Abstract
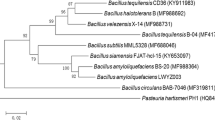
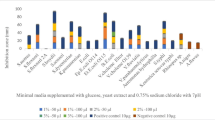
The aim of this study was to isolate bacteria that are resistant to the strong antimicrobial metabolites characteristic of Aplysina aerophoba. For this purpose, bacterial isolation was performed on agar plates to which sponge tissue extract had been added. Following screening for antifungal and antimicrobial activities, 5 strains were chosen for more detailed analyses. 16S ribosomal DNA sequencing revealed that all isolates belonged to the genus Bacillus, specifically B. subtilis and B. pumilus. Using a combination of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ ionization mass spectrometry typing of whole cells and antimicrobial bioassays against selected reference strains, the bioactive metabolites were identified as lipopeptides.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pabel, C., Vater, J., Wilde, C. et al. Antimicrobial Activities and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry of Bacillus Isolates from the Marine Sponge Aplysina aerophoba . Mar. Biotechnol. 5, 424–434 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-002-0088-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-002-0088-8