Abstract
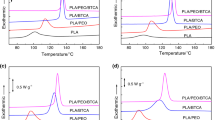
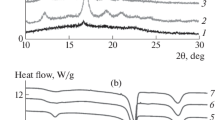
For a polymer/polymer dismissible blend with two crystallizable components, the crystallization behavior of different components and the reciprocal influences between different crystals are interesting and important, but did not investigate in detail. In this study, the L-poly(lactic acid)/polypropylene (PLLA/PP) blends with different weight ratios were prepared by melt mixing and the crystallization behavior of the blends were investigated. Results showed that the crystalline structures of PLLA and PP were not altered by the composition. For the crystallization of PLLA, both the diffusion of chain segments and crystallization rate were enhanced under the existence of PP crystals. For the crystallization of PP, its crystallization rate was depressed under the existence of amorphous PLLA molecular chains. When the PP crystallized from the existence of PLLA crystals, although the diffusion rate of PP was reduced by PLLA crystals, the nucleation positions were obviously enhanced, which accelerated the formation of PP crystals. This investigation would supply more basic data for the application of PLLA/PP blend.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The related data (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3104-x) for this paper is available in the (Data Repository of China Association for Science and Technology) database (https://www.scidb.cn/c/cjps).
References
Tyler, B.; Gullotti, D.; Mangraviti, A.; Utsuki, T.; Brem, H. Polylactic acid (PLA) controlled delivery carriers for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 163–175.
Pascual-Gonzalez, C.; Thompson, C.; de la Vega, J.; Biurrun Churruca, N.; Fernandez-Blazquez, J. P.; Lizarralde, I.; Herraez-Molinero, D.; Gonzalez, C.; Llorca, J. Processing and properties of PLA/Mg filaments for 3D printing of scaffolds for biomedical applications. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 884–894.
Zhang, S.; Yan, D.; Zhao, L.; Lin, J. Composite fibrous membrane comprising PLA and PCL fibers for biomedical application. Compos. Commun. 2022, 34, 101268.
Miros-Kudra, P.; Gzyra-Jagieta, K.; Kudra, M. Physicochemiaal assessment of the biodegradability of agricultural nonwovens made of PLA. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2021, 145, 26–34.
Parida, M.; Shajkumar, A.; Mohanty, S.; Biswal, M.; Nayak, S. K. Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)-based mulch films: evaluation of mechanical, thermal, barrier properties and aerobic biodegradation characteristics in real-time environment. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 3649–3674.
Zhou, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, B.; Chen, K. Development and characterization of bilayer films based on pea starch/polylactic acid and use in the cherry tomatoes packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 114912.
Mangaraj, S.; Thakur, R. R.; Yadav, A. Development and characterization of PLA and Cassava starch-based novel biodegradable film used for food packaging application. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16314.
Ordoñez, R.; Atarés, L.; Chiralt, A. Antibacterial properties of cinnamic and ferulic acids incorporated to starch and PLA monolayer and multilayer films. Food Control. 2022, 136, 108878.
Zaaba, N. F.; Jaafar, M. A review on degradation mechanisms of polylactic acid: hydrolytic, photodegradative, microbial, and enzymatic degradation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2061–2075.
Xiaodong, W.; Xuan, G.; Rakshit, S. Direct fermentative production of lactic acid on cassava and other starch substrates. Biotechnol. Lett. 1997, 19, 841–843.
Oh, H.; Wee, Y. J.; Yun, J. S.; Han, S. H.; Jung, S.; Ryu, H. W. Lactic acid production from agricultural resources as cheap raw materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1492–1498.
Groot, W. J.; Borén, T. Life cycle assessment of the manufacture of lactide and PLA biopolymers from sugarcane in Thailand. Int. J. Life Cycle Ass. 2010, 15, 970–984.
Lee, W.; Lee, J.; Chung, J. W.; Kwak, S.Y. Enhancement of tensile toughness of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) through blending of a polydecalactone-grafted cellulose copolymer: the effect of mesophase transition on mechanical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1103–1113.
Takayama, T.; Todo, M. Improvement of impact fracture properties of PLA/PCL polymer blend due to LTI addition. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 4989–4992.
Takayama, T.; Todo, M.; Tsuji, H.; Arakawa, K. Effect of LTI content on impact fracture property of PLA/PCL/LTI polymer blends. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 6501–6504.
