Abstract
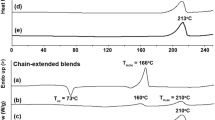
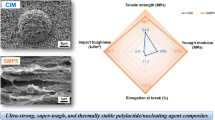
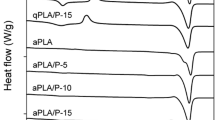
Poly(lactide), PLA, suffers from brittleness and low heat deflection temperature (HDT), which limits its application as an engineering plastic. In this work, poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide)/ethylene-vinyl acetate-glycidyl methacrylate random copolymer (PLLA/PDLA/EVM-GMA = 1/1/x) composites were prepared by melt blending, and the in situ formed EVM-g-PLA copolymers improved the compatibility between PLA and EVM-GMA. Subsequently, the blends were subjected to a two-step annealing process during compression molding, i.e. first annealing at 120 °C to rapidly form a certain amount of stereocomplex (sc) crystallites as nucleation sites, and then annealing at 200 °C to guide the formation of new sc crystallites. Both differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and wide angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD) measurements confirmed the formation of highly stereocomplexed PLA products. Mechanical results showed that the PLLA/PDLA blend with 20 wt% of EVM-GMA had a notched impact strength up to 65 kJ/m2 and an elongation at break of 48%, while maintaining a tensile strength of 40 MPa. Meanwhile, dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) and heat deflection tests showed that the PLA composite had an HDT up to 142 °C which is 90 °C higher than that of normal PLA products. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) confirmed the fine dispersion of EVM-GMA particles, which facilitated to understand the toughening mechanism. Furthermore, the highly stereocomplexed PLA composites simultaneously exhibited excellent chemical and hydrolysis resistance. Therefore, these fascinating properties may extend the application range of sc-PLA material as an engineering bioplastic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reddy, M. M.; Vivekanandhan, S.; Misra, M.; Bhatia, S. K.; Mohanty, A. K. Biobased plastics and bionanocomposites: current status and future opportunities. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1653–1689.
Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Li, L.; Qian, L.; Xin, F. Terminal group effects of phosphazene-triazine bi-group flame retardant additives in flame retardant polylactic acid composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 140, 166–175.
Yang, W.; Fortunati, E.; Dominici, F.; Giovanale, G.; Mazzaglia, A.; Balestra, G. M.; Kenny, J. M.; Puglia, D. Effect of cellulose and lignin on disintegration, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of PLA active films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 360–368.
Yang, W.; Weng, Y.; Puglia, D.; Qi, G.; Dong, W.; Kenny, J. M.; Ma, P. Poly(lactic acid)/lignin films with enhanced toughness and anti-oxidation performance for active food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 102–110.
Ma, P.; Shen, T.; Xu, P.; Dong, W.; Lemstra, P. J.; Chen, M. Superior performance of fully biobased poly(lactide) via stereocomplexation-induced phase separation: structure versus property. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1470–1478.
Rhim, J. W.; Park, H. M.; Ha, C. S. Bio-nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1629–1652.
Wang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Leng, X.; Shen, K.; Li, Y. Highly toughened polylactide with epoxidized polybutadiene by in-sttu reactive compatibilization. Polymer 2016, 92, 74–83.
Nagarajan, V.; Mohanty, A. K.; Misra, M. Perspective on polylactic acid (PLA) based sustainable materials for durable applications: focus on toughness and heat resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2899–2916.
Oyama, H. T.; Abe, S. Stereocomplex poly(lactic acid) alloys with superb heat resistance and toughness. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3245–3252.
Nagarajan, V.; Zhang, K.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A. K. Overcoming the fundamental challenges in improving the impact strength and crystallinity of PLA biocomposites: influence of nucleating agent and mold temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11203–11214.
Dong, W.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, L.; You, J.; Cao, X.; Li, Y. PLLA microalloys versus PLLA nanoalloys: preparation, morphologies, and properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3667–3675.
Spinella, S.; Cai, J.; Samuel, C.; Zhu, J.; McCallum, S. A.; Habibi, Y.; Raquez, J. M.; Dubois, P.; Gross, R. A. Polylactide/poly(ω-hydroxytetradecanoic acid) reactive blending: a green renewable approach to improving polylactide properties. Biomacromolectles 2015, 16, 1818–1826.
