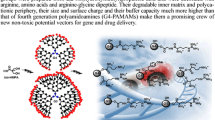
Abstract
Dendrimers are macromolecules characterized by high controlled size, shape and architecture, presence of inner cavities able to accommodate small molecules and many peripheral functional groups to bind target entities. They are of eminent interest for biomedical applications, including gene transfection, tissue engineering, imaging, and drug delivery. The well-known pharmacological activities of ursolic and oleanolic acids are limited by their small water solubility, non-specific cell distribution, low bioavailability, poor pharmacokinetics, and their direct administration could result in the release of thrombi. To overcome such problems, in this paper we described their physical incorporation inside amino acids-modified polyester-based dendrimers which made them highly water-soluble. IR, NMR, zeta potential, mean size of particles, buffer capacity and drug release profiles of prepared materials were reported. The achieved water-soluble complexes harmonize a polycationic character and a buffer capacity which presuppose efficient cell penetration and increased residence time with a biodegradable cell respectful scaffold, thus appearing as a promising team of not toxic prodrugs for safe administration of ursolic and oleanolic acids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hourani, R.; Kakkar, A. Advances in the elegance of chemistry in designing dendrimers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 947–974
Sowinska, M.; Urbanczyk-Lipkowska, Z. Advances in the chemistry of dendrimers. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 2168–2203
Madaan, K.; Kumar, S.; Poonia, N.; Lather, V.; Pandita, D. Dendrimers in drug delivery and targeting: Drug-dendrimer interactions and toxicity issues. J. Pharm. Bioall. Sci. 2014, 6, 139–150
Hu, X. L.; Liu, G. H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. R.; Liu, S. Y. Cellpenetrating hyperbranched polyprodrug amphiphiles for synergistic reductive milieu-triggered drug release and enhanced magnetic resonance signals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 362–368
Li, X.; Qian, Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, X.; Zhang, G.; You, Y.; Liu, S. Amphiphilic multiarm star block copolymer-based multifunctional unimolecular micelles for cancer targeted drug delivery and MR imaging. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6595–605
Xu, J.; Luo, S. Z.; Shi, W. F.; Liu, S. Y. Two-stage collapse of unimolecular micelles with double thermoresponsive coronas. Langmuir 2006, 22, 989–997
Luo, S. Z.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Z. Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, S. Y. Phase transition behavior of unimolecular micelles with thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) coronas. J. Physic. Chem. 2006, 110, 9132–9139
Xu, H. X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, X. Z.; Zhu, Z. Y.; Rao, J. Y.; Yin, J.; Wu, T.; Liu, H. W.; Liu, S. Y. Thermosensitive unimolecular micelles surface-decorated with gold nanoparticles of tunable spatial distribution. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2489–2494
Luo, S.; Hu, X.; Ling, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Han, M. Multiarm star-like unimolecular micelles with a dendritic core and a dual thermosensitive shell. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 717–724
Kesharwani, P.; Jain, K.; Jain, N. Dendrimer as nanocarrier for drug delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 268–307
Datija, J.; Sai, V. V. R.; Mukherji, S. Dendrimers in biosensors: concept and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 14367–14386
Caminade, A M. in "Dendrimers: towards catalytic, material and biomedical uses, Chapter 15", ed. By Caminade, A. M.; Turrin, C. O.; Laurent, R.; Ouali, A.; Delavaux-Nicot, B. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, UK., 2011, p. 375–392
Kim, J. H.; Park, K.; Nam, H. Y., Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I. C. Polymers for bioimaging. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 1031–1053
Wang, Z.; Niu, G.; Chen, X. Polymeric materials for theranostic applications. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1358–1376
