Abstract
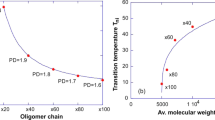
Regulation of phase structure has been recognized as one of the most effective ways to fabricate self-healing polymers with high mechanical strength. The mechanical properties of the resultant polymers are certainly affected by the size of separated phase domain. However, the study on this aspect is absence, because it can hardly exclude the influence of variation in monomer proportion required for tuning the separated phase size. Here, we report the first study on tuning the phase size through reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization without changing the proportion of monomers. As expected, the size of separated phase has been successfully mediated from 15 nm to 9 nm by tuning the molecular weight of the chain transfer agent. It is found that the mechanical strength and the self-healing efficiency of the resultant polymers increase simultaneously with the decrease of phase size. The study on the formation kinetics of hydrogen bonds reveals that the decrease of phase size can facilitate the re-bonding rate of hydrogen bonds, even if the migration of polymer chains is restricted.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The associated data of this article (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3097-5) can be accessed from the Chinese Journal of Polymer Science database (https://www.cjps.org).
References
Sumerlin, B. S. Next-generation self-healing materials. Science 2018, 362, 150–151.
Zhang, M. Self-healing polymeric materials: on a winding road to success. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 40, 1315–1316.
Xu, J.; Zhu, L.; Nie, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, S.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Yan, S. Advances and challenges of self-healing elastomers: a mini review. Materials 2022, 15, 5993.
Zheng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Tan, Y.; Liu, F.; Wu, Y. Rapid self-healing and strong adhesive elastomer via supramolecular aggregates from core-shell micelles of silicon hydroxyl-functionalized cis-polybutadiene. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 41, 84–94.
Guo, Z.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Sun, J. Engineering of chain rigidity and hydrogen bond cross-linking toward ultra-strong, healable, recyclable and water-resistant elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300286.
Li, C.; Liu, J.; Qiu, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X. Photoswitchable and reversible fluorescent eutectogels for conformal information encryption. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, 13971.
Wang, Y.; Shu, R.; Zhang, X. Strong, supertough and self-healing biomimetic layered nanocomposites enabled by reversible interfacial polymer chain sliding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, 03446.
Yang, T.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, J. Healable, recyclable, and scratch-resistant polyurethane elastomers cross-linked with multiple hydrogen bonds. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 2830–2839.
Zhao, C.; Guo, M.; Mao, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, H.; Xiang, D.; Li, H. Self-healing, stretchable, temperature-sensitive and strain-sensitive hydrogel-based flexible sensors. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 41, 334–344.
Zhang, L.; You, Z. Dynamic oxime-urethane bonds, a versatile unit of high performance self-healing polymers for diverse applications. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 39, 1281–1291.
Neal, J. A.; Mozhdehi, D.; Guan, Z. Enhancing mechanical performance of a covalent self-healing material by sacrificial non-covalent bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4846–4850.
Chen, Y.; Guan, Z. Multivalent hydrogen bonding block copolymers self-assemble into strong and tough self-healing materials. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10868–10870.
Li, M.; Rong, M.; Zhang, M. Reversible mechanochemistry enabled autonomous sustaining of robustness of polymers—an example of next generation self-healing strategy. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 39, 545–553.
Eom, Y.; Kim, S.-M.; Lee, M.; Jeon, H.; Park, J.; Lee, E. S.; Hwang, S. Y.; Park, J.; Oh, D. X. Mechano-responsive hydrogen-bonding array of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer captures both strength and self-healing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 621.
Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X. Mechano-responsive hydrogen-bonding array of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer captures both strength and self-healing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1291.
Sun, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Qi, Q.; Hang, Z.; Chen, K.; Xu, J.; Fu, J. Vascular smooth muscle-inspired architecture enables soft yet tough self-healing materials for durable capacitive strain-sensor. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 130.
Tie, J.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, H. Strong and ultratough ionogel enabled by ingenious combined ionic liquids induced microphase separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2307367.
Li, H.; Li, X.; Liu, N.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, F. A tough and strain-stiffening ionogel enabled by moderate microphase separation for epidermal multi-sensor. Polymer 2023, 282, 126166.
Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Xu, X.; Jiang, P.; Wang, X. A tough and strain-stiffening ionogel enabled by moderate microphase separation for epidermal multi-sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2210395.
Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S. High Mechanical Strength and Multifunctional Microphase-Separated Supramolecular Hydrogels Fabricated by Liquid-Crystalline Block copolymer. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 44, 2200829.
