Abstract
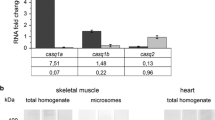
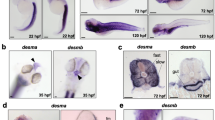
Aspolin is a muscular protein having unique structural characteristics where the most part of its primary structure is occupied by aspartic acid. Aspolin has been found exceptionally in fish muscle, suggesting its specific role in this tissue. However, biological functions of aspolin have remained unknown. In the present study, we cloned full-length cDNAs encoding zebrafish Danio rerio aspolins 1 and 2, revealed their genomic organization, and examined in vivo function using knockdown techniques. Genomic analysis clearly showed that aspolin is a paralog of the histidine-rich calcium binding protein gene, which encodes a calcium binding protein in sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). Expression analysis showed that the transcripts and their translated products, aspolins 1 and 2, are distributed in myotomal skeletal muscle, but not in cardiac muscle. Injection of antisense morpholino oligo targeting both aspolins 1 and 2 increased the mRNA levels of calsequestrin 1, another calcium binding protein in SR. These lines of evidence suggest that aspolins regulate calcium concentrations in SR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho E, Vornanen M (1999) Contractile properties of atrial and ventricular myocardium of the heart of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: effects of thermal acclimation. J Exp Biol 202:2663–2677
Amores A, Force A, Yan YL, Joly L, Amemiya C, Fritz A, Ho RK, Langeland J, Prince V, Wang YL, Westerfield M, Ekker M, Postlethwait JH (1998) Zebrafish hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science 282:1711–1714
Arvanitis DA, Vafiadaki E, Fan GC, Mitton BA, Gregory KN, Del Monte F, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Sanoudou D, Kranias EG (2007) Histidine-rich Ca-binding protein interacts with sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H1581–H1589
Barbazuk WB, Korf I, Kadavi C, Heyen J, Tate S, Wun E, Bedell JA, McPherson JD, Johnson SL (2000) The syntenic relationship of the zebrafish and human genome. Genome Res 10:1351–1358
Beard NA, Laver DR, Dulhunty AF (2004) Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 85:33–69
Bowler K, Tirri R (1990) Temperature-dependence of the heart isolated from the cold or warm acclimated perch (Perca fluviatilis). Comp Biochem Physiol A 96:177–180
Damiani E, Picello E, Saggin L, Margreth A (1995) Identification of triadin and of histidine-rich Ca2+-binding protein as substrates of 60 kDa calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum of rabbit fast muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 209:457–465
Fliegel L, Ohnishi M, Carpenter MR, Khanna VK, Reithmeier RAF, MacLennan DH (1987) Amino acid sequence of rabbit fast-twitch skeletal muscle calsequestrin deduced from cDNA and peptide sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1167–1171
Gregory KN, Ginsburg KS, Bodi I, Hahn H, Marreez YM, Song Q, Padmanabhan PA, Mitton BA, Waggoner JR, Del Monte F, Park WJ, Dorn GW, Bers DM, Kranias EG (2006) Histidine-rich Ca binding protein: a regulator of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium sequestration and cardiac function. J Mol Cell Cardiol 40:653–665
Haverinen J, Vornanen M (2009) Comparison of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium content in atrial and ventricular myocytes of three fish species. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:R1180–R1187
Hofmann SL, Goldstein JL, Orth K, Moomaw CR, Slaughter CA, Brown MS (1989) Molecular cloning of a histidine-rich Ca2+-binding protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum that contains highly conserved repeated elements. J Biol Chem 264:18083–18090
Jaehnig EJ, Heidt AB, Greene SB, Cornelissen I, Black BL (2006) Increased susceptibility to isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and impaired weight gain in mice lacking the histidine-rich calcium-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol 26:9315–9326
