Abstract
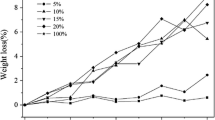
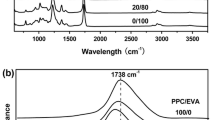
The effects of temperature and relative humidity on the hydrolytic degradation of poly(p-dioxanone) (PPDO) were investigated. The hydrolytic degradation behaviors were monitored by tracing the changes of water absorption, mechanical and crystalline properties, molecular weight and its distribution, surface morphologies, as well as infrared absorption peaks and hydrogen chemical shifts during the degradation. It is found that the water absorption increases whilst the intrinsic viscosity, tensile strength and elongation at break decrease as the temperature or relative humidity increases. With degradation time growing, the molecular weight drops and its distribution broadens. The crystallinity of PPDO has a tendency to increase at first and then to decrease, while the crystalline structure is not significantly changed. At the same time, some cracks are observed on the surface and keep growing and deepening. All results show that temperature plays more significant roles than relative humidity during the degradation. The analyses of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveal that the degradation of PPDO is a predominant hydrolysis of ester linkages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, C.Y., Ding, S.D., Liu, Z.P. and Wang, Y.Z., Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese), 2007, (12): 1201
Li, H.Z., Pang, D.L., Lai, C.Y., Li, F., Wang, X.L. and Wang, Y.Z., Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese), 2011, (6): 633
Fang, Q., Zheng, H., Shen, G.R. and Shen, Z.Q., Chinese J. Polym. Sci., 2007, 25(4): 427
Ray, J.A., Doddi, N., Regula, D., Williams, J.A. and Melveger, A., Surg. Gynecol. Obstet., 1981, 153(4): 497
Wang, Y.Z., Zhou, Q., Zheng, C.Y., Yang, K.K., Wang, X.L. and Ding, S.D., 2007, CN. Pat., 1.325.162
Raquez, J.M., Coulembier, O., Duda, A., Narayan, R. and Dubois, P., Polimery, 2009, 54: 165
Ding, S.D., Liu, Z.P., Yang, T., Zheng, G.C. and Wang, Y.Z., J. Polym. Res., 2010, 17(1): 63
Nishida, H., Yamashita, M., Hattori, N., Endo, T. and Tokiwa, Y., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2000, 70(3): 485
Zeng, J.B., Srinivansan, M., Li, Y.D., Narayan, R. and Wang, Y.Z., J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem., 2010, 48(24): 5885
Ding, S.D., Zheng, G.C., Zeng, J.B., Zhang, L., Li, Y.D. and Wang, Y.Z., Eur. Polym. J., 2009, 45(11): 3043
Zhang, J.J., Niu, Y., Huang, C.L., Xiao, L.P., Chen, Z.T., Yang, K.K. and Wang, Y.Z., Polym. Chem., 2012, 3(6): 1390
Zheng, H., Shen, G.R., Ni, X.F. and Shen, Z.Q., Chinese J. Polym. Sci., 2008, 26(6): 799
Sabino M.A., González S., Márquez, L. and Feijoo, J.L., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2000, 69(2):209
Ooi, C.P. and Cameron, R.E., J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2002, 63(3): 280
Sabino, M.A., Albuerne, J., Muller, A.J., Brisson, J. and Prud’homme, R.E., Biomacromolecules, 2004, 5(3): 358
Lin, H.L., Chu, C.C. and Grubb, D., J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 1993, 27(2): 153
Zheng, G.C., Ding, S.D., Zheng, J.B., Wang, Y.Z. and Li, Y.D., J. Macromol. Sci. B., 2010, 49(2): 269
Zhang, X.Q., Espiritu, M., Bilyk, A. and Kurniawan, L., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2008, 93(10): 1964
Ho, K.L.G., Pometto, III.A.L. and Hinz, P.N., J. Environ. Polym. Degr., 1999, 7(2): 83
Copinet, A., Bertrand, C., Govindin, S., Coma, V. and Couturier, Y., Chemosphere, 2004, 55(5): 763
Duek, E.A.R., Zavaglia, C.A.C. and Belangero, W.D., Polymer, 1999, 40: 6465
Weir, N.A., Buchanan, F.J., Orr, J.F. and Dickson G.R., Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs. Part H: J. Eng. Med., 2004, 218(5): 307
Weir, N.A., Buchanan, F.J., Orr, J.F., Farrar, D.F. and Dickson, G.R., Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs. Part H: J. Eng. Medicine, 2004, 218(5): 321
Rockland, L.B., Anal. Chem., 1960, 32(10): 1375
Greenspan, L.J., Res. Natl. Bur. Stand., 1997, 81A: 89
O’brien, F.E.M., J. Sci. Instrum., 1948, 25(3): 73
Yu, J.M., Fu, G.R., Bian, D.C., Zhou, X.F., Liu, C.Y. and Yu, J.L., Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese), 1996, (6): 675
Liang, B.Q., Pang, D.L., Jin, C., Li, F. and Wang, Y.Z., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2012, 97(11): 2162
Loo, S.C.J., Ooi, C.P. and Boey, Y.C.F., Biomaterials, 2005, 26(18): 3809
Wang, D., Fredericks, P.M., Haddad, A., Hill, D.J.T., Rasoul, F. and Whittaker, A.K., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2011, 96(1): 123
Pamuła, E., Błażewicz, M., Paluszkiewicz, C. and Dobrzyński, P., J. Mol. Struct., 2001, 596(1): 69
Chu, C.C., Zhang, L. and Coyne, L.D., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 1995, 56(10): 1275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51121001), High-Tech Research & Development Program (No. 2012AA062904) and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Teams in Universities of China (IRT 1026).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Y., Ding, Sd., Zhao, Yq. et al. Hydrolytic degradation behaviors of poly(p-dioxanone) in ambient environments. Chin J Polym Sci 32, 1678–1689 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-014-1545-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-014-1545-3