Dufes, C.; Uchegbu, I. F.; Schätzlein, A. G. Dendrimers in gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2005, 57, 2177–2202
Eliyahu, H.; Barenholz, Y.; Domb, A. J. Polymers for DNA delivery. Molecules 2005, 10, 34–64
Pack, D. W.; Hoffman, A. S.; Pun, S.; Stayton, P. S. Design and development of polymers for gene delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 581–593
Schaffert, D.; Wagner, E. Gene therapy progress and prospects: synthetic polymer-based systems. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 1131–1138
Mintzer, M. A.; Simanek, E. E. Nonviral vectors for gene delivery. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 259–302
O’Rorke, S.; Keeney, M.; Pandit, A. Non-viral polyplexes: scaffold mediated delivery for gene therapy. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 441–458
Marvaniya, H. M.; Parikh, P. K.; Patel, V. R.; Modi, K. N.; Sen, D. J. Dendrimer nanocarriers as versatile vectors in gene delivery. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2010, 2, 97–108
Guo, X.; Huang, L. Recent advances in nonviral vectors for gene delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 971–979
Yue, Y.; Wu, C. Progress and perspectives in developing polymeric vectors for in vitro gene delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 152–170
Biswas, S.; Torchilin, V. P. Dendrimers for siRNA delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 161–183
Pourianazar, N. T.; Mutulu, P.; Gunduz, U. Bioapplications of poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers in nanomedicine. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2342/1-2342/38
Newkome, G. R.; Shreiner, C. D. Poly(amidoamine), polypropylenimine, and related dendrimers and dendrons possessing different 1 - 2 branching motifs: An overview of the divergent procedures. Polymer 2008, 49, 1–173
Eichman, J. D.; Bielinska, A. U.; Kukowska-Latallo, J. F.; Baker Jr, J. R. The use of PAMAM dendrimers in the efficient transfer of genetic material into cells. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 232–245
Zong, H.; Shah, D.; Selwa, K.; Tsuchida, R. E.; Rattan, R.; Mohan, J.; Stein, A. B.; Otis, J. B.; Goonewardena, S. N. Design and evaluation of tumor-specific dendrimer epigenetic therapeutics chemistryopen. Chem. Open 2015, 4, 335–341
Han, L.; Huang, R.; Liu, S.; Huang, S.; Jiang, C. Peptideconjugated PAMAM for targeted doxorubicin delivery to transferrin receptor overexpressed tumors. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 2156–2165
Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Xie, X.; Wang, C.; You, J.; Mo, F.; Jin, B.; Chen, J.; Shao, J.; Chen, H.; Jia, L. Dendrimeric anticancer prodrugs for targeted delivery of ursolic acid to folate receptor-expressing cancer cells: synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 70, 55–63
Zhang, Y.; Thomas, T. P.; Lee, K. H.; Li, M.; Zong, H.; Desai, A. M.; Kotlyar, A.; Huang, B.; Banaszak H. M. M.; Baker, J. R. Jr. Polyvalent saccharide-functionalized generation 3 poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-methotrexate conjugate as a potential anticancer agent. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2557–2564
Mekuria, S. L.; Debele, T. A.; Chou, H Y.; Tsai, H C. IL-6 antibody and RGD peptide conjugated poly(amidoamine) dendrimer for targeted drug delivery of HeLa cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 123–130
Kolhatkar, R. B.; Kitchens, K. M.; Swaan, P. W.; Ghandehari, H. Surface acetylation of polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers decreases cytotoxicity while maintaining membrane permeability. Bioconj. Chem. 2007, 18, 2054–2060
Waite, C. L.; Sparks, S. M.; Uhrich, K. E.; Roth, C. M. Acetylation of PAMAM dendrimers for cellular delivery of siRNA. BMC Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 9–38
Liu, J. F.; Liu, J. J.; Chu, L. P.; Tong, L. L.; Gao, H. J.; Yang, C. H.; Wang, D. Z.; Shi, L. Q.; Kung, D. L.; Li, Z. J. Synthesis, biodistribution, and imaging of PEGylatedacetylated polyamidoamine dendrimers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 3305–3312
