Abstract
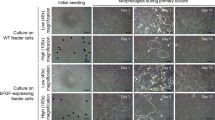
We report a pluripotent embryonic stem cell-like cell line designated as SBES from blastula stage embryos of Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer), which is an economically important cultivable and edible marine fish species in India. The SBES cells were cultured at 28°C in Leibovitz L-15 medium supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum without a feeder layer. The ES-like cells were round or polygonal and grew exponentially in culture. The SBES cells exhibited an intense alkaline phosphatase activity and expression of transcription factor Oct 4. The undifferentiated state of these cells was maintained at low seeding densities and the cells formed embryoid bodies when seeded in bacteriological plates. On treatment with all-trans retinoic acid, these cells differentiated into neuron-like cells, muscle cells, and beating cardiomyocytes, indicating their pluripotency. This embryonic ES-like cell line derived from an oviparous fish blastula conserved several peculiar features of viviparous mammalian embryonic stem cell lines. The present study highlights the importance and potential of piscine ES-like cell line for stem cell research without evoking ethical issues and invasive interventions sparing mammalian embryos.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson GB (1992) Isolation and use of embryonic stem cells from livestock species. Anim Biotechnol 3, 165–175
Bejar J, Hong Y, Alvarez MC (1999) Towards obtaining ES cells in the marine fish species Sparus aurata; multipassage maintenance, characterization and transfection. Genet Anal Biomol Engng 15, 125–129
Blanc KL (2003) Immunomodulatory effects of fetal and adult mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotherapy 5, 485–489
Bradley A, Evans M, Kaufman MH, Robertson E (1984) Formation of germ-line chimeras from embryo derived teratocarcinoma cell lines. Nature 309, 255–256
Campbell KHS, McWhir J, Ritchie WA, Wilmut I (1996) Sheep cloned by nuclear transfer from a cultured cell line. Nature 380, 64–66
Chen S, Hong Y, Schartl M (2002) Development of a positive-negative selection procedure for gene targeting in fish cell. Aquaculture 214, 67–79
Chen SL, Sha ZX, Ye HQ (2003a) Establishment of a pluripotent embryonic cell line from sea perch (Lateolabrax japonicus) embryos. Aquaculture 218, 141–151
Chen SL, Ye HQ, Sha ZX, Hong Y (2003b) Derivation of a pluripotent embryonic cell line from red sea bream blastulas. J Fish Biol 63, 795–805
Chen SS, Revoltella RP, Papini S, Michelini M, Fitzgerald W, Zimmerberg J, Margolis L (2003) Multilineage differentiation of Rhesus monkey embryonic stem cells in three-dimensional culture systems. Stem Cells 21, 281–295
Chen SL, Sha ZX, Ye HQ, Liu Y, Tian YS, Hong Y, Tang QS (2007) Pluripotency and chimera competence of an embryonic stem cell line from the sea perch (Lateolabrax japonicus). Mar Biotechnol 9, 82–91
Collodi P, Kamei Y, Sharps A, Weber D, Barnes D (1992) Fish embryo cell cultures for derivation of stem cells and transgenic chimeras. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 1, 257–265
Conover JC, Ip NY, Poueymirou WT, Bates B, Goldfarb MP, DeChinara TM, Yancopoulos GD (1993) Ciliary neurotrophic factor maintains the pluripotentiality of embryonic stem cells. Development 119, 559–565
Cool SM, Nurcombe V (2005) Substrate induction of osteogenesis from marrow-derived mesenchymal precursors. Stem Cells Dev 14, 632–642
Evans MG, Kaufman MH (1981) Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 292, 154–156
Goossler A, Doetschman T, Korn R, Serfling E, Kembler R (1986) Transgenesis by means of blastocyst derived embryonic stem cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83, 9065–9069
Handyside AH, O’Neill GT, Jones M, Hooper ML (1989) Use of BRL-conditioned medium in combination with feeder layers to isolate a diploid embryonal stem cell line. Rouxs Arch Dev Biol 198, 48–55
Hasty P, Ramirez-Solis R, Krumlauf R, Bradley A (1991) Introduction of a subtle mutation into the Hox-2.6 locus in embryonic stem cells. Nature 350, 243–246
Holen E, Hamre K (2003) Towards obtaining long term embryonic stem cell like cultures from a marine flatfish, Scophtalmus maximus. Fish Physiol Biochem 29, 245–252
Hong Y, Winkler C, Schartl M (1996) Pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cell lines from the medakafish (Oryzias latipes). Mech Dev 60, 33–44
Hong Y, Winkler C, Schartl M (1998) Production of medakafish chimeras from a stable embryonic stem cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 3679–3684
Koestenbauer S, Zech NH, Juch H, Vanderzwalmen P, Schoonjans L, Dohr G (2006) Embryonic stem cells: similarities and differences between human and murine embryonic stem cells. Am J Reprod Immunol 55, 169–180
