Abstract
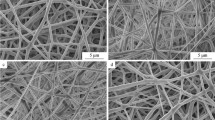
In recent years, the hybrid shish-kebab structure with excellent physical properties and functionalities has attracted much attention because it provides a way of blending nanofibers with different properties into polymer matrix in a regular arrangement. It is often not easy to induce the formation of the hierarchically ordered structure for the semi-crystalline polymer in heterogeneous shish-kebab structure. A poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) heterogeneous shish-kebab structure, i.e., the PCL crystals periodically crystallized onto PLA nanofibers, was successfully created and the interfacial crystal morphology of the PLA/PCL heterogeneous shish-kebab structure was observed using scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. NaOH aqueous solution was applied to modify the surface of the PLA nanofibers to produce adsorption sites and carboxyl groups. The total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) results demonstrated that the formation of the heterogeneous shish-kebab structure was mainly due to the hydrogen bonding interaction between the kebab and shish interface, and the growth process of the kebab crystals also promoted the crystallization of the shish fibers. This heterogeneous nanostructure of biodegradable polymers will have great applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartnikowski, M.; Dargaville, T. R.; Ivanovski, S.; Hutmacher, D. W. Degradation mechanisms of polycaprolactone in the context of chemistry, geometry and environment. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 96, 1–20.
Hamad, K.; Kaseem, M.; Ayyoob, M.; Joo, J.; Deri, F. Polylactic acid blends: the future of green, light and tough. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 85, 83–127.
Carosio, F.; Colonna, S.; Fina, A.; Rydzek, G.; Hemmerlé, J.; Jierry, L.; Schaaf, P.; Boulmedais, F. Efficient gas and water vapor barrier properties of thin poly(lactic acid) packaging films: functionalization with moisture resistant nafion and clay multilayers. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 5459–5466.
Broz, M. Structure and mechanical properties of poly(D,L-lactic acid)/poly(ε-caprolactone) blends. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4181–4190.
Yao, Q.; Cosme, J. G. L.; Xu, T.; Miszuk, J. M.; Picciani, P. H. S.; Fong, H.; Sun, H. Three dimensional electrospun PCL/PLA blend nanofibrous scaffolds with significantly improved stem cells osteogenic differentiation and cranial bone formation. Biomaterials 2017, 115, 115–127.
Zhao, J. J.; Lee, D. T.; Yaga, R. W.; Hall, M. G.; Barton, H. F.; Woodward, I. R.; Oldham, C. J.; Walls, H. J.; Peterson, G. W.; Parsons, G. N. Ultra-fast degradation of chemical warfare agents using MOF-nanofiber kebabs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13224–13228.
Bu, L.; Pentzer, E.; Bokel, F. A.; Emrick, T.; Hayward, R. C. Growth of polythiophene/perylene tetracarboxydiimide donor/acceptor shish-kebab nanostructures by coupled crystal modification. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 10924–10929.
Hu, J.; Liu, A.; Jin, H.; Ma, D.; Yin, D.; Ling, P.; Wang, S.; Lin, Z.; Wang, J. A Versatile strategy for shish-kebab-like multi-heterostructured chalcogenides and enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11004–11010.
Li, C. Y.; Li, L.; Cai, W.; Kodjie, S. L.; Tenneti, K. K. Nanohybrid shish-kebabs: periodically functionalized carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1198–1202.
Van de Voorde, K. M.; Pokorski, J. K.; Korley, L. T. J. Exploring morphological effects on the mechanics of blended poly(lactic acid)/poly(ε-caprolactone) extruded fibers fabricated using multilayer coextrusion. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 5047–5055.
Kakroodi, A. R.; Kazemi, Y.; Rodrigue, D.; Park, C. B. Facile production of biodegradable PCL/PLA in situ nanofibrillar composites with unprecedented compatibility between the blend components. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 976–984.
Li, L.; Li, C. Y.; Ni, C. Polymer crystallization-driven, periodic patterning on carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1692–1699.
Huang, W.; Markwart, J. C.; Briseno, A. L.; Hayward, R. C.; Markwart, J. C. Orthogonal ambipolar semiconductor nanostructures for complementary logic gates. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8610–9.
Xiong, R.; Lu, C.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, S.; Kim, S.; Korolovych, V. F.; Ma, R.; Tsukruk, V. V.; Kim, H. S.; Yingling, Y. G. Template-guided assembly of silk fibroin on cellulose nanofibers for robust nanostructures with ultrafast water transport. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12008–12019.
Jing, X.; Mi, H. Y.; Wang, X. C.; Peng, X. F.; Turng, L. S. Shish-kebab-structured poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers hierarchically decorated with chitosan-poly(ε-caprolactone) copolymers for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6955–6965.