Ciolkowski, M.; Petersen, J. F.; Ficker, M.; Janaszewska, A.; Christensen, J. B.; Klajnert, B.; Bryszewska, M. Surface modifi-cation of PAMAM dendrimer improves its biocompatibility. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 815–817
Ghilardi, A.; Pezzoli, D.; Bellucci, M. C.; Malloggi, C.; Negri, A.; Sgnappa, A.; Tedeschi, G.; Candiani, G.; Volonterio, A. Synthesis of multifunctional PAMAM-aminoglycoside conjugates with enhanced transfection efficiency. Bioconj. Chem. 2013, 24, 1928–1963
Arima, H.; Motoyama, K.; Higashi, T. Sugar-appended polyamidoamine dendrimer conjugates with cyclodextrins as cell-specific non-viral vectors. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2013, 65, 1204–1214
Navath, R. S. Menjoge, A. R.; Wang, B.; Romero, R.; Kannan, S.; Kannan, R. M. Amino acid-functionalized dendrimers with heterobifunctional chemoselective peripheral groups for drug delivery applications. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1544–1536
Park, J. H.; Park, J. S.; Choi, J. S. Basic amino acidconjugated polyamidoamine dendrimers with enhanced gene transfection efficiency. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 500–508
Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Shao, N.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y. Synergistic effect of amino acids modified on dendrimer surface in gene delivery. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9187–9198
Lam, S. J.; Sulistio, A.; Ladewig, K.; Wong, E. H. H.; Blencowe, A.; Qiao, G. G. Peptide-based star polymers as potential siRNA carriers. Austr. J. Chem. 2014, 67, 592–597
Nam, H. Y.; Nam, K.; Hahn, H. J.; Kim, B. H.; Lim, H. J.; Kim, H. J.; Choi, J. S.; Park, J. S. Biodegradable PAMAM ester for enhanced transfection efficiency with low cytotoxicity. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 665–673
Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Xue, Y. N.; Liu, W. M.; Zhuo, R. X.; Huang, S. W. Poly(beta-aminoester)s with pendant primary amines for efficient gene delivery. Bioconj. Chem 2009, 20, 2317–2323
Eltoukhy, Q. Effect of molecular weight of amine endmodified poly(P-amino ester)s on gene delivery efficiency and toxicity. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3594–3603
Bishop, C. J.; Ketola, T M.; Tzeng, S. Y.; Sunshine, J. C.; Urttio, A.; Lemmetyinen, H., Vuorimaa-Laukkanen, E., Yliperttula, M.; Green, J. J. The effect and role of carbon atoms in poly(beta-amino ester)s for DNA Binding and Gene Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6951–6957
Chang, K. L.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawakami, S.; Yamashita, F.; Hashida, M. Development of lysine-histidine dendron modified chitosan for improving transfection efficiency in HEK293 cells. J. Control. Release 2011, 156, 195–202
Wen, Y.; Guo, Z.; Du, Z.; Fang, R.; Wu, H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, C.; Feng, M.; Pan, S. Serum tolerance and endosomal escape capacity of histidine-modified pDNA-loaded complexes based on polyamidoamine dendrimer derivatives. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8111–8121
Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Shao, N.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y. Synergistic effect of amino acids modified on dendrimer surface in gene delivery. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9187–9198
Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, C.; Qu, F.; Rossi, J. J.; Rocchi, P.; Peng, L. Promoting siRNA delivery via enhanced cellular uptake using an arginine-decorated amphiphilic dendrimer. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 3867–3875
Kim, J. B.; Choi, J. S.; Nam, K.; Lee, M.; Park, J. S.; Lee, J. K. Enhanced transfection of primary cortical cultures using arginine-grafted PAMAM dendrimer, PAMAM-Arg. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 110–117
Kim, T.; Bai, C. Z.; Nam, K.; Park, J. Comparison between arginine conjugated PAMAM dendrimers with structural diversity for gene delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2009, 136, 132–139
Liu, J. Pharmacology of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid. J. Ethnopharmacol 1995, 49, 57–68
