hamaguchi S (2000) The vasa-like gene, olvas, identifies the migration path of primordial germ cells during embryonic body formation stage in the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Develop Growth Differ 42:317–326
Škugor A, Slanchev K, Torgersen JS, Tveiten H, Andersen Ø (2014) Conserved mechanisms for germ cell-specific localization of nanos3 transcripts in teleost species with aquaculture significance. Mar Biotechnol 16:256–264
Slanchev K, Stebler J, Goudarzi M, Cojocaru V, Weidinger G, Raz E (2009) Control of Dead end localization and activity-implications for the function of the protein in antagonizing miRNA function. Mech Dev 126:270–277
Suzuki H, Saba R, Sada A, Saga Y (2010) The Nanos3-3′ UTR is required for germ cell specific NANOS3 expression in mouse embryos. PLoS One 5:e9300
Tanaka SS et al (2000) The mouse homolog of Drosophila Vasa is required for the development of male germ cells. Genes Dev 14:841–853
Tsuda M, Sasaoka Y, Kiso M, Abe K, Haraguchi S, Kobayashi S, Saga Y (2003) Conserved role of nanos proteins in germ cell development. Science 301:1239–1241
Weidinger G, Stebler J, Slanchev K, Dumstrei K, Wise C, Lovell-Badge R, Thisse C, Thisse B, Raz E (2003) Dead end, a novel vertebrate germ plasm component, is required for zebrafish primordial germ cell migration and survival. Curr Biol 13:1429–1434
Wolke U, Weidinger G, Köprunner M, Raz E (2002) Multiple levels of posttranscriptional control lead to germ line-specific gene expression in the zebrafish. Curr Biol 12:289–294
Wylie C (1999) Germ cells. Cell 96:165–174
Wylie C (2000) Germ cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:410–413
Ye H, Yue HM, Yang XG, Li CJ, Wei QW (2016) Identification and sexually dimorphic expression of vasa isoforms in Dabry’ s sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus), and functional analysis of vasa 3′-untranslated region. Cell Tissue Res 366:203–218
Yoon C, Kawakami K, Hopkins N (1997) Zebrafish vasa homologue RNA is localized to the cleavage planes of 2- and 4-cell-stage embryos and is expressed in the primordial germ cells. Development 124:3157–3165
Yoshizaki G, Sakatani S, Tominaga H, Takeuchi T (2000) Cloning and characterization of a vasa-like gene in rainbow trout and its expression in the germ cell lineage. Mol Reprod Dev 55:364–371
Yoshizaki G, Tago Y, Takeuchi Y, Sawatari E, Kobayashi T, Takeuchi T (2005) Green fluorescent protein labeling of primordial germ cells using a nontransgenic method and its application for germ cell transplantation in salmonidae. Biol Reprod 73:88–93
Zhou L, Feng Y, Wang F, Dong X, Jiang L, Liu C, Zhao Q, Li K (2018) Generation of all-male-like sterile zebrafish by eliminating primordial germ cells at early development. Sci Rep 8:1834
Zuker M (1989) On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science 244:48–52
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31572602), National Key Research and Development Program (2018YFD0901205, 2018YFD0901204), the Marine S&T Fund of Shandong Province for Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology(Qingdao)(2018SDKJ0302-4, 2018SDKJ0502-2),China Agriculture Research System (CARS-47), STS project (KFZD-SW-106, 2017T3017), Shandong Province Key Research and Invention Program (2017CXGC010K), the National Infrastructure of Fishery Germplasm Resource (2019DKA30470).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This study was conceived and designed by Li Zhou, Qinghua Liu, Xueying Wang, and Jun Li; Li Zhou and Xueying Wang contributed experimental work; Li Zhou and Qinghua Liu contributed the manuscript writing and revision, respectively; Shihong Xu, Haixia Zhao, Mingming Han, and Yunong Wang contributed experimental materials. All authors read and approve the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All experiments were performed in accordance with the relevant national and international guidelines and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Wang, X., Liu, Q. et al. Visualization of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Primordial Germ Cells in vivo Using Fluorescent Protein Mediated by the 3′ Untranslated Region of nanos3 or vasa Gene. Mar Biotechnol 21, 671–682 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-019-09911-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-019-09911-z