Abstract
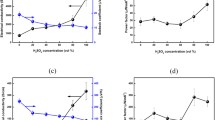
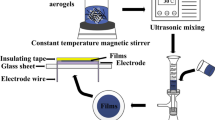
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) is one of the most successful conductive polymers that recently has been used in wearable sensors for human health monitoring. In this work, we prepared a series of PEDOT hybrids consisting of PEDOT, sodium poly(styrene sulfonate) (PSSNa) and polyethylene oxide (PEO), and their preparation could be scaled-up via an adapted solid-state polymerization process. The resistance of the as-prepared PEDOT:PSS/PEO hybrid shows clear temperature response, i.e., it decreases almost linearly with the temperature increase. To understand this phenomenon, the in situ synchrotron radiation wide- and small-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS/SAXS) characterizations were undertaken to study the temperature-dependent microstructure change of the PEDOT:PSS/PEO hybrid. It demonstrated that PEDOT formed conductive paths in the hybrids, which were not destroyed by the PEO crystallization. As temperature increased, the PEO crystals’ melting and the accompanying reorganization of PEDOT chains endowed the hybrid sample temperature responsiveness. Based on these fundamental knowledges, the hybrid materials were used to fabricate flexible wearable sensor that showing temperature sensing performance with an accuracy of 1 °C. These findings shed lights on the scalable manufacturing of wearable sensors for body temperature monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lou, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, K.; Wei, Z.; Shen, G. Reviews of wearable healthcare systems: materials, devices and system integration. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2020, 140, 100523.
Ma, L. Y.; Soin, N. Recent progress in printed physical sensing electronics for wearable health-monitoring devices: a review. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 3844–3859.
Nakata, S.; Arie, T.; Akita, S.; Takei, K. Wearable, flexible, and multifunctional healthcare device with an ISFET chemical sensor for simultaneous sweat pH and skin temperature monitoring. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 443–448.
Ates, H. C.; Nguyen, P. Q.; Gonzalez-Macia, L.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Güder, F.; Collins, J. J.; Dincer, C. End-to-end design of wearable sensors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 887–907.
Grant, A.; Smarr, B. Feasibility of continuous distal body temperature for passive, early pregnancy detection. PLOS Digit. Health. 2022, 1, e0000034.
Tang, Z.; Kong, N.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, P.; Mou, S.; Liljeström, P.; Shi, J.; Tan, W.; Kim, J. S.; Cao, Y.; Langer, R.; Leong, K. W.; Farokhzad, O. C.; Tao, W. A materials-science perspective on tackling COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 847–860.
Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Nyein, H. Y. Y.; Challa, S.; Chen, K.; Peck, A.; Fahad, H. M.; Ota, H.; Shiraki, H.; Kiriya, D.; Lien, D. H.; Brooks, G. A.; Davis, R. W.; Javey, A. Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature 2016, 529, 509–514.
Hasanpour, S.; Karperien, L.; Walsh, T.; Jahanshahi, M.; Hadisi, Z.; Neale, K. J.; Christie, B. R.; Djilali, N.; Akbari, M. A hybrid thread-based temperature and humidity sensor for continuous wound monitoring. Sens. Actuators B 2022, 370, 132414.
T, K.; Rajini, G. K.; Maji, D. Cost-effective, disposable, flexible, and printable MWCNT-based wearable sensor for human body temperature monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 16756–16763.
Tharakan, S.; Nomoto, K.; Miyashita, S.; Ishikawa, K. Body temperature correlates with mortality in COVID-19 patients. Crit. Care. 2020, 24, 298.
Smarr, B. L.; Aschbacher, K.; Fisher, S. M.; Chowdhary, A.; Dilchert, S.; Puldon, K.; Rao, A.; Hecht, F. M.; Mason, A. E. Feasibility of continuous fever monitoring using wearable devices. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21640.
Honda, W.; Harada, S.; Arie, T.; Akita, S.; Takei, K. Wearable, human-interactive, health-monitoring, wireless devices fabricated by macroscale printing techniques. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3299–3304.
Hall, J. E.; Hall, M. E. Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology e-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences: 2020.