Lai, Y.; Kuang, X.; Zhu, P.; Huang, M.; Dong, X.; Wang, D. Colorless, transparent, robust, and fast scratch-self-healing elastomers via a phase-locked dynamic bonds design. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802556.
Wang, B.; Zhai, W.; Fan, J. B.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Feng, X. An interfacially polymerized self-healing organo/hydro copolymer with shape memory. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6846–6851.
An, N.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Sun, J. Healable and mechanically super-strong polymeric composites derived from hydrogen-bonded polymeric complexes. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904882.
Xun, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, B.; Ouyang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y. Tough and degradable self-healing elastomer from synergistic soft-hard segments design for biomechano-robust artificial skin. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 20656–20665.
Xie, Z.; Hu, B.; Li, R.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogen bonding in self-healing elastomers. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9319–9333.
Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Shi, X.; Feng, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Yan, S. A fast self-healable and stretchable conductor based on hierarchical wrinkled structure for flexible electronics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 211, 108834.
Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Feng, X.; Xu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yan, S. Robust and ultra-fast self-healing elastomers with hierarchically anisotropic structures and used for wearable sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137305.
Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Yan, S. Mechanically robust, instant self-healing polymers towards elastic entropy driven artificial muscles. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140100.
Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, X.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Yan, S. High-strength, fast self-healing, aging-insensitive elastomers with shape memory effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35445–35452.
Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Sui, C.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Yan, S. Highly entangled elastomer with ultra-fast self-healing capability and high mechanical strength. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147689.
Lai, J.; Filla, D.; Shea, R. Functional polymers from novel carboxyl-terminated trithiocarbonates as highly efficient RAFT agents. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 6754–6756.
Pan, J.; Zeng, H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H. Hierarchical multiscale hydrogels with identical compositions yet disparate properties via tunable phase separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110277.
Chen, Y.; Kushner, A.; Williams, G.; Guan, Z. Multiphase design of autonomic self-healing thermoplastic elastomers. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 467–472.
Wang, X.; Zhan, S.; Lu, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Men, Y.; Sun, J. Healable, recyclable, and mechanically tough polyurethane elastomers with exceptional damage tolerance. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2005759.
Xiang, H.; Li, X.; Wu, B.; Sun, S.; Wu, P. Highly damping and self-healable ionic elastomer from dynamic phase separation of sticky fluorinated polymers. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209581.
Yao, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. An unparalleled H-bonding and ion-bonding crosslinked waterborne polyurethane with super toughness and unprecedented fracture energy. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 2742.
Zhang, Q.; Niu, S.; Wang, L.; Lopez, J.; Chen, S.; Cai, Y.; Du, R.; Liu, Y.; Lai, J.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Yan, X.; Liu, C.; Tok, J.; Jia, X.; Bao, Z. An elastic autonomous self-healing capacitive sensor based on a dynamic dual crosslinked chemical system. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801435.
Peng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, C.; Yang, Y.; Song, C.; Wu, Q.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. Super tough and strong self-healing elastomers based on polyampholytes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 19066.
Zhao, P.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Xia, J.; Bian, L. Mussel cuticle-mimetic ultra-tough, self-healing elastomers with double-locked nanodomains exhibit fast stimuli-responsive shape transformation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 12463.
Su, G.; Yin, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, F.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, T.; Yu, G. Balancing the mechanical, electronic, and self-healing properties in conductive self-healing hydrogel for wearable sensor applications. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1795.
Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Nishiura, M.; Higaki, Y.; Hou, Z. Terpolymerization of ethylene and two different methoxyaryl-substituted propylenes by scandium catalyst makes tough and fast self-healing elastomers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 26192–26198.
Tang, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, M.; Qin, Y.; Gong, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, L. Ultrafast self-healing and self-adhesive polysiloxane towards reconfigurable on-skin electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 1750–1759.
Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Fu, J. A fast room-temperature self-healing glassy polyurethane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7947–7955.
Tee, B. C. K.; Wang, C.; Allen, R.; Bao, Z. A fast room-temperature self-healing glassy polyurethane. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 825–832.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2022MB122), “Qingchuang science and technology plan” project of colleges and Universities in Shandong Province (No. 2020KJC005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no interest conflict.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Zhu, L., Feng, XQ. et al. Effect of Phase Separation Size on the Properties of Self-healing Elastomer. Chin J Polym Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3097-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3097-5