Arrieta, M. P.; Samper, M. D.; Aldas, M.; López, J. On the use of PLA-PHB blends for sustainable food packaging applications. Materials 2017, 10, 1008.
Piekarska, K.; Piorkowska, E.; Bojda, J. The influence of matrix crystallinity, filler grain size and modification on properties of PLA/calcium carbonate composites. Polym. Test. 2017, 62, 203–209.
Rahmatabadi, D.; Ghasemi, I.; Baniassadi, M.; Abrinia, K.; Baghani, M. 3D printing of PLA-TPU with different component ratios: fracture toughness, mechanical properties, and morphology. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 3970–3981.
Nofar, M.; Zhu, W.; Park, C. B.; Randall, J. Crystallization kinetics of linear and long-chain-branched polylactide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 13789–13798.
Korber, S.; Moser, K.; Diemert, J. Development of high temperature resistant stereocomplex PLA for injection moulding. Polymers 2022, 14, 384.
Ebadi-Dehaghani, H.; Barikani, M.; Khonakdar, H. A.; Jafari, S. H. Microstructure and non-isothermal crystallization behavior of PP/PLA/clay hybrid nanocomposites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 121, 1321–1332.
Klonos, P. A.; Lazaridou, M.; Samiotaki, C.; Kyritsis, A.; Bikiaris, D. N. Dielectric and calorimetric study in renewable polymer blends based on poly(ethylene adipate) and poly(lactic acid) with microphase separation. Polymer 2022, 259, 125329.
Li, C.; Dou, Q.; Bai, Z.; Lu, Q. Non-isothermal crystallization behaviors and spherulitic morphology of poly(lactic acid) nucleated by a novel nucleating agent. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 122, 407–417.
Karimi, S.; Ghasemi, I.; Abbassi-Sourki, F. A study on the crystallization kinetics of PLLA in the presence of graphene oxide and PEG-grafted-graphene oxide: effects on the nucleation and chain mobility. Compos. BEng. 2019, 158, 302–310.
Prasitnok, K.; In-noi, O. Functionalized graphenes as nanofillers for polylactide: molecular dynamics simulation study. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 294–305.
Črešnar, K. P.; Klonos, P. A.; Zamboulis, A.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Xanthopoulou, E.; Papadopoulos, L.; Kyritsis, A.; Kuzmič, K.; Zemljič, L. F.; Bikiaris, D. N. Structure-Properties relationships in renewable composites based on polylactide filled with Tannin and Kraft Lignin-crystallization and molecular mobility. Thermochim. Acta 2021, 703, 178998.
Kudryavtseva, V. L.; Zhao, L.; Tverdokhlebov, S. I.; Sukhorukov, G. B. Fabrication of PLA/CaCO3 hybrid micro-particles as carriers for water-soluble bioactive molecules. Colloids Surf. B 2017, 157, 481–489.
Ye, B.; Jia, C.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, H. Solution-blow spun PLA/SiO2 nanofiber membranes toward high efficiency oil/water separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49103.
Messin, T.; Marais, S.; Follain, N.; Guinault, A.; Gaucher, V.; Delpouve, N.; Sollogoub, C. Biodegradable PLA/PBS multinanolayer membrane with enhanced barrier performances. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117777.
Fang, P.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, D.; Xin, J.; Xu, J.; Shi, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, S. Controlled alcoholysis of PET to obtain oligomers for the preparation of PET-PLA copolymer. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138988.
Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Zhao, H.; Lin, J.; Zhao, G.; Park, C. B. Strong and super thermally insulating in-situ anoofibrillar PLA/PET composite foam fabricated by high-pressure microcellular injection molding. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124520.
Yusoff, N. H.; Pal, K.; Narayanan, T.; de Souza, F. G. Recent trends on bioplastics synthesis and characterizations: polylactic acid (PLA) incorporated with tapioca starch for packaging applications. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1232, 129954.
Moji, R. G.; Motloung, S. V.; Motaung, T. E.; Koao, L. F. Characterization of the incorporated SiO2 co-doped with Sr2+ and Tb3+ phosphors into PLA polymer matrix. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1263, 133176.