Chen, X.; Wang, W. D.; Cheng, S.; Dong, B.; Li, C. Y. Mimicking bone nanostructure by combining block copolymer self-assembly and 1D crystal nucleation. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8251–8257.
Liu, L.; Shang, Y.; Li, C.; Jiao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L. Hierarchical nanostructured electrospun membrane with periosteum-mimic microenvironment for enhanced bone regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2170106.
Laird, E. D.; Wang, W.; Cheng, S.; Li, B.; Presser, V.; Dyatkin, B.; Gogotsi, Y.; Li, C. Y. Polymer single crystal-decorated superhydrophobic buckypaper with controlled wetting and conductivity. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1204–1213.
Arras, M. M. L.; Jana, R.; Muehlstaedt, M.; Maenz, S.; Andrews, J.; Su, Z.; Grasl, C.; Jandt, K. D. In situ formation of nanohybrid shish-kebabs during electrospinning for the creation of hierarchical shish-kebab structures. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3550–3558.
Xie, Q.; Han, L.; Shan, G.; Bao, Y.; Pan, P. Polymorphic crystalline structure and crystal morphology of enantiomeric poly(lactic acid) blends tailored by a self-assemblable aryl amide nucleator. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2680–2688.
Wang, X.; Salick, M. R.; Wang, X.; Cordie, T.; Han, W.; Peng, Y.; Li, Q.; Turng, L. S. Poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers with a self-induced nanohybrid shish-kebab structure mimicking collagen fibrils. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3557–3569.
Chen, X.; Dong, B.; Wang, B.; Shah, R.; Li, C. Y. Crystalline block copolymer decorated, hierarchically ordered polymer nanofibers. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 9918–9927.
Gleeson, S. E.; Kim, S.; Qian, Q.; Yu, T.; Marcolongo, M.; Li, C. Y. Biomimetic mineralization of hierarchical nanofiber shish-kebabs in a concentrated apatite-forming solution. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 571–580.
Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Harniman, R.; Winnik, M.; Manners, I. Hierarchical assembly of cylindrical block comicelles mediated by spatially confined hydrogen-bonding interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12902–12912.
Mukherjee, T.; Sani, M.; Kao, N.; Gupta, R. K.; Quazi, N.; Bhattacharya, S. Improved dispersion of cellulose microcrystals in polylactic acid (PLA) based composites applying surface acetylation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 101, 655–662.
Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.; Whiteside, B.; Wyborn, J.; Norris, K.; Wu, Z.; Coates, P.; Men, Y. Tensile deformation of oriented poly(ε-caprolactone) and its miscible blends with poly(vinyl methyl ether). Macromolecules 2013, 46, 6981–6990.
Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y. C.; Han, S.; Ma, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q. Endothelial cell migration on poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers coated with a nanohybrid shish-kebab structure mimicking collagen fibrils. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1202–1213.
Bai, H.; Zhang, W.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Control of crystal morphology in poly(L-lactide) by adding nucleating agent. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1233–1237.
Xu, H.; Xu, Y.; Pang, X.; He, Y.; Jung, J.; Xia, H.; Lin, Z. A general route to nanocrystal kebabs periodically assembled on stretched flexible polymer shish. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500025.
Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Payne, S. A.; Zhu, J. Y.; Li, R. Comparison between cellulose nanocrystal and cellulose nanofibril reinforced poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers and their novel shish-kebab-like crystalline structures. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3409–3416.
Zhang, J. M.; Sato, H.; Tsuji, H.; Noda, I.; Ozaki, Y. Infrared spectroscopic study of CH3⋯O=C interaction during poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) stereocomplex formation. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1822–1828.
Pan, P.; Yang, J.; Shan, G.; Bao, Y.; Weng, Z.; Cao, A.; Yazawa, K.; Inoue, Y. Temperature-variable FTIR and solid-state 13C NMR investigations on crystalline structure and molecular dynamics of polymorphic poly(L-lactide) and poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) stereocomplex. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 189–197.
Semba, T.; Kitagawa, K.; Ishiaku, U. S.; Hamada, H. The effect of crosslinking on the mechanical properties of polylactic acid/polycaprolactone blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 1816–1825.
Shukor, F.; Hassan, A.; Saiful Islam, M.; Mokhtar, M.; Hasan, M. Effect of ammonium polyphosphate on flame retardancy, thermal stability and mechanical properties of alkali treated kenaf fiber filled PLA biocomposites. Mater. Design 2014, 54, 425–429.