Laue C, Kaiser A, Wendl K (2001) Reversal of streptozotocin-diabetes after transplantation of piscine principal islets to nude mice. Transplant Proc 33, 3504–3510
Ma C, Fan L, Ganassin R, Bols N, Collodi P (2001) Production of zebrafish germ-line chimeras from embryo cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 2461–2466
Martin GR (1981) Isolation of a pluripotent cell line from mouse embryo cultures in medium conditioned by tetracarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78, 7634–7638
Nakano T, Kodama H, Honjo T (1994) Generation of lymphohematopoietic cells from embryonic stem cells in culture. Science 265, 1098–1101
Nichols J, Chambers I, Smith A (1994) Derivation of germline competent embryonic stem cells with a combination of interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptor. Exp Cell Res 215, 237–239
Pease S, Braghetta P, Gearing D, Grail D, Williams RL (1990) Isolation of embryonic stem (ES) cells in media supplemented with recombinant leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Dev Biol 141, 344–352
Piquet-Pellorce C, Grey L, Mereau A, Heath JK (1994) Are LIF and related cytokines functionally equivalent? Exp Cell Res 213, 340–347
Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, Trounson A, Bongso A (2000) Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol 18, 399–404
Robertson EJ (1987) Embryo-derived stem cell lines in teratocarcinomas and embryonic Stem cells: a practical approach, Robertson EJ (ed). (Oxford: IRL Press), pp. 71–112
Rocha A, Ruiz S, Estepa A, Coll JM (2004) Application of inducible and targeted gene strategies to produce transgenic fish: a review. Mar Biotechnol 6, 118–127
Sims M, First NL (1993) Production of calves by transfer of nuclei from cultured inner cell mass cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90, 6143–6147
Sukoyan MA, Golubitsa AN, Zhelezova AL, Shilov AG, Vatolin SY, Maximovsky LP, Andereeva LE, McWhir J, Pack SD, Bayborodin SI, Kerkis AY, Kizilova HI, Serov OL (1992) Isolation and cultivation of blastocyst-derived stem cell lines from American mink (Mustela vision). Mol Reprod Dev 33, 418–431
Sun L, Bradford CS, Ghosh C, Collodi P, Barnes DW (1995) ES-like cell cultures derived from early zebrafish embryos. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 4, 193–199
Thompson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282, 1145–1147
Wakamatsu Y, Ozato K, Sasado T (1994) Establishment of a pluripotent cell line derived from a medaka (Oryzias latipes) blastula embryo. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3, 185–191
Wakamatsu Y, Ju B, Pristyaznhyuk I, Niwa K, Ladygina T, Kinoshita M, Araki K, Ozato K (2001) Fertile and diploid nuclear transplants derived from embryonic cells of a small laboratory fish, medaka (Oryzias latipes). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 1071–1076
Wombus AM (2001) Potential of embryonic stem cells. Mol Aspects Med 22, 149–164
Wombus AM, Holzhausen H, Jakel P, Schoneich J (1984) Characterization of a pluripotent stem cell line derived from a mouse embryo. Exp Cell Res 152, 212–219
Wright JR Jr, Pohajdak B (2001) Cell therapy for diabetes using piscine islet tissue. Cell Transplant 10, 125–143
Wright JR Jr, Yang H (1997) Tilapia Brockmann bodies: an inexpensive, simple model for discordant islet xenotransplantation. Ann Transplant 2, 72–75
Wurst W, Joyner AL (1993) Production of targeted embryonic stem cell clones. In Joyner AL (ed.), Gene Targeting (Oxford: IRL Press), pp 33–61
Yoshida K, Chambers I, Nichols J, Smith A, Saito M, Yasukawa K, Shoyab M, Taga T, Kishimoto T (1994) Maintenance of the pluripotential phenotype of embryonic stem cells through direct activation of gp130 signalling pathways. Mech Dev 45, 163–171
Acknowledgment
The authors thank the management of C. Abdul Hakeem College for providing the facilities to carry out this work. The authors also thank the Director, Central Institute of Brackishwater Aquaculture, Chennai, for providing the experimental animals. Thanks are also due to Director, NCCS, Pune, for providing excellent infrastructure facilities for this study. The financial assistance provided by the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
movie supplement
(AVI 3.38 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parameswaran, V., Shukla, R., Bhonde, R. et al. Development of a Pluripotent ES-like Cell Line from Asian Sea Bass (Lates calcarifer)—An Oviparous Stem Cell Line Mimicking Viviparous ES Cells. Mar Biotechnol 9, 766–775 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-007-9028-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-007-9028-y