Choi, E. Y.; Kim, C. K.; Park, C. B. Fabrication of MA-EPDM grafted MWCNTs by reactive extrusion for enhanced interfacial adhesion and mechanical properties of PP/MA-EPDM composite. Compos. B Eng. 2022, 242, 110043.
Zhang, A.; Wang, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, G.; Wang, G. Strong PP/PTFE microfibril reinforced composites achieved by enhanced crystallization under CO2 environment. Polym. Test. 2022, 112, 107630.
Bai, Z.; Dou, Q. Rheology, morphology, crystallization behaviors, mechanical and thermal properties of poly(lactic acid)/polypropylene/maleic anhydride-grafted polypropylene blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 26, 959–969.
Sui, G.; Jing, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. A comparison study of high shear force and compatibilizer on the phase morphologies and properties of polypropylene/polylactide (PP/PLA) blends. Polymer 2018, 154, 119–127.
Jonoobi, M.; Harun, J.; Mathew, A. P.; Oksman, K. Mechanical properties of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) prepared by twin screw extrusion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1742–1747.
Nagarajan, V.; Mohanty, A. K.; Misra, M. Crystallization behavior and morphology of polylactic acid (PLA) with aromatic sulfonate derivative. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43673.
Fatriansyah, J. F.; Surip, S. N.; Jaafar, W. N. R. W.; Phasa, A.; Uyup, M. K. A.; Suhariadi, I. Isothermal crystallization kinetics and mechanical properties of PLA/Kenaf biocomposite: comparison between alkaline treated kenaf core and bast reinforcement. Mater. Lett. 2022, 319, 132294.
Feng, C.; Chen, Y.; Shao, J.; Hou, H. The crystallization behavior of poly(L-lactic acid)/poly(D-lactic acid) electrospun fibers: effect of distance of isomeric polymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 8480–8491.
Clarkson, C. M.; Azrak, S. M. E. A.; Schueneman, G. T.; Snyder, J. F.; Youngblood, J. P. Crystallization kinetics and morphology of small concentrations of cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) and cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) melt-compounded into poly(lactic acid) (PLA) with plasticizer. Polymer 2020, 187, 122101.
Sharafi, Z. S.; Fathi, B.; Ajji, A.; Robert, M.; Elkoun, S. Phase transition and crystallization behavior of grafted starch nanocrystals in PLA nanocomposites. Express Polym. Lett. 2022, 16, 1253–1266.
Kang, H.; Lu, X.; Xu, Y. Properties of immiscible and ethylene-butyl acrylate-glycidyl methacrylate terpolymer compatibilized poly(lactic acid) and polypropylene blends. Polym. Test. 2015, 43, 173–181.
Zhang, Y. C.; Wu, H. Y.; Qiu, Y. P. Morphology and properties of hybrid composites based on polypropylene/polylactic acid blend and bamboo fiber. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7944–50.
Kaczmarek, H.; Nowicki, M.; Vuković-Kwiatkowska, I.; Nowakowska, S. Crosslinked blends of poly(lactic acid) and polyacrylates: AFM, DSC and XRD studies. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 91.
De Rosa, C.; Auriemma, F.; Corradini, P. Crystal structure of form I of syndiotactic polypropylene. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 7452–7459.
Saeidlou, S.; Huneault, M. A.; Li, H.; Park, C. B. Poly(lactic acid) crystallization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1657–1677.
Feng, C.S.; Chen, Y.; Shao, J.; Li, G.; Hou, H.Q. The crystallization and melting behaviors of PDLA-b-PBS-b-PDLA triblock copolymers. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 298–310.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51403089 and 21574060), the Major Special Projects of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No. 20114ABF05100), the Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (No. GJJ170229), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019M652282), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (No. 2018KY37) and the Technology Plan Landing Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (No. GCJ2011-243).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no interest conflict.
Electronic Supplementary Information
10118_2024_3104_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
The Crystallization Behavior of L-Poly(lactic acid)/Polypropylene Blends: The Acceleration for Both L-Poly(lactic acid) and Polypropylene
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, SC., Zhou, WJ., Wu, WJ. et al. The Crystallization Behavior of L-Poly(lactic acid)/Polypropylene Blends: The Acceleration for Both L-Poly(lactic acid) and Polypropylene. Chin J Polym Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3104-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3104-x