Su, Y.; Ma, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Luo, W.; Peng, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, L.; Tan, Y.; Omisore, O. M.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, H. Printable, highly sensitive flexible temperature sensors for human body temperature monitoring: a review. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 200.
Xia, Y.; Sun, K.; Ouyang, J. Solution-processed metallic conducting polymer films as transparent electrode of optoelectronic devices. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2436–2440.
Meng, X.; Xing, Z.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y. Large-area flexible organic solar cells: printing technologies and modular design. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 40, 1522–1566.
Bubnova, O.; Khan, Z. U.; Malti, A.; Braun, S.; Fahlman, M.; Berggren, M.; Crispin, X. Optimization of the thermoelectric figure of merit in the conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 429–433.
Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas sensors based on conducting polymers. Sens. 2007, 7, 267–307.
Lu, Y.; Wen, Y. P.; Lu, B. Y.; Duan, X. M.; Xu, J. K.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y. Electrosynthesis and characterization of poly(hydroxymethylated-3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) film in aqueous micellar solution and its biosensing application. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 30, 824–836.
Jian, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Natural biopolymers for flexible sensing and energy devices. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 459–490.
Dimov, I. B.; Moser, M.; Malliaras, G. G.; McCulloch, I. Semiconducting polymers for neural applications. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 4356–4396.
Guimard, N. K.; Gomez, N.; Schmidt, C. E. Conducting polymers in biomedical engineering. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 876–921.
Kayser, L. V.; Lipomi, D. J. Stretchable conductive polymers and composites based on PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806133.
Li, P.; Sun, K.; Ouyang, J. Stretchable and conductive polymer films prepared by solution blending. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18415–18423.
Sanviti, M.; Martínez-Tong, D. E.; Rebollar, E.; Ezquerra, T. A.; García-Gutiérrez, M. C. Crystallization and phase separation in PEDOT:PSS/PEO blend thin films: influence on mechanical and electrical properties at the nanoscale. Polymer 2022, 125475.
Lo, L. W.; Zhao, J.; Wan, H.; Wang, Y.; Chakrabartty, S.; Wang, C. An inkjet-printed PEDOT:PSS-based stretchable conductor for wearable health monitoring device applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21693–21702.
Corradi, R.; Armes, S. P. Chemical synthesis of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Synth. Met. 1997, 84, 453–454.
Zhou, Z.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, P. Scalable manufacturing of solid polymer electrolytes with superior room-temperature ionic conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 32994–33003.
Li, Y. W.; Liu, G. F.; Wu, H. J.; Zhou, P.; Hong, C. X.; Li, N.; Bian, F. G. BL19U2: small-angle X-ray scattering beamline for biological macromolecules in solution at SSRF. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2020, 31, 117.
Hopkins, J. B.; Gillilan, R. E.; Skou, S. BioXTAS RAW: improvements to a free open-source program for small-angle X-ray scattering data reduction and analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017, 50, 1545–1553.
Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Tang, Z.; Guo, B. Scalable fabrication of thermally conductive elastomer/boron nitride nanosheets composites by slurry compounding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 123, 179–186.
Groenendaal, L.; Jonas, F.; Freitag, D.; Pielartzik, H.; Reynolds, J. R. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) and its derivatives: past, present, and future. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 481–494.
Gueye, M. N.; Carella, A.; Faure-Vincent, J.; Demadrille, R.; Simonato, J. P. Progress in understanding structure and transport properties of PEDOT-based materials: a critical review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 108, 100616.
Zozoulenko, I.; Singh, A.; Singh, S. K.; Gueskine, V.; Crispin, X.; Berggren, M. Polarons, bipolarons, and absorption spectroscopy of PEDOT. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 1, 83–94.
Elschner, A.; Kirchmeyer, S.; Lovenich, W.; Merker, U.; Reuter, K. PEDOT: principles and applications of an intrinsically conductive polymer. CRC Press: 2010.
Meng, H.; Perepichka, D. F.; Wudl, F. Facile solid-state synthesis of highly conducting poly(ethylenedioxythiophene). Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 658–661.
Dörr, T. S.; Pelz, A.; Zhang, P.; Kraus, T.; Winter, M.; Wiemhöfer, H. D. An ambient temperature electrolyte with superior lithium ion conductivity based on a self-assembled block copolymer. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 8061–8065.