Andersson, D.; Cheng, Y.; Duan, R. D. Ursolic acid inhibits the formation of aberrant crypt foci and affects colonic sphingomyelin hydrolyzing enzymes in azoxymethane-treated rats. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol 2008, 134, 101–107
Furtado, R. A.; Rodrigues, E. P.; Araujo, F. R. R.; Oliveira, W. L.; Furtado, M. A.; Castro, M. B.; Cunha, W. R.; Tavares, D. C. Ursolic acid and oleanolic acid suppress preneoplastic lesions induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine in rat colon. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 576–580
Gao, J. Hepatoprotective activity of terminalia catappa l. leaves and its two triterpenoids. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 1449–1455
Liu, J. The Effects of 10 triterpenoid compounds on experimental liver injury in mice. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1994, 22, 34–40
Martin-Aragon, S.; de Las Heras, B.; Sanchez-Reus, M. I.; Benedi, J. Pharmacological modification of endogenous antioxidant enzymes by ursolic acid on tetrachloride-induced liver damage in rats and primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2001, 53, 199–206
Saravanan, R.; Viswanathan, P.; Pugalendi, K. V. Protective effect of ursolic acid on ethanol-mediated experimental liver damage in rats. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 713–718
Somova, L. O.; Nadar, A.; Rammanan, P.; Shode, F. O. Cardiovascular, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects of oleanolic and ursolic acids in experimental hypertension. Phytomedicine 2003, 10, 115–121
Ovesna, Z.; Kozics, K.; Slamenov", D. Protective effects of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid in leukemic cells. Mutation Res 2006, 600, 131–137
Shishodia, S.; Majumdar, S.; Banerjee, S.; Aggarwal, B. B. Ursolic acid inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activation induced by carcinogenic agents through suppression of IkappaBalpha kinase and p65 phosphorylation: correlation with downregulation of cyclooxygenase 2, matrix metalloproteinase 9, and cyclin D1. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4375–83
Moon H. K.; Yang, E. S.; Park, J. W. Protection of peroxynitrite-induced DNA damage by dietary antioxidant. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2006, 29, 213–217
Lee, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y. H.; Leonard, J. Ursolic acid-induced changes in tumor growth, O2 consumption, and tumor interstitial fluid pressure. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 2827–2833
Yim, E. K.; Lee, M. J.; Lee, K. H., Um, S. J.; Park, J. S. Antiproliferative and antiviral mechanisms of ursolic acid and dexamethasone in cervical carcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer. 2006, 16, 2023–2031
Huang, M. T.; Ho, C. T.; Wang, Z. Y.; Ferraro, T.; Lou, Y. R.; Stauber, K.; Ma, W.; Georgiadis, C.; Laskin, J. D.; Conney, A. K. Inhibition of skin tumorigenesis by rosemary and its constituents carnosol and ursolic acid. Cancer. Res. 1994, 54, 701–708
Tokuda, H.; Ohigashi, H.; Koshimizu, K.; Ito, Y. Inhibitory effects of ursolic and oleanolic acid on skin tumor promotion by 12-0-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Cancer Lett. 1986, 33, 279–285
Kim, K. A.; Lee, J. S.; Park, H. J.; Kim, J. W.; Kim, C. J.; Shim, I. S.; Kim, N. J.; Han, S. M.; Lim, S. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 activities by oleano-lic acid and ursolic acid in human liver microsomes. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2769–2779
Ramos, A. A.; Lima, C. F.; Pereira, M. L.; Fernandes-Ferreira, M.; Pereira-Wilson, C. Antigenotoxic effects of quercetin, rutin and ursolic acid on HepG2 cells: evaluation by the comet assay. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 177, 66–73
Chiang, L. C.; Chiang, W.; Chang, M. Y.; Ng, L. T.; Lin, C. C. Antileukemic activity of selected natural products in Taiwan. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2003, 31, 37–46
Fan, Y. M.; Xu, L. Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X. H. Zhao, X. N.; Zhang, Z. X. Phytochemical and antiinflammatory studies on Terminalia catappa. Fitoterapia 2004, 75, 253–260