Liu, H.; Song, W.; Chen, F.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J. Interaction of microstructure and interfacial adhesion on impact performance of polylactide (PLA) ternary blends. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1513–1522.
Zhang, K.; Nagarajan, V.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A. K. Supertoughened renewable PLA reactive multiphase blends system: phase morphology and performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12436–12448.
Wu, B.; Xu, P.; Yang, W.; Hoch, M.; Dong, W.; Chen, M.; Bai, H.; Ma, P. Super-toughened heat-resistant poly(lactic acid) alloys by tailoring the phase morphology and the crystallization behaviors. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 500–509.
Pan, G.; Xu, H.; Mu, B.; Ma, B.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y. Complete stereocomplexation of enantiomeric polylactides for scalable continuous production. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 759–767.
Jing, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, R.; Bai, D.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Ultrahigh-performance electrospun polylactide membranes with excellent oil/water separation ability via interfacial stereocomplex crystallization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 19729–19737.
Brzezinski, M.; Bogusławska, M.; Ilcikova, M.; Mosnacek, J.; Biela, T. Unusual thermal properties of polylactides and polylactide stereocomplexes containing polylactide-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 8714–8721.
Li, Z.; Tan, B. H.; Lin, T.; He, C. Recent advances in stereocomplexation of enantiomeric PLA-based copolymers and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 62, 22–72.
Tan, B. H.; Muiruri, J. K.; Li, Z.; He, C. Recent progress in using stereocomplexation for enhancement of thermal and mechanical property of polylactide. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5370–5391.
Pholharn, D.; Cheerarot, O.; Baimark, Y. Stereocomplexation and mechanical properties of polylactide-b-poly(propylene glycol)-b-polylactide blend films: effects of polylactide block length and blend ratio. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 35, 1391–1401.
Wang, M.; You, L. C.; Guo, Y. Q; Jiang, N.; Gan, Z. H.; Ning, Z. B. Enhanced crystallization rate of poly(L-lactide)/hydroxyapatite-graft-poly(D-lactide) composite with different processing temperatures. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 599–610.
Li, Y.; Yu, Y. C.; Han, C. Y.; Wang, X. H.; Huang, D. X. Sustainable blends of poly(propylene carbonate) and stereocomplex polylactide with enhanced rheological properties and heat resistance. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-020-2408-8.
Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acids). 9. Stereocomplexation from the melt. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 6918–6926.
Feng, Y.; Lv, P.; Jiang, L.; Ma, P.; Chen, M.; Dong, W.; Chen, Y. Enhanced crystallization kinetics of symmetric poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) stereocomplex in the presence of nanocrystalline cellulose. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 146, 113–120.
Ma, P.; Jiang, L.; Xu, P.; Dong, W.; Chen, M.; Lemstra, P. J. Rapid stereocomplexation between enantiomeric comb-shaped cellulose-g-poly(L-lactide) nanohybrids and poly(D-lactide) from the melt. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3723–3729.
Deng, S.; Bai, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Toward supertough and heat-resistant stereocomplex-type polylactide/elastomer blends with impressive melt stability via in situ formation of graft copolymer during one-pot reactive melt blending. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1718–1730.
Han, L.; Shan, G.; Bao, Y.; Pan, P. Exclusive stereocomplex crystallization of linear and multiarm star-shaped high-molecular-weight stereo diblock poly(lactic acid) s. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 14270–14279.
Zhang, Z. C.; Sang, Z. H.; Huang, Y. F.; Ru, J. F.; Zhong, G. J.; Ji, X.; Wang, R.; Li, Z. M. Enhanced heat deflection resistance via shear flow-induced stereocomplex crystallization of polylactide systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1692–1703.
Zhang, Z. C.; Gao, X. R.; Hu, Z. J.; Yan, Z.; Xu, J. Z.; Xu, L.; Zhong, G. J.; Li, Z. M. Inducing stereocomplex crystals by template effect of residual stereocomplex crystals during thermal annealing of injection-molded polylactide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 10896–10905.