Keen JE, Vianzon DM, Farrell AP, Tibbits GF (1994) Effect of temperature and temperature acclimation on the ryanodine sensitivity of the trout myocardium. J Comp Physiol B 164:438–443
Kimura M, Takeuchi K, Kimura I, Seki N (2005) The existence of aspolin and its trimethylamine-N-oxide demethylating activity in the muscle of freshwater fish. Fish Sci 71:904–913
Korajoki H, Vornanen M (2009) Expression of calsequestrin in atrial and ventricular muscle of thermally acclimated rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 212:3403–3414
Lamb GD (2000) Excitation–contraction coupling in skeletal muscle: comparisons with cardiac muscle. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 27:216–224
Lee HG, Kang H, Kim DH, Park WJ (2001) Interaction of HRC (histidine-rich Ca2+-binding protein) and triadin in the lumen of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 276:39533–39538
Orr I, Shoshan-Barmatz V (1996) Modulation of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor by endogenous phosphorylation of 160/150-kDa proteins of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta 1283:80–88
Ozawa M, Muramatsu T (1993) Reticulocalbin, a novel endoplasmic reticulum resident Ca2+-binding protein with multiple EF-hand motifs and a carboxyl-terminal HDEL sequence. J Biol Chem 268:699–705
Pelham HR (1990) The retention signal for soluble proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem Sci 15:483–486
Ridgeway AG, Petropoulos H, Siu A, Ball JK, Skerjanc IS (1999) Cloning, tissue distribution, subcellular localization and overexpression of murine histidine-rich Ca2+ binding protein. FEBS Lett 456:399–402
Sacchetto R, Damiani E, Turcato F, Nori A, Margreth A (2001) Ca2+-dependent interaction of triadin with histidine-rich Ca2+-binding protein carboxyl-terminal region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:1125–1134
Shimizu S, Dennis EJ, Masaki T, Fischman DA (1985) Axial arrangement of the myosin rod in vertebrate thick filaments: immunoelectron microscopy with a monoclonal antibody to light meromyosin. J Cell Biol 101:115–123
Shin DW, Ma J, Kim DH (2001) The Asp-rich region at the carboxyl-terminus of calsequestrin binds to Ca2+ and interacts with triadin. FEBS Lett 486:178–182
Takeuchi K, Hatanaka A, Kimura M, Seki N, Kimura I, Yamada S, Yamashita S (2003) Aspolin, a novel extremely aspartic acid-rich protein in fish muscle, promotes iron-mediated demethylation of trimethylamine-N-oxide. J Biol Chem 278:47416–47422
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Ushio H, Watabe S (1993) Effects of temperature acclimation on Ca2+-ATPase of the carp sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Exp Biol 265:9–17
Wang S, Trumble WR, Liao H, Wesson CR, Dunker AK, Kang CH (1998) Crystal structure of calsequestrin from rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nat Struct Biol 5:476–483
Watabe S, Ushio H, Hashimoto K (1991) Purification and characterization of a calsequestrin-like calcium-binding protein from carp (Cyprinus carpio) sarcoplasmic reticulum. Comp Biochem Physiol B 199:545–552
Weis K, Griffiths G, Lamond AI (1994) The endoplasmic reticulum calcium-binding protein of 55 kDa is a novel EF-hand protein retained in the endoplasmic reticulum by a carboxyl-terminal His-Asp-Glu-Leu motif. J Biol Chem 269:19142–19150
Westerfield M (2000) The zebrafish book. A guide for the laboratory use of zebrafish (Danio rerio), 4th edn. University of Oregon Press, Eugene
Yano K, Zarain-Herzberg A (1994) Sarcoplasmic reticulum calsequestrins: structural and functional properties. Mol Cell Biochem 135:61–70
Zhou X, Fan GC, Ren X, Waggoner JR, Gregory KN, Chen G, Jones WK, Kranias EG (2007) Overexpression of histidine-rich Ca-binding protein protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury. Cardiovasc Res 75:487–497
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kinoshita, S., Katsumi, E., Yamamoto, H. et al. Molecular and Functional Analyses of Aspolin, a Fish-Specific Protein Extremely Rich in Aspartic Acid. Mar Biotechnol 13, 517–526 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-010-9322-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-010-9322-y