Zardalidis, G.; Mars, J.; Allgaier, J.; Mezger, M.; Richter, D.; Floudas, G. Influence of chain topology on polymer crystallization: poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) rings vs. linear chains. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 8124–8134.
Takahashi, Y.; Tadokoro, H. Structural studies of polyethers, (−(CH2)m−O−)n. X. Crystal structure of poly(ethylene oxide). Macromolecules 1973, 6, 672–675.
Liu, Z.; Wu, L.; Qian, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, R.; Xu, Y.; Shi, X.; Qi, C.; Ye, S. Tuned transport behavior of the IPA-treated PEDOT:PSS flexible temperature sensor via screen printing. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 2356–2364.
Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Islam, M.; Peng, S.; Wu, S.; Lim, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C. H. Multi-modal strain and temperature sensor by hybridizing reduced graphene oxide and PEDOT:PSS. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 187, 107959.
Kiebooms, R.; Aleshin, A.; Hutchison, K.; Wudl, F.; Heeger, A. Doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) films: thermal, electromagnetical and morphological analysis. Synth. Met. 1999, 101, 436–437.
Ju, D.; Kim, D.; Yook, H.; Han, J. W.; Cho, K. Controlling electrostatic interaction in PEDOT:PSS to overcome thermoelectric tradeoff relation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905590.
Chu, B.; Hsiao, B. S. Small-angle X-ray scattering of polymers. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1727–1762.
Li, T.; Senesi, A. J.; Lee, B. Small angle X-ray scattering for nanoparticle research. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11128–11180.
Zhang, P.; Zou, R.; Wu, S.; Meyer, L. A.; Wang, J.; Kraus, T. Gold nanoprobes exploring the ice structure in the aqueous dispersion of poly(ethylene glycol)-gold hybrid nanoparticles. Langmuir 2022, 38, 2460–2466.
Yeh, S.-W.; Wu, T. L.; Wei, K. H.; Sun, Y. S.; Liang, K. S. Effect of incorporated CdS nanoparticles on the crystallinity and morphology of poly(styrene-b-ethylene oxide) diblock copolymers. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 1220–1229.
Fu, K.; Lv, R.; Na, B.; Zou, S.; Zeng, R.; Wang, B.; Liu, H. Mixed ion-electron conducting PEO/PEDOT:PSS miscible blends with intense electrochromic response. Polymer 2019, 184, 121900.
Li, X.; Zou, R.; Liu, Z.; Mata, J.; Storer, B.; Chen, Y.; Qi, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, P. Deciphering the superior thermoelectric property of post-treatment-free PEDOT:PSS/IL hybrid by X-ray and neutron scattering characterization. npj Flexible Electron. 2022, 6, 6.
Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zou, R.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, P. Deciphering the quaternary structure of PEDOT:PSS aqueous dispersion with small-angle scattering. Polymer 2022, 261, 125415.
Li, X.; He, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, G.; Qi, W.; Rauber, D.; W. M. Kay, C.; Zhang, P. High-performance post-treatment-free PEDOT based thermoelectric with the establishment of long-range ordered conductive paths. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140047.
Daoud, W. A.; Xin, J. H.; Szeto, Y. S. Polyethylenedioxythiophene coatings for humidity, temperature and strain sensing polyamide fibers. Sens. Actuators, B 2005, 109, 329–333.
Yu, Y.; Peng, S.; Blanloeuil, P.; Wu, S.; Wang, C. H. Wearable temperature sensors with enhanced sensitivity by engineering microcrack morphology in PEDOT:PSS-PDMS sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 36578–36588.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U2032101 and 11905306), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 19lgpy14) and “100 Top Talents Program” of Sun Yat-sen University. Ms. Huiyun Deng is thanked for her help during the sample preparation. This work was carried out with the support of 19U2 beamline at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no interest conflict.
Electronic Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, ZH., Liu, GF., Zhou, ZK. et al. Understand the Temperature Sensing Behavior of Solid-state Polymerized PEDOT Hybrid Based on X-ray Scattering Studies. Chin J Polym Sci 42, 105–112 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-023-3005-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-023-3005-4