Shao, J.; Sun, J.; Bian, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, X. Investigation of poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: 3-armed poly(L-lactide) blended with linear and 3-armed enantiomers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 9983–9991.
Wang, X. F.; He, Z. Z.; Yang, J. H.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z. W. Super toughened immiscible poly(L-lactide)/poly(ethylene vinyl acetate) (PLLA/EVA) blend achieved by in situ cross-linking reaction and carbon nanotubes. Compos. Part. A-Appl. S. 2016, 91, 105–116.
Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Qi, Z.; Wang, F. Effect of morphology on the brittle ductile transition of polymer blends: 1. A new equation for correlating morphological parameters. Polymer 1997, 38, 5267–5273.
Van den Oever, M.; Beck, B.; Müssig, J. Agrofibre reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites: effect of moisture on degradation and mechanical properties. Compos. Part. A-Appl. S. 2010, 41, 1628–1635.
Zhang, M. C.; Guo, B. H.; Xu, J. A review on polymer crystallization theories. Crystals 2017, 7, 4.
Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Remarkably enhanced impact toughness and heat resistance of poly(L-lactide)/thermoplastic polyurethane blends by constructing stereocomplex crystallites in the matrix. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 111–120.
Bai, H.; Bai, D.; Xiu, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.; Deng, H.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q.; Chiu, F. C. Towards high-performance poly(L-lactide)/elastomer blends with tunable interfacial adhesion and matrix crystallization via constructing stereocomplex crystallites at the interface. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 49374–49385.
Tsuji, H. Poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: formation, structure, properties, degradation, and applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 569–597.
Wu, B.; Zeng, Q.; Niu, D.; Yang, W.; Dong, W.; Chen, M.; Ma, P. Design of supertoughened and heat-resistant PLLA/elastomer blends by controlling the distribution of stereocomplex crystallites and the morphology. Macromolecules 2019, 22, 1092–1103.
Wu, S. Phase structure and adhesion in polymer blends: a criterion for rubber toughening. Polymer 1985, 26, 1855–1863.
Corté, L.; Leibler, L. A model for toughening of semicrystalline polymers. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 5606–5611.
Shi, Y. Y.; Zhang, W. B.; Yang, J. H.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, G. P.; Zhang, C. L. Super toughening of the poly(L-lactide)/thermoplastic polyurethane blends by carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 26271–26282.
Kayano, Y.; Keskkula, H.; Paul, D. R. Fracture behaviour of some rubber-toughened nylon 6 blends. Polymer 1998, 39, 2835–2845.
Kim, G. M.; Michler, G. Micromechanical deformation processes in toughened and particle filled semicrystalline polymers: Part 2. model representation for micromechanical deformation processes. Polymer 1998, 39, 5699–5703.
Xiong, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wen, T.; de Vos, S.; Joziasse, C.; Wang, D. Temperature dependence of crystalline transition of highly-oriented poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) blend: in-situ synchrotron X-ray scattering study. Polymer 2013, 54, 964–971.
Anderson, K. S.; Schreck, K. M.; Hillmyer, M. A. Toughening polylactide. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 85–108.
Jang, K. S. Mechanics and rheology of basalt fiber-reinforced polycarbonate composites. Polymer 2018, 147, 133–141.
Deshmukh, G. S.; Peshwe, D.; Pathak, S.; Ekhe, J. A study on effect of mineral additions on the mechanical, thermal, and structural properties of poly(butylene terephthalate) (PBT) composites. J. Polym. Res. 2011, 18, 1081–1090.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51873082 and 51903106) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. JUSRP11928).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Information
10118_2020_2443_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Stereocomplexed Poly(lactide) Composites toward Engineering Plastics with Superior Toughness, Heat Resistance and Anti-hydrolysis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, BG., Yang, WJ., Niu, DY. et al. Stereocomplexed Poly(lactide) Composites toward Engineering Plastics with Superior Toughness, Heat Resistance and Anti-hydrolysis. Chin J Polym Sci 38, 1107–1116 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-020-2443-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-020-2443-5