Peng, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Y.; Hoffman, L.; Yang, X. Hyperbranched lysine-arginine copolymer for gene delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2015, 26, 1163–1177
Resende, F. A.; Mattos de Andrade Barcala, C. A.; da Silva Faria, M. C.; Kato, F. H.; Cunha, W. R.; Tavares, D. C. Antimutagenicity of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid against doxorubicin-induced clastogenesis in Balb/c mice. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 1268–1273
Lu, J.; Zheng, Y. L.; Wu, D. M.; Luo, L.; Sun, D. X.; Shan, Q. Ursolic acid ameliorates cognition deficits and attenuates oxidative damage in the brain of senescent mice induced by D-galactose. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1078–1090
Saravanan, R. Pugalendi, V. Impact of ursolic acid on chronic ethanol-induced oxidative stress in the rat heart. Pharmacol. Rep. 2006, 58, 41–47
Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Deng, S. Ursolic acid reduces the metalloprotease/anti-metalloprotease imbalance in cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. Drug Des., Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 1663–1674
Senthil, S.; Chandramohan, G.; Pugalendi, K. V. Isomers (oleanolic and ursolic acids) differ in their protective effect against isoproterenol-induced myocardial ischemia in rats. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 119, 131–133
Radhiga, T.; Rajamanickam, C.; Senthil, S.; Pugalendi, K. V. Effect of ursolic acid on cardiac marker enzymes, lipid profile and macroscopic enzyme mapping assay in isoproterenolinduced myocardial ischemic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3971–3977
Aguirre-Crespo, F.; Vergara-Galicia, J.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Lopez-Guerrero, J. J.; Navarrete-Vazquez, G.; Estrada-Soto, S. Ursolic acid mediates the vasorelaxant activity of Lepechinia caulescens via NO release in isolated rat thoracic aorta. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 1062–1068
Martinez-Gonzalez, J.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, R.; Gonzalez-Diez, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Herrera, M. D.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Badimon, L. Oleanolic acid induces prostacyclin release in human vascular smooth muscle cells through a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent mechanism. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 443–448
Somova, L. O.; Nadar, A.; Rammanan, P.; Shode, F. O. Cardiovascular, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects of oleanolic and ursolic acids in experimental hypertension. Phytomedicine 2003, 10, 115–121
Somova, L. I.; Shode, F. O.; Mipando, M. Cardiotonic and antidysrhythmic effects of oleanolic and ursolic acids, methyl maslinate and uvaol. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 121–129
Ikeda, Y.; Murakami, A.; Ohigashi, H. Ursolic acid: an antiand pro-inflammatory triterpenoid. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 26–42
Messner, B. Ursolic acid causes DNA damage, p53-mediated, mitochondria-and caspase-dependent human endothelial cell apoptosis, and accelerates atherosclerotic plaque formation in vivo. Atherosclerosis 2011, 219, 402–408
Liu, Y.; Oh, S. J.; Chang, K. H.; Kim, Y. G.; Lee, M. Y. Antiplatelet effect of AMP-activated protein kinase activator and its potentiation by the phosphodiesterase inhibitor dipyridamole. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 914–925
Kim, M.; Han, C. H.; Lee, M. Y. Enhancement of platelet aggregation by ursolic acid and oleanolic acid. Biomol. Ther 2014, 22, 254–259
Liu, J. Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid: research perspectives. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 92–94
Nahak, P.; Karmakar, G.; Chettri, P.; Roy, B.; Guha, P.; Besra, S. E.; Soren, A.; Bykov, A. G.; Akentiev, A. V.; Noskov, B. A.; Panda, A. K. Influence of lipid core material on physicochemical characteristics of an ursolic acid-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier: an attempt to enhance anticancer activity. Langmuir 2016, 32, 9816–9825
