Abstract
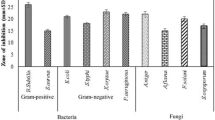
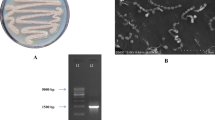
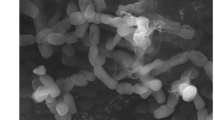
Strain GB-2 is a marine microbe with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, isolated from soil taken from the coastal city Lianyungang in the JiangSu province of China. Analysis of its morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics as well as chemical components of the cell wall strongly suggested that the strain GB-2 belonged to the Streptomyces sp. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the 16S rRNA gene of Streptomyces sp. GB-2 strain showed a strong similarity (98%) with the 16 rRNA gene of Streptomyces fradiae. Application to antibacterial substance of strain Streptomyces sp. GB-2 by various separation steps led to isolation of one active molecule having a retention time of 9.495 min, P 9.495 min, which possessed antibacterial activity against Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli. Through analysis by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and mass/mass spectrometry of the peak, the molecular weight of the antibacterial substance (P 9.495 min sample) was 447.5 Da and it was determined to be sisomicin according to the analysis of ion fragments. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of the peak also demonstrated that the antibacterial substance was sisomicin. This study is the first to introduce the finding of sisomicin produced from marine Streptomyces sp. This work provides a preference for the production of sisomicin in pharmaceutical industries and a probability for studying the biodiversity of marine microbe.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berdy J (2005) Bioactive microbial metabolites. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 58:1–26
Bruntner C, Binder T, Pathom-aree W, Goodfellow M, Bull AT, Potterat O, Puder C, Horer S, Schmid A, Bolek W (2005) Frigocyclinone, a novel angucyclinone antibiotic produced by a Streptomyces griseus strain from Antarctica. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 58:346–349
Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (1974) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 7th edn, London. Bergey Taxon 24, pp 377–378
Cragg GM, Kingston DGI, Newman DJ (eds) (2005) Anticancer agents from natural products. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Crowe CC, Sanders E (1973) Sisomicin: evaluation in vitro and comparison with gentamicin and tobramycin. Antimicrob Ag Chemother 3:24–28
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gyselmymck AM, Forrey A, Cutler R (1971) Pharmacokinetics of gentamicin: distribution and plasma and renal clearance. J Infect Dis 124:570–576
Hu PF, Chess EK, Brynjelsen S, Jakubowski G, Melchert J, Hammond RB (2000) Collisionally activated dissociations of aminocyclitol-aminoglycoside antibiotics and their application in the identification of a new compound in tobramycin samples. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 11:200–209
Jensen PR, Gontang E, Mafnas C, Mincer TJ, Fenical W (2005) Culturable marine actinomycete diversity from tropical Pacific Ocean sediments. Environ Microbiol 7:1039–1048
Jiao ZQ, Liu XM (2001) The new hot spot of classification and identification of bacteria: intergenic spacer of 16S–23S rDNA. Chinese Microbiol 28:85–89
Kim TK, Garson MJ, Fuerst JA (2005) Marine actinomycetes related to the alinospora group from the Great Barrier Reef sponge Pseudoceratina clavata. Environ Microbiol 7:509–518
Kin SL (2006) Discovery of novel metabolites from marine actinomycetes. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:245–251
Klasterky J, Henri A, Hensgens C, Vandenborre L, Daneau D (1973) Antipseudomonal drugs: comparative study of gentamicin, sisomicin and tobramycin in vitro and in human volunteers. Eur J Cancer 9:641–648
Kokare CR, Mahadik KR, Kadam SS, Chopade BA (2004) Isolation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of marine halophilic Actinopolyspora species AH1 from the west coast of India. Curr Sci 86:593–597
Levison ME, Kaye D (1974) In vitro comparison of four aminoglycoside antibiotics: sisomicin, gentamicin, tobramycin, and BB-K8. Antimicrob Ag Chemother 5:667–669
Liu S, Lu YJ, Lu ZX (2007) Antibacterial activity and property of the fermentation product of marine Streptomyces sp. GB-2. Chinese J Biotechnol 23:1077–1081
Macherla VR, Liu J, Bellows C, Teisan S, Lam KS, Potts BCM (2005) Glaciapyrroles A, B and C, pyrrolosesquiterpenes from a Streptomyces sp. isolated from an Alaskan marine sediment. J Nat Prod 68:780–783
Magarvey NA, Keller JM, Bernan V, Dworkin M, Sherman DH (2004) Isolation and characterization of novel marine-derived actinomycete taxa rich in bioactive metabolites. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7520–7529
Mann J (2001) Natural products as immunosuppressive agents. Nat Prod Rep 18:417–430
Maskey RP, Sevvana M, Uson I, Helmke E, Laatsch H (2004) Gutingimycin: a highly complex metabolite from a marine streptomycete. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 43:1281–1283
Moran MA, Miller WL (2007) Resourceful heterotrophs make the most of light in the coastal ocean. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:792–800
Mincer TJ, Jensen PR, Kauffman CA, Fenical W (2002) Widespread and persistent populations of a major new marine actinomycete taxon in ocean sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(10):5005–5011
Sanchez LJM, Martinez IM, Perez BJ, Fernandez PJL, Canedo HLM (2003) New Cytotoxic indolic metabolites from a marine Streptomyces. J Nat Prod 66:863–864
Soria-Mercado IE, Prieto-Davo A, Jensen PR, Fenical W (2005) Antibiotic terpenoid chloro-dihydroquinones from a new marine actinomycete. J Nat Prod 68:904–910
Staneck JL, Roberts GD (1974) Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin layer chromatography. Appl Microbiol 28:226–231
Strohl WR (2004) Antimicrobials in microbial diversity and bioprospecting. ASM, Washington, DC, pp 336–355
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acid Res 22:4673–4680
Xu LH, Lee WJ (2006) Actinomycete systematic—principle, methods and practice. Science, Beijing, pp 381–387
Waitz JA, Moss EL, Drube CG, Weinstein MJ (1972) Comparative activity of sisomicin, gentamicin, kanamycin and tobramycin. Antimicrob Ag Chemother 2:31–436
Watve MG, Tickoo R, Jog MM, Bhole BD (2001) How many antibiotics are produced by the genus Streptomyces. Arch Microbiol 176:386–390
Zengler K, Toledo G, Rappe M, Elkins J, Mathur EJ, Short JM (2002) Cultivating the uncultured. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:15681–6
Zhang L, An R, Wang J, Sun N, Zhang S, Hu J (2005) Exploring novel bioactive compounds from marine microbes. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:276–281
Zheng ZH, Zeng W, Huang YJ (2000) Detection of antitumor and antimicrobial activities in marine organism associated actinomycetes isolated from the Taiwan Strait, China. FEMS Microbiol Lett 188:87–91
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank National Nature and Science Fund of China (grant no. 30671460) and Ministry of Science & Technology of China (2006AA10Z346) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
The 1H NMR and 13C NMR were used in order to further confirm whether the antibacterial substance was sisomicin. Through comparison with the 1H-NMR spectrum and the 13C NMR spectrum of P9.495 min molecular and standard sisomicin, it was found that both spectrums were same (Fig.1 and Fig.2). The results further demonstrated that the antibacterial substance (P9.495 min sample) was sisomicin (DOC 2 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Dong, X., Liu, S. et al. Characterization and Identification of a Novel Marine Streptomyces sp. Produced Antibacterial Substance. Mar Biotechnol 11, 717–724 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-009-9186-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-009-9186-1