Yousif, B. F.; Shalwan, A.; Chin, C. W.; Ming, K. C. Flexural properties of treated and untreated kenaf/epoxy composites. Mater. Design 2012, 40, 378–385.
Yang, X. S.; Zhao, K.; Chen, G. Q. Effect of surface treatment on the biocompatibility of microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1391–1397.
Ning, N.; Fu, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, F.; Wang, K.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Realizing the enhancement of interfacial interaction in semicrystalline polymer/filler composites via interfacial crystallization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1425–1455.
Li, L. Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, G. L.; Chen, X. M.; Hsiao, B. S.; Chu, B.; Spanier, J. E.; Li, C. Y. Patterning polyethylene oligomers on carbon nanotubes using physical vapor deposition. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1007–1012.
Yan, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Ozaki, Y.; Shen, D.; Yan, D.; Shi, A. C.; Yan, S. Surface-induced anisotropic chain ordering of polycarprolactone on oriented polyethylene substrate: epitaxy and soft epitaxy. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 8041–8048.
Shen, B.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Han, C. C. Shear-induced crystallization at polymer-substrate interface: the slippage hypothesis. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6919–6927.
Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Preparation and characterization of poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites reinforced with lignin-containing cellulose nanofibrils. Polymer 2014, 38, 464–470.
Tsai, C. C.; Gan, Z.; Chen, T.; Kuo, S. W. Competitive hydrogen bonding interactions influence the secondary and hierarchical self-assembled structures of polypeptide-based triblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3017–3029.
Zhang, J. M.; Tsuji, H.; Noda, I.; Ozaki, Y. Structural changes and crystallization dynamics of poly(L-lactide) during the cold-crystallization process investigated by infrared and two-dimensional infrared correlation spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 6433–6439.
Na, Y. H.; He, Y.; Shuai, X.; Kikkawa, Y.; Doi, Y.; Inoue, Y. Compatibilization Effect of poly(ε-caprolactone)-b-poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymers and phase morphology analysis in immiscible poly(lactide)/poly(ε-caprolactone) blends. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1179–1186.
Zhang, C.; Zhai, T.; Turng, L. S.; Dan, Y. Morphological, mechanical, and crystallization behavior of polylactide/polycaprolactone blends compatibilized by l-lactide/caprolactone copolymer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 9505–9511.
Ding, W.; Jahani, D.; Chang, E.; Alemdar, A.; Park, C. B.; Sain, M. Development of PLA/cellulosic fiber composite foams using injection molding: crystallization and foaming behaviors. Compos. Part A-Appl. S 2016, 83, 130–139.
Bai, H.; Huang, C.; Xiu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, K.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Significantly improving oxygen barrier properties of polylactide via constructing parallel-aligned shish-kebab-like crystals with well-interlocked boundaries. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1507–1514.
Xu, H.; Zhong, G.-J.; Fu, Q.; Lei, J.; Jiang, W.; Hsiao, B. S.; Li, Z. M. Formation of shish-kebabs in injection-molded poly(L-lactic acid) by application of an intense flow field. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6774–6784.
Gazzano, M.; Gualandi, C.; Zucchelli, A.; Sui, T.; Korsunsky, A. M.; Reinhard, C.; Focarete, M. L. Structure-morphology correlation in electrospun fibers of semicrystalline polymers by simultaneous synchrotron SAXS-WAXD. Polymer 2015, 63, 154–163.
Yang, L.; Somani, R. H.; Sics, I.; Hsiao, B. S.; Kolb, R.; Fruitwala, H.; Ong, C. Shear-induced crystallization precursor studies in model polyethylene blends by in-situ rheo-SAXS and rheo-WAXD. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4845–4859.
Xie, X. L.; Li, Y.; Xu, J. Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhong, G. J.; Li, Z. M. Largely enhanced mechanical performance of poly(butylene succinate) multiple system via shear stress-induced orientation of the hierarchical structure. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13373–13385.
Gu, X.; Shaw, L.; Gu, K.; Toney, M. F.; Bao, Z. The meniscus-guided deposition of semiconducting polymers. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 534.
Acknowledgments
The authors affiliated with the Zhengzhou University acknowledge the research facility, the financial support from the National Center for International Joint Research of Micro-Nano Molding Technology in China, the International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (No. 2015DFA30550).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Electronic Supplementary Information
10118_2022_2747_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Structure and Morphology of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Heterogeneous Shish-Kebab Structure Induced by Poly(lactic acid) Nanofibers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, ZH., Wang, DF., Xu, YY. et al. Structure and Morphology of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Heterogeneous Shish-Kebab Structure Induced by Poly(lactic acid) Nanofibers. Chin J Polym Sci 40, 1223–1232 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2747-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2747-8