Alfei, S.; Castellaro, S. Synthesis and characterization of polyester-based dendrimers containing peripheral arginine or mixed amino acids as potential vectors for gene and drug delivery. Macromol. Res. 2017, 25(12), 1172–1186
Bisio, A.; Romussi, G.; Russo, E.; Cafaggi, S.; Schito, A. M.; Repetto, B.; De Tommasi, N. Antimicrobial activity of the ornamental species salvia corrugata, a potential new crop for extractive purposes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10468–10472
Von Seel, F. in "Grundlagen der analytischen Chemie, Vol. 82", ed. By Geier, G., Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, 1970, p. 962
Aravindan, L.; Bicknell, K. A.; Brooks, G.; Khutoryanskiya, V. V.; Williams, A. C. Effect of acyl chain length on transfection efficiency and toxicity of polyethylenimine. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 378, 201–210
Benns, J. M.; Choi, J. S.; Mahato, R. I.; Park, J. S.; Kim, S. W. pH-sensitive cationic polymer gene delivery vehicle: N-Acpoly( L-histidine)-graft-poly(L-lysine) comb shaped polymer. Bioconj. Chem. 2000, 11, 637–645
Fernandez, L. Solubilization and release properties of dendrimers evaluation as prospective drug delivery systems. J. Supramol. Chem. 2006, 18, 633–643
Santo, M.; Fox, M. A. Hydrogen bonding interactions between Starburst dendrimers and several molecules of biological interest. Phys. Org. Chem. 1999, 12, 293–307
Cheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ma, M.; Xu, T. Dendrimers as drug carriers: applications in different routes of drug administration. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 123–143
Milhem, O. M.; Myles, C.; McKeown, N. B.; Attwood, D.; D’Emanuele, A. Polyamidoamine Starburst dendrimers as solubility enhancers. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 197, 239–241
Kolhe, P.; Misra, E.; Kannan, R. M.; Kannan, S.; Lieh-Lai, M. Drug complexation, in vitro release and cellular entry of dendrimers and hyperbranched polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 259, 143–160
Twyman, L. J.; Beezer, A. E.; Esfand, R.; Hardy, M. J.; Mitchell, J. C. The synthesis of water soluble dendrimers, and their application as possible drug delivery systems. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 1743–1746
Alfei, S.; Castellaro, S.; Taptue, G. B. Synthesis and NMR characterization of dendrimers based on 2, 2-bis-(hydroxymethyl)-propanoic acid (bis-HMPA) containing peripheral amino acid residues for gene transfection. Org. Commun. 2017, 10, 144–177
Seebacher, W.; Simic, N.; Weis, R.; Saf, R.; Kunert, O. Spectral assignments and reference data. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2003, 41, 636–638
Eichman, J. D.; Bielinska, A. S. U.; Kukowska-Latallo, J. F.; Baker J. R. Jr. The use of PA-MAM dendrimers in the efficient transfer of genetic material into cells. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 232–245
Wang, J. Q.; Mao, W. W.; Lock, L. L.; Tang, J. B.; Sui, M. H.; Sun, W. L.; Cui, H. G.; Xu, D.; Shen, Y. Q. The role of micelle size in tumor accumulation, penetration, and treatment. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7195–7206
Yu, H.; Cui, Z.; Yu, P.; Guo, C.; Feng, B.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S.; Yin, Q.; Zhong, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. pH-and NIR light-responsive micelles with hyperthermia-triggered tumor penetration and cytoplasm drug release to reverse doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2489–2500.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very thankful to Mr Gagliardo Osvaldo for Elemental Analysis and to University of Genova.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
10118_2018_2124_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Synthesis of Water-soluble, Polyester-based Dendrimer Prodrugs for Exploiting Therapeutic Properties of Two Triterpenoid Acids
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alfei, S., Taptue, G.B., Catena, S. et al. Synthesis of Water-soluble, Polyester-based Dendrimer Prodrugs for Exploiting Therapeutic Properties of Two Triterpenoid Acids. Chin J Polym Sci 36, 999–1010 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-018-2124